Abstract
Rationale
The possible role of GABA in human aggression was evaluated by administering gabapentin to subjects with and without a history of conduct disorder and comparing the effects on laboratory measures of aggression and escape.
Methods
Eighteen male and two female subjects with a history of criminal behavior participated in experimental sessions, which measured aggressive and escape responses. Ten subjects had a history of childhood conduct disorder (CD+) and ten subjects with no history (non-CD controls). Aggression was measured using the Point Subtraction Aggression Paradigm (PSAP), which provided subjects aggressive, escape and monetary reinforced response options.
Results
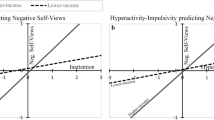
Acute doses (200, 400 and 800 mg) of gabapentin had similar effects on aggressive responses among CD+ subjects compared to non-CD control subjects. Aggressive responses of CD+ and non-CD control subjects increased at lower gabapentin doses, and decreased at the highest 800 mg gabapentin dose. Gabapentin increased escape responses for both CD+ and non-CD controls CD− subjects at the lowest dose, but then produced dose-related decreases at the two higher doses in both groups. No changes in monetary reinforced responses were observed, indicative of no CNS stimulation or sedation.
Conclusions
Gabapentin produced similar bitonic effects upon aggressive and escape responses in subjects with and without a history of childhood conduct disorder. This is in marked contrast to prior differential effects of baclofen on aggressive responses between CD+ and non-CD control subjects in a previous study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afaq I, Riaz J, Sedky K, Chung DJ, Vanina Y, el-Mallkh R, Lippmann S (2002) Divalproex as a calmative adjunct for aggressive schizophrenic patients. J Ky Med Assoc 100:17–22
Barratt ES (1985) Impulsiveness defined within a systems model of personality. In: Spielberger ED, Butcher JN (eds) Advances in personality assessment, vol 5. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, N.J., pp 113–132
Ben-Porath DD, Taylor SP (2002) The effects of diazepam (Valium) and aggressive disposition on human aggression. An experimental investigation. Addict Behav 27:167–177
Berman ME, Taylor S (1995) The effects of triazolam on aggression in men. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 3:411–416
Biancosino B, Facchi A, Marmai L, Grassi L (2002) Gabapentin treatment of impulsive-aggressive behaviour. Can J Psychiatry 47:483–484
Bjork JM, Moeller FG, Kramer GL, Kram M, Suris A, Rush AJ, Petty F (2001) Plasma GABA levels correlate with aggressiveness in relatives of patients with unipolar depressive disorder. Psychiatry Res 101:131–136
Bond AJ, Silviera JC (1993) The combination of alprazolam and alcohol on aggressive behavior. J Stud Alcohol Suppl 11:30–39
Bowery N, Hill D, Hudson A (1983) Characteristic of GABAb receptor binding sites on rat whole brain synaptic membranes. Br J Pharmacol 78:191–206
Buss A (1961) The psychology of aggression. Wiley, New York
Buss AH, Perry M (1992) The aggression questionnaire. J Person Soc Psychol 63:452–459
Cherek DR (1992) Point subtraction aggression paradigm (PSAP). University of Texas, Houston
Cherek DR, Lane SD (1999) Effects of d,l-fenfluramine on aggressive and impulsive responding in adult males with a history of conduct disorder. Psychopharmacology 146:473–481
Cherek DR, Lane SD (2001) Acute effects of d-fenfluramine on simultaneous measures of aggressive escape and impulsive responses of adult males with and without a history of conduct disorder. Psychopharmacology 157:221–227
Cherek DR, Steinberg JL, Kelly TH, Robinson DE, Spiga R (1990) Effects of acute administration of diazepam and d-amphetamine on aggressive and escape responding of normal male subjects. Psychopharmacology 100:173–181
Cherek DR, Spiga R, Roache JD, Cowan KA (1991) Effects of triazolam on human aggressive, escape and point-maintained responding. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:835–839
Cherek DR, Lane SD, Pietras SJ, Sharon J, Steinberg JL (2002) Acute effects of baclofen, a γ-aminobutyric acid-B agonist, on laboratory measures of aggressive and escape responses of adult male parolees with and without a history of conduct disorder. Psychopharmacology 164:160–167
Cheu JW, Siegel A (1998) GABA receptor mediated suppression of defensive rage behavior elicited from the medial hypothalamus of the cat: role of the lateral hypothalamus. Brain Res 783:293–304
Conchillo MP, Martinez-Sanchis S, Salvador A, Simon VM (2002) The GABAergic effect of low doses of lorazepam on social behavior. Aggress Behav 28:248–256
Cutler MG, Rodgers RJ, Jackson JE (1997) Behavioural effects in mice of subchronic chlordiazepoxide, maprotiline, and fluvoxamine, I: social interactions. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57:119–125
de-Paris F, Busnello JV, Vianna MRM, Salgueiro JB, Quevedo J, Izquierdo I, Kapczinski F (2000) The anticonvulsant compound gabapentin possesses anxiolytic but not amnesic effects in rats. Behav Pharmacol 11:169–173
Elwes RD, Binnie CD (1996) Clinical pharmacokinetics of newer antiepileptic drugs. Lamotrigine, vigabatrin, gabapentin and oxcarbazepine. Clin Pharmacokinet 30:403–415
File SE, Andrews N (1991) Low but not high doses of buspirone reduce the anxiogenic effects of diazepam withdrawal. Psychopharmacology 105:578–582
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1996) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders. Biometrics Research Department, NY State Psychiatric Institute
Frankenburg FR, Zanarini MC (2002) Divalproex sodium treatment of women with borderline personality disorder and bipolar II disorder: a double-blind placebo-controlled pilot study. J Clin Psychiatry 63:442–446
Goff DC, Heckers S, Freudenreich O (2001) Schizophrenia. Med Clin N Am 85:663–689
Gonzales LE, Andrews N, File SE (1996) 5-HT1a and benzodiazepine receptors in the basolateral amygdala modulate anxiety in the social interaction test, but not in the elevated plus-maze. Brain Res 732:145–153
Griffith JL (1985) Treatment of episodic behavioral disorders with rapidly absorbed benzodiazepines. J Nerv Ment Dis 173:312–315
Haas S, Vincent K, Holt J, Lippmann S (1997) Divalproex: a possible treatment alternative for demented, elderly aggressive patients. Ann Clin Psychiatry 9:145–147
Herrmann N, Lanctot K, Myszak M (2000) Effctiveness of gabapentin for the treatment of behavioral disorders in dementia. J Clin Psychopharmacol 20:90–93
Kuzniecky R, Ho S, Pan J, Martin R, Gilliam F, Faught E, Hetherington H (2002) Modulation of cerebral GABA by topiramate, lamotrigine, and gabapentin in healthy adults. Neurology 58:368–372
LaBuda CJ, Fuchs PN (2000) Morphine and gabapentin decrease mechanical hyperalgesia and escape/avoidance behavior in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett 290:137–140
Lanneau C, Green A, Hirst WD, Wise A, Brown JT, Donnier E, Charles, KJ, Wood M, Davies CH, Pangalos MN (2001) Gabapentin is not a GABA-B receptor agonist. Neuropharmacology 41:965–975
Lindenmayer JP, Kotsaftis A (2000) Use of sodium valproate in violent and aggressive behaviors: a critical review. J Clin Psychiatry 61:123–128
Low RA, Brandes M (1999) Gabapentin for the management of agitation. J Clin Psychopharmacol 19:482–483
Magnus L (1999) Nonepileptic uses of gabapentin. Epilepsia 40:S66–S72
McCormick DA, Williamson A (1989) Convergence and divergence of neurotransmitter action in human cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8098–8102
McLean MJ (1994) Clinical pharmacokinetics of gabapentin. Neurology 44:S17–S22
Miczek KA, DeBold JF, van Erp AM, Tornatzky W (1997) Alcohol, GABAA-benzodiazepine receptor complex, and aggression. Recent Dev Alcohol 13:139–171
Miczek KA, Fish EW, DeBold JF, Almeda RMM (2002) Social and neuronal determinants of aggressive behavior: pharmacotherapeutic targets at serotonin, dopamine and gamma-aminobutyric acid system. Psychopharmacology 163:434–458
Miller LJ (2001) Gabapentin for treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Ann Pharmacother 35:427–431
Molina VA, Ciesielski L, Gobaille S, Mandel P (1987) Effects of the potentiation of the GABAergic neurotransmission on the olfactory bulbs on mouse killing behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 24:657–664
Petroff OAC, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Lamoureux D, Mattson RH (1996) The effect of gabapentin on brain gamma-aminobutyric acid in patients with epilepsy. Ann Neurol 39:95–99
Puglisi-Allegra S, Mack G, Oliverio A, Mandel P (1979) Effects of apomorphrine and sodium di-N-propylacetate on the aggressive behaviour of three strains of mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol 3:491–502
Rodgers RJ, Depaulis A (1982) GABAergic influences on defensive fighting in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:451–456
Ryback R, Ryback L (1995) Gabapentin for behavioral dyscontrol (letter). Am J Psychiatry 152:1399
Sakaue M, Ago Y, Murakami C, Sowa C, Sakamoto Y, Koyama Y, Baba A, Matsuda T (2001) Involvement of benzodiazepine binding sites in an antiaggressive effect by 5-HT1a receptor activation in isolated mice. Eur J Pharmacol 432:163–166
Shipley Boyle B (1967) The Shipley Institute of Living Scale. Western Psychological Services, Los Angeles
Siegel A, Roeling TA, Gregg TR, Kruk MR (1999) Neuropharmacology of brain-stimulation-evoked aggression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 18:359–389
Singh L, Field MJ, Ferris P, Hunter JC, Oles RJ, Williams RG, Woodruff GN (1996) The antiepileptic agent gabapentin (Neurontin) possesses anxiolytic-like and antinociceptive actions that are reversed by d-serine. Psychopharmacology 127:1–9
Sival RC, Haffmans PM, Jansen PA, Duursma SA, Eikelenboom P (2002) Sodium valproate in the treatment of aggressive behavior inpatients with dementia- a randomized placebo controlled clinical trial. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 17:579–585
Solderpalm B, Andersson G, Enerback C, Engel JA (1997) In vivo administration of the 5-HT1a receptor agonist 8-OH-DPAT interferes with brain GABA A/benzodiazepine complexes. Neuropharmacology 36:1071–1077
Soreni N, Apter A, WeizmanA, Don-Tufeled O, Leschiner S, Karp L, Gavish M (1999) Decreased platelet peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in adolescent inpatients with repeated suicide attempts. Biol Psychiatry 46:484–448
Sorgi P, Ratey J, Knoedler DW, Markert RJ, Reichman M (1991) Rating aggression in the clinical setting: a retrospective adaptation of the Overt Aggression Scale. J Neuropsychiatr Clin Neurosci 3:S52–S56
Spielberger CD, Johnson EH, Russell SF, Crane RS, Jacobs GA, Worden TJ (1985) The experience and expression of anger: construction and validation of an anger expression scale. In: Chesney MA, Rosenman RH (eds) Anger and hostility in cardiovascular and behavioral disorders. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 5–30
Stanford MS, Houston RJ, Mathias CW, Greve KW, Villemarette-Pittmen NR, Adams D ( 2001) A double-blind placebo-controlled crossover study of phenytoin in individuals with impulsive aggression. Psychiatry Res 103:193–203
Taylor CP, Gee NS, SU T-Z, Kocsis JD, Welty DF, Brown JP, Dooley DJ, Boden P, Singh L (1998) A summary of mechanistic hypotheses of gabapentin pharmacology. Epilepsy Res 29:23–249
Valzelli L (1984) Reflections on experimental and human pathology of aggression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 8:311–325
Van Laar M, Volkerts E, Verbaten M (2001) Subchronic effects of the GABA-agonist lorazepem and the 5-HT2a/2c antagonist ritaserin on driving performance, slow wave sleep and daytime sleepiness in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 154:189–197
Vollmer KO, von Hodenberg A, Kolle EU (1986) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of gabapentin in rat, dog and man. Arzneimittelforschung 36:830–839
Weerts EM, Miczek KA (1996) Primate vocalizations during social separation and aggression: effects of alcohol and benzodiazepines. Psychopharmacology 127:255–264
Weisman AM, Berman ME, Taylor SP (1998) Effects of chlorazepate, diazepam, and oxazepam on a laboratory measurement of aggression in men. Clin Psychopharmacol 13:183–188
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Yudofsky SC, Silver JM, Hales RE (1995) Treatment of aggressive disorders. In: Schatzberg AE, Nemeroff CB (eds) Textbook of psychopharmacology. American Psychiatric Press, Washington D.C., pp 735–751
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NIH Grant DA 03166-17 from the National Institute on Drug Abuse. The authors wish to thank Jennifer Sharon and Ehren Bradbury for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cherek, D.R., Tcheremissine, O.V., Lane, S.D. et al. Acute effects of gabapentin on laboratory measures of aggressive and escape responses of adult parolees with and without a history of conduct disorder. Psychopharmacology 171, 405–412 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1590-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-003-1590-z