Abstract
Rationale
Cyamemazine (Tercian) is an antipsychotic drug with anxiolytic properties. Recently, an in vitro study showed that cyamemazine possesses high affinity for serotonin 5-HT2A receptors, which was fourfold higher than its affinity for dopamine D2 receptors (Hameg et al. 2003).
Objectives
The aim of this study is to confirm these previous data in vivo in patients treated with clinically relevant doses of Tercian.
Methods
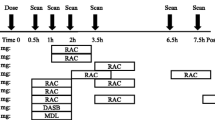
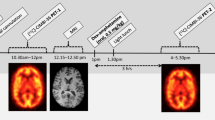
Eight patients received 37.5, 75, 150 or 300 mg/day of Tercian depending on their symptomatology. Dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptor occupancies (RO) were assessed at steady-state plasma levels of cyamemazine with positron emission tomography (PET), using [11C]raclopride and [11C]N-methyl-spiperone, respectively. The effective plasma level of the drug leading to 50% of receptor occupancy was estimated by fitting RO with plasma levels of cyamemazine at the time of the PET scan.
Results
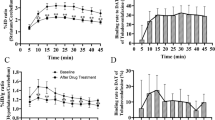
Cyamemazine induced near saturation of 5-HT2A receptors (RO=62.1–98.2%) in the frontal cortex even at low plasma levels of the drug. On the contrary, occupancy of striatal D2 receptors increased with plasma levels, and no saturation was obtained even at high plasma levels (RO=25.2–74.9%). The effective plasma level of cyamemazine leading to 50% of D2 receptor occupancy was fourfold higher than that for 5-HT2A receptors. Accordingly, individual 5-HT2A/D2 RO ratios ranged from 1.26 to 2.68. No patients presented relevant increased prolactin levels, and only mild extrapyramidal side effects were noticed on Simpson and Angus Scale.
Conclusion
This in vivo binding study conducted in patients confirms previous in vitro findings indicating that cyamemazine has a higher affinity for serotonin 5-HT2A receptors compared to dopamine D2 receptors. In the dose range 37.5–300 mg, levels of dopamine D2 occupancy remained below the level for motor side effects observed with typical antipsychotics and is likely to explain the low propensity of the drug to induce extrapyramidal side effects.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonini A, Leenders K, Reist H, Thomann R, Beer H, Locher J (1993) Effects of age on D2 dopamine receptors in normal human brain measured by positron emission tomography and 11C-raclopride. Arch Neurol 50(5):474–480
Barnes TRE (1989) A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154:672–676
Bigliani V, Pilowski LS (1999) In vivo neuropharmacology of schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 194(suppl 38):23–33
Bourin M, Nic Dhonnchadha BA, Colombel MC, Dib M, Hascoët M (2001) Cyamemazine as an anxiolytic drug on the elevated plus maze and light/dark paradigm in mice. Behav Brain Res 124:87–95
Bourin M, Dailly E, Hameg A, Dib M, Garay RP, Hascoët M (2004a) A study of the antipsychotic action of cyamemazine in mouse behavioral models. Collegium Internationale Neuro-Psychopharmacologicum/XXIVth CINP Congress. Paris, June 20–24, 2004
Bourin M, Dailly E, Hascoet M (2004b). Preclinical and clinical pharmacology of cyamemazine: anxiolytic effects and prevention of alcohol and benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome. CNS Drug Rev 10(3):219–229
Brunot A, Lachaux B, Sontag H, Casadebaig F, Philippe A, Rouillon F et al (2002) Pharmaco-epidemiological study on antipsychotic drug prescription in French psychiatry: patient characteristics, antipsychotic treatment, and care management for schizophrenia. Encephale 28(2):129–138
Daniel D (1995) Metabolism of psychotropic drugs: pharmacological and clinical relevance. Pol J Pharmacol 47:367–379
Dannals RF, Ravert HT, Wilson AA, Wagner HN (1986) An improved synthesis of (3-N-[11C]methyl)spiperone. Appl Radiat Isotopes 37:433–434
Ehrin E, Gawell L, Högberg T, de Paulis S, Ström P (1987). Synthesis of [methoxy-3H]- and [methoxy-11C]-labelled raclopride. Specific dopamine-D2 receptor ligands. J Labelled Compd Radiopharm 24:931–940
Farde L, Eriksson L, Blomquist G, Halldin C (1989) Kinetic analysis of central [11C]-raclopride binding to D2-dopamine receptors studied by PET—a comparison to the equilibrium analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9:696–708
Farde L, Wiesel FA, Stone-Elander S, Halldin C, Nordström AL, Hall H, Sedvall G (1990) D2 dopamine receptors in neuroleptic naive schizophrenic patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:213–219
Farde L, Nordstrom AL, Wiesel FA, Pauli S, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1992) Positron emission tomography analysis of central D1 and D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine: relation to extrapyramidal side effects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:538–544
Farde L, Nordstrom AL, Nyberg S, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1994) D1-, D2- and 5-HT2 receptor occupancy in clozapine treated patients. J Clin Psychiatry 55:9(suppl B):67–69
Fourrier A, Gasquet I, Allicar MP, Bouhassira M, Lépine JP, Bégaud B (2000) Patterns of neuroleptic drug prescription: a national cross-sectional survey of a random sample of French psychiatrists. J Clin Pharmacol 49:80–86
Gury C, Berchot F, Fabre C, Surugue J, Welcomme N (2000) Analysis of neuroleptics prescriptions in five specialized hospitals: comparison between hospital prescriptions and discharge prescriptions. Inf Psychiatr 8:954–963
Gury C, Simo E, Fabre C, Surugue J, Welcomme N (2004) Prescriptions of antipsychotic drugs in five specialized hospital centers in 2002: comparative analysis with 1998. Collegium Internationale Neuro-Psychopharmacologicum/XXIVth CINP Congress. Paris, June 20–24, 2004
Guy W (1976) Clinical Global Impression. ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology, ECDEU: National Institutes of Health, pp 218–222
Halldin C, Farde L, Hogberg T, Mohell N, Hall H, Suhara T, Karlsson P, Nakashima Y, Swahn CG (1995) Carbon-11-FLB457: a radioligand for extrastriatal D2 dopamine receptors. J Nucl Med 36:1275–1281
Hameg A, Bayle F, Nuss P, Dupuis P, Garay PR, Dib M (2003) Affinity of cyamemazine, an anxiolytic antipsychotic drug, for human recombinant dopamine versus serotonin receptor subtypes. Biochem Pharmacol 7497:1–6
Hamilton M (1959) The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol 32:50–55
Hietala J, Syvalahti E, Vuorio K, Nagren K, Lehikoinen P, Ruotsalainen U, Rakkolainen V, Lehtinen V, Wagelius U (1994) Stratial D2 dopamine receptor characteristics in neuroleptic-naive scizophrenic patients studied with positron emission tomography. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51(2):116–123
Iyo M, Yamasaki T (1993) The detection of age-related decrease of dopamine D1, D2 and serotonin 5-HT2 receptors in living human brain. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:415–421
Kapur S, Zipursky R, Jones C, Remington G, Wilson A, DaSilva J, Houle S (1996) The D2 receptor occupancy profile of loxapine determined using PET. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:562–566
Kapur S, Zipursky R, Roy P, Jones C, Remington G, Reed K, Houle S (1997) The relationship between D2 receptor occupancy and plasma levels on low dose oral haloperidol: a PET study. Psychopharmacology 131:148–152
Kapur S, Zipursky RB, Remington G, Jones C, Da Silva J, Wilson AA, Houle S (1998) 5-HT2 and D2 receptor occupancy of olanzapine in schizophrenia: a PET investigation. Am J Psychiatry 155(7):921–928
Kapur S, Zipursky R, Remington G (1999) Clinical and theoretical implications of 5-HT2 and D2 receptor occupancy of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 156(2):286–293
Kapur S, Zipursky R, Jones C, Remington G, Houle S (2000) Relationship between dopamine D2 occupancy, clinical response and side effects: a double blind PET study of first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157:514–520
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Lammerstma AA, Hume SP (1996) Simplified reference tissue model for PET receptor studies. NeuroImage 4:153–158
Logan J, Fowler JS, Wolf AP, Fowler JS, Brodie JD, Angrist B, Volkow ND, Gatley SJ (1996) Distribution volume ratios without blood sampling from graphical analysis of PET data. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:834–840
Martinot JL, Paillère-Martinot ML, Lo’ch C, Hardy P, Poirier MF, Mazoyer B, Beaufils B, Maziere B, Allilaire JF, Syrota A (1991) The estimated density of D2 striatal receptors in schizophrenia. A study with positron emission tomography and 76Br bromolisuride. Br J Psychiatry 158:346–350
Nordström AL, Farde L, Wiesel FA, Forslund K, Pauli S, Halldin G, Uppfeldt G (1993). Central D2-dopamine receptor occupancy in relation to antipsychotic drug effects—a double blind PET study of schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry 33:227–235
Nordström AL, Farde L, Nyberg S, Karlsson P, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1995) D1, D2 and 5-HT2 receptor occupancy in relation to clozapine serum concentration: a PET study of schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 152 (10):1444–1449
Nyberg S, Farde L, Eriksson L, Halldin C, Eriksson B (1993) 5-HT2 and D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in the living human brain. A PET study with risperidone. Psychopharmacology 110:265–272
Nyberg S, Nakashima Y, Nordström AL, Halldin C, Farde L (1996) Positron emission tomography of in-vivo binding characteristics of atypical antipsychotic drugs. Review of D2 and 5-HT2 receptor occupancy studies and clinical response. Br J Psychiatry 168(suppl 29):40–44
Nyberg S, Nilsson U, Okubo Y, Halldin C, Farde L (1998) Implication of brain imaging for the management of schizophrenia. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 13(suppl 3):S15–S20
Nyberg S, Eriksson L, Oxenstierna G, Halldin C, Farde L (1999) Suggested minimal effective dose of risperidone based on PET-measured D2 and 5-HT2A receptor occupancy in schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 156(6):869–875
Okubo Y, Sahara T, Suzuki K, Kobayashi K, Inoue O, Terasaki O, Someya Y, Sassa T, Sudo Y, Matsushima E, Iyo M, Tateno Y, Toru M (2000) Serotonin 5-HT2 receptors in schizophrenic patients studied by positron emission tomography. Life Sci 66(25):2455–2464
Radat F (1995) Cyamemazine:traitement symptomatique desdimensions anxieuses, impulsives et agressives. Inf Psychiatr 10:967–968
Reimold M, Mueller-Schauenburg W, Becker GA, Reischl G, Dohmen BM, Bares R (2004) Non-invasive assessment of distribution volume ratios and binding potential: tissue heterogeneity and interindividually averaged time–activity curves. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31(4):564–577
Richelson E (1999) Receptor pharmacology of neuroleptics: relation to clinical effects. J Clin Psychiatry 60(suppl 10):5–14
Sedvall G, Pauli S, Farde L, Karlsson P, Nyberg S, Nordström AL (1995). Recent developments in PET scan imaging of neuroreceptors in schizophrenia. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci 32(1):22–29
Simpson GM, Angus JWS (1970) A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 212:11–19
Trichard C, Paillère-Martinot ML, Attar-Levy D, Recassens C, Monnet F, Martinot JL (1998) Binding of antipsychotic drugs to cortical 5-HT2A receptors: a PET study of chlorpromazine, clozapine, and amisulpiride in schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 155:505–508
Varga J, Szabo Z (2002) Modified regression model for the Logan plot. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:240–244
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Logan J et al (1996) Measuring age-related changes in dopamine D2 receptors with 11C-raclopride and 18F-N-methylspiroperidol. Psychiatry Res 67:11–16
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Logan J, Fowler JS et al (1995) Evaluation of age-related changes in serotonin 5-HT2 and dopamine D2 receptor availability in healthy human subjects. Life Sci 56(14):249–253
Yang YK, Yu L, Yeh TL, Chiu NT, Chen PS, Lee IH (2004) Associated alterations of stratial dopamine D2/D3 receptor and transporter binding in drug-naive patients with schizophrenia: a dual-isotope SPECT study. Am J Psychiatry 161(8):1496–1498
Acknowledgements
We thank H.-J. Machulla for his help in radiotracer preparations, B.M. Dohmen for the administrative management at the PET site, M.-P. Thomas for her clinical research assistance, C. Staner for healthy volunteer management and C. Ziegler for patient management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hodé, Y., Reimold, M., Demazières, A. et al. A positron emission tomography (PET) study of cerebral dopamine D2 and serotonine 5-HT2A receptor occupancy in patients treated with cyamemazine (Tercian). Psychopharmacology 180, 377–384 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2172-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2172-z