Abstract
Rationale
Regulation of dopamine release and synthesis occurs via pre-synaptic dopamine (DA) D2/D3 autoreceptors (DARs). Mapping of DAR function in vivo is difficult and is usually best assessed using invasive measures of DA release, such as microdialysis at discrete sites. We wished to show that pharmacological magnetic resonance imaging (phMRI) may prove useful for this purpose.
Objective
To demonstrate that the relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) changes induced by amphetamine can be modulated by DA D2 receptor antagonists and agonists in a manner consistent with modulation of DAR function and to compare these effects with microdialysis.
Methods
We used phMRI with iron oxide contrast agents to map changes in rCBV in response to an amphetamine challenge, pre-treatment and post-treatment with varying doses of the D2 antagonist eticlopride and the D2 agonist quinpirole. We also compared the effects of D2 antagonism using microdialysis measurements of DA release.
Results
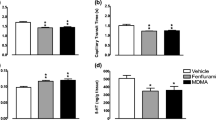
Antagonism of D2 receptors with eticlopride potentiated rCBV changes induced by amphetamine in the nucleus accumbens and caudate putamen in a dose-dependent manner. The amphetamine-induced increase in rCBV in the accumbens in animals pre-treated with eticlopride was paralleled by a similar percentage increase in DA release measured by means of microdialysis. Conversely, agonism of D2 receptors using quinpirole reduced amphetamine-induced rCBV changes in the caudate putamen and nucleus accumbens. The effects of both quinpirole and eticlopride on amphetamine-induced rCBV changes were largest in the nucleus accumbens.
Conclusions
These results suggest that phMRI may potentially prove useful to map DAR function non-invasively in multiple brain regions simultaneously.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen SL, Gazzara RA (1994) The development of D2 autoreceptor-mediated modulation of K(+)-evoked dopamine release in the neostriatum. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 78:123–130
Booze RM, Wallace DR (1995) Dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in the rat striatum and nucleus accumbens: use of 7-OH-DPAT and [125I]-iodosulpride. Synapse 19:1–13
Bouthenet ML, Souil E, Martres MP, Sokoloff P, Giros B, Schwartz JC (1991) Localization of dopamine D3 receptor mRNA in the rat brain using in situ hybridization histochemistry: comparison with dopamine D2 receptor mRNA. Brain Res 564:203–219
Breiter H, Gollub R, Weisskoff R, Kennedy D, Makris N, Berke J, Goodman J, Kantor R, Gastfriend D, Riorden J, Mathew R, Rosen B, Hyman S (1997) Acute effects of cocaine on human brain activity and emotion. Neuron 19:591–611
Cass WA, Gerhardt GA, Mayfield RD, Curella P, Zahniser NR (1992) Differences in dopamine clearance and diffusion in rat striatum and nucleus accumbens following systemic cocaine administration. J Neurochem 59:259–266
Chen Q, Andersen AH, Zhang Z, Ovadia A, Gash DM, Avison MJ (1996) Mapping drug-induced changes in cerebral R2* by multiple gradient recalled echo functional MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 14:469–476
Chen YI, Galpern WR, Brownell AL, Matthews RT, Bogdanov M, Isacson O, Beal MF, Rosen BR, Jenkins BG (1997) Detection of dopaminergic neurotransmitter activity using pharmacologic MRI: correlation with PET, microdialysis, and behavioral data. Magn Reson Med 38:389–398
Chen YI, Brownell AL, Galpern W, Isacson O, Bogdanov M, Beal MF, Livni E, Rosen BR, Jenkins BG (1999) Detection of dopaminergic cell loss and neural transplantation using pharmacological MRI, PET and behavioral assessment. Neuroreport 10:2881–2886
Chen YC, Mandeville JB, Nguyen TV, Talele A, Cavagna F, Jenkins BG (2001) Improved mapping of pharmacologically induced neuronal activation using the IRON technique with superparamagnetic blood pool agents. J Magn Reson Imaging 14:517–524
Christian BT, Narayanan T, Shi B, Morris ED, Mantil J, Mukherjee J (2004) Measuring the in vivo binding parameters of [18F]-fallypride in monkeys using a PET multiple-injection protocol. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:309–322
Cooper JR, Bloom FE, Roth RH (2003) The biochemical basis of neuropharmacology, 8th edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Cory-Slechta DA, Widzowski DV, Pokora MJ (1993) Functional alterations in dopamine systems assessed using drug discrimination procedures. Neurotoxicology 14:105–114
Dubowitz DJ, Bernheim KA, Chen DY, Bradley WG Jr, Andersen RA (2001) Enhancing fMRI contrast in awake-behaving primates using intravascular magnetite dextran nanoparticles. Neuroreport 12:2335–2340
Endres CJ, Kolachana BS, Saunders RC, Su T, Weinberger D, Breier A, Eckelman WC, Carson RE (1997) Kinetic modeling of [11C]raclopride: combined PET-microdialysis studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:932–942
Furmidge L, Tong ZY, Petry N, Clark D (1991) Effects of low, autoreceptor selective doses of dopamine agonists on the discriminative cue and locomotor hyperactivity produced by d-amphetamine. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 86:61–70
Garris PA, Wightman RM (1994) Different kinetics govern dopaminergic transmission in the amygdala, prefrontal cortex, and striatum: an in vivo voltammetric study. J Neurosci 14:442–450
Glick SD, Rossman K, Wang S, Dong N, Keller RW Jr (1993) Local effects of ibogaine on extracellular levels of dopamine and its metabolites in nucleus accumbens and striatum: interactions with d-amphetamine. Brain Res 628:201–208
Guix T, Hurd YL, Ungerstedt U (1992) Amphetamine enhances extracellular concentrations of dopamine and acetylcholine in dorsolateral striatum and nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats. Neurosci Lett 138:137–140
Hamilton WC (1965) Significance tests on the crystallographic R factor. Acta Crystallogr 18:502–510
Han S, Rowell PP, Carr LA (1999) D2 autoreceptors are not involved in the down-regulation of the striatal dopamine transporter caused by alpha-methyl-p-tyrosine. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 104:331–338
Innis RB, Malison RT, al-Tikriti M, Hoffer PB, Sybirska EH, Seibyl JP, Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, Laruelle M, Smith EO et al (1992) Amphetamine-stimulated dopamine release competes in vivo for [123I]IBZM binding to the D2 receptor in nonhuman primates. Synapse 10:177–184
Jenkins BG, Armstrong E, Lauffer RB (1991) Site-specific water proton relaxation enhancement of iron(III) chelates noncovalently bound to human serum albumin. Magn Reson Med 17:164–178
Jenkins BG, Chen YI, Mandeville JB (2002) Pharmacologic magnetic resonance imaging (phMRI). In: van Bruggen N, Roberts T (eds) Biomedical imaging in experimental neuroscience. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 155–209
Joseph JD, Wang YM, Miles PR, Budygin EA, Picetti R, Gainetdinov RR, Caron MG, Wightman RM (2002) Dopamine autoreceptor regulation of release and uptake in mouse brain slices in the absence of D(3) receptors. Neuroscience 112:39–49
Kalivas PW, Duffy P (1991) A comparison of axonal and somatodendritic dopamine release using in vivo dialysis. J Neurochem 56:961–967
Kennan RP, Scanley BE, Innis RB, Gore JC (1998) Physiological basis for BOLD MR signal changes due to neuronal stimulation: separation of blood volume and magnetic susceptibility effects. Magn Reson Med 40:840–846
Kennedy RT, Jones SR, Wightman RM (1992) Dynamic observation of dopamine autoreceptor effects in rat striatal slices. J Neurochem 59:449–455
Khan ZU, Gutierrez A, Martin R, Penafiel A, Rivera A, De La Calle A (1998) Differential regional and cellular distribution of dopamine D2-like receptors: an immunocytochemical study of subtype-specific antibodies in rat and human brain. J Comp Neurol 402:353–371
Koeltzow TE, Xu M, Cooper DC, Hu XT, Tonegawa S, Wolf ME, White FJ (1998) Alterations in dopamine release but not dopamine autoreceptor function in dopamine D3 receptor mutant mice. J Neurosci 18:2231–2238
Kuczenski R, Segal DS (1999) Dynamic changes in sensitivity occur during the acute response to cocaine and methylphenidate. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 147:96–103
Laruelle M (2000) Imaging synaptic neurotransmission with in vivo binding competition techniques: a critical review. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:423–451
Lehmann J, Briley M, Langer SZ (1983) Characterization of dopamine autoreceptor and [3H]spiperone binding sites in vitro with classical and novel dopamine receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 88:11–26
Li SJ, Biswal B, Li Z, Risinger R, Rainey C, Cho JK, Salmeron BJ, Stein EA (2000) Cocaine administration decreases functional connectivity in human primary visual and motor cortex as detected by functional MRI. Magn Reson Med 43:45–51
Mandeville JB, Marota JJ, Kosofsky BE, Keltner JR, Weissleder R, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM (1998) Dynamic functional imaging of relative cerebral blood volume during rat forepaw stimulation. Magn Reson Med 39:615–624
Mandeville JB, Jenkins BG, Kosofsky BE, Moskowitz MA, Rosen BR, Marota JJ (2001) Regional sensitivity and coupling of BOLD and CBV changes during stimulation of rat brain. Magn Reson Med 45:443–447
Marota JJ, Mandeville JB, Weisskoff RM, Moskowitz MA, Rosen BR, Kosofsky BE (2000) Cocaine activation discriminates dopaminergic projections by temporal response: an fMRI study in Rat. Neuroimage 11:13–23
Missale C, Castelletti L, Govoni S, Spano PF, Trabucchi M, Hanbauer I (1985) Dopamine uptake is differentially regulated in rat striatum and nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 45:51–56
Morgan D, Grant KA, Gage HD, Mach RH, Kaplan JR, Prioleau O, Nader SH, Buchheimer N, Ehrenkaufer RL, Nader MA (2002) Social dominance in monkeys: dopamine D2 receptors and cocaine self-administration. Nat Neurosci 5:169–174
Nguyen TV, Brownell AL, Iris Chen YC, Livni E, Coyle JT, Rosen BR, Cavagna F, Jenkins BG (2000) Detection of the effects of dopamine receptor supersensitivity using pharmacological MRI and correlations with PET. Synapse 36:57–65
Olsson H, Halldin C, Farde L (2004) Differentiation of extrastriatal dopamine D2 receptor density and affinity in the human brain using PET. Neuroimage 22:794–803
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, New York
Pehek EA (1999) Comparison of effects of haloperidol administration on amphetamine-stimulated dopamine release in the rat medial prefrontal cortex and dorsal striatum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:14–23
Phillips PE, Hancock PJ, Stamford JA (2002) Time window of autoreceptor-mediated inhibition of limbic and striatal dopamine release. Synapse 44:15–22
Rayevsky KS, Gainetdinov RR, Grekhova TV, Sotnikova TD (1995) Regulation of dopamine release and metabolism in rat striatum in vivo: effects of dopamine receptor antagonists. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 19:1285–1303
Robertson GS, Tham CS, Wilson C, Jakubovic A, Fibiger HC (1993) In vivo comparisons of the effects of quinpirole and the putative presynaptic dopaminergic agonists B-HT 920 and SND 919 on striatal dopamine and acetylcholine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:1344–1351
Santiago M, Westerink BH (1991) The regulation of dopamine release from nigrostriatal neurons in conscious rats: the role of somatodendritic autoreceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 204:79–85
Schmitz Y, Schmauss C, Sulzer D (2002) Altered dopamine release and uptake kinetics in mice lacking D2 receptors. J Neurosci 22:8002–8009
Schoemaker H, Claustre Y, Fage D, Rouquier L, Chergui K, Curet O, Oblin A, Gonon F, Carter C, Benavides J, Scatton B (1997) Neurochemical characteristics of amisulpride, an atypical dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with both presynaptic and limbic selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:83–97
Shen T, Weissleder R, Papisov M, Bogdanov A Jr, Brady TJ (1993) Monocrystalline iron oxide nanocompounds (MION): physicochemical properties. Magn Reson Med 29:599–604
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres MP, Bouthenet ML, Schwartz JC (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146–151
Stamford JA, Kruk ZL, Millar J (1988) Actions of dopamine antagonists on stimulated striatal and limbic dopamine release: an in vivo voltammetric study. Br J Pharmacol 94:924–932
Stein EA (2001) fMRI: a new tool for the in vivo localization of drug actions in the brain. J Anal Toxicol 25:419–424
Tang L, Todd RD, O’Malley KL (1994) Dopamine D2 and D3 receptors inhibit dopamine release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:475–479
Tidey JW, Bergman J (1998) Drug discrimination in methamphetamine-trained monkeys: agonist and antagonist effects of dopaminergic drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 285:1163–1174
Villringer A, Rosen BR, Belliveau JW, Acerman JL, Lauffer RB, Buxton RB, Chao YS, Wedeen VJ, Brady TJ (1988) Dynamic imaging with lanthanide chelates in normal brain: contrast due to magnetic susceptibility effects. Magn Reson Med 6:164–174
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ (1999) Imaging studies on the role of dopamine in cocaine reinforcement and addiction in humans. J Psychopharmacol 13:337–345
Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Ding YS, Sedler M, Logan J, Franceschi D, Gatley J, Hitzemann R, Gifford A, Wong C, Pappas N (2001) Low level of brain dopamine D2 receptors in methamphetamine abusers: association with metabolism in the orbitofrontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry 158:2015–2021
Wechsler LR, Savaki HE, Sokoloff L (1979) Effects of d- and l-amphetamine on local cerebral glucose utilization in the conscious rat. J Neurochem 32:15–22
Weissleder R, Elizondo G, Wittenberg J, Rabito CA, Bengele HH, Josephson L (1990) Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide: characterization of a new class of contrast agents for MR imaging. Radiology 175:489–493
Widzowski DV, Cory-Slechta DA (1993) Apparent mediation of the stimulus properties of a low dose of quinpirole by dopaminergic autoreceptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 266:526–534
Wu Q, Reith ME, Kuhar MJ, Carroll FI, Garris PA (2001) Preferential increases in nucleus accumbens dopamine after systemic cocaine administration are caused by unique characteristics of dopamine neurotransmission. J Neurosci 21:6338–6347
Wu Q, Reith ME, Walker QD, Kuhn CM, Carroll FI, Garris PA (2002) Concurrent autoreceptor-mediated control of dopamine release and uptake during neurotransmission: an in vivo voltammetric study. J Neurosci 22:6272–6281
Zaharchuk G, Mandeville JB, Bogdanov AA Jr, Weissleder R, Rosen BR, Marota JJ (1999) Cerebrovascular dynamics of autoregulation and hypoperfusion. An MRI study of CBF and changes in total and microvascular cerebral blood volume during hemorrhagic hypotension. Stroke 30:2197–2204 (discussion 2204–2205)
Zhang Z, Andersen A, Grondin R, Barber T, Avison R, Gerhardt G, Gash D (2001) Pharmacological MRI mapping of age-associated changes in basal ganglia circuitry of awake rhesus monkeys. Neuroimage 14:1159–1167
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by NIH NIDA:RO1 DA16187, NIH NIDA 5PO1DA09467 and the Office of National Drug Control Policy CTAC program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YC.I., Choi, JK., Andersen, S.L. et al. Mapping dopamine D2/D3 receptor function using pharmacological magnetic resonance imaging. Psychopharmacology 180, 705–715 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2034-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-2034-0