Abstract
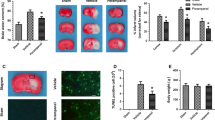
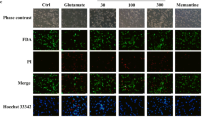
The present study evaluates the effect of modulating α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionate receptor (AMPAR) by inhibiting them in the acute phase and activating them in the sub-acute phase on post-stroke recovery in middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) model of stroke in rats. After 90 min of MCAo, perampanel (an AMPAR antagonist, 1.5 mg/kg i.p) and aniracetam (an AMPA agonist, 50 mg/kg i.p.) were administered for different durations after MCAo. Later, after obtaining the best time point for the antagonist and the agonist treatment protocols, sequential treatment with perampanel and aniracetam were given, and the effect on neurological damage and post stroke recovery were assessed. Perampanel and aniracetam significantly protected MCAo-induced neurological damage and diminished the infarct percentage. Furthermore, treatment with these study drugs improved the motor coordination and grip strength. Sequential treatment with perampanel and aniracetam reduced the infarct percentage as assessed by MRI. Moreover, these compounds diminished the inflammation via reducing the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β) and increasing the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10) along with reductions in GFAP expression. Moreover, the neuroprotective markers (BDNF and TrkB) were found to be significantly increased. Levels of apoptotic markers (Bax, cleaved-caspase-3; Bcl2 and TUNEL positive cells) and neuronal damage (MAP-2) were normalized with the AMPA antagonist and agonist treatment. Expressions of GluR1 and GluR2 subunits of AMPAR were significantly enhanced with sequential treatment. The present study thus showed that modulation of AMPAR improves neurobehavioral deficits and reduces the infarct percentage through anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and anti-apoptotic effects.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Altinova H, Hammes S, Palm M, Gerardo-Nava J, Achenbach P, Deumens R, Hermans E, Führmann T, Boecker A, van Neerven SG, Bozkurt A (2019) Fibroadhesive scarring of grafted collagen scaffolds interferes with implant–host neural tissue integration and bridging in experimental spinal cord injury. Regen Biomater 6:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1093/rb/rbz006
Baranova AI, Whiting MD, Hamm RJ (2006) Delayed, post-injury treatment with aniracetam improves cognitive performance after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma 23:1233–1240. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2006.23.1233
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski HM (1986) Evaluation of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 17:1304–1308. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.17.6.1304
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40:331–339. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.531632
Centonze D, Rossi S, Tortiglione A, Picconi B, Prosperetti C, De Chiara V, Bernardi G, Calabresi P (2007) Synaptic plasticity during recovery from permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Neurobiol Dis 27:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2007.03.012
Clarkson AN, Overman JJ, Zhong S, Mueller R, Lynch G, Carmichael ST (2011) AMPA receptor induced local brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling mediates motor recovery after stroke. J Neurosci 31:3766–3775. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5780-10.2011
Clausen BH, Lambertsen KL, Dagnæs-Hansen F, Babcock AA, von Linstow CU, Meldgaard M, Kristensen BW, Deierborg T, Finsen B (2016) Cell therapy centered on IL-1Ra is neuroprotective in experimental stroke. Acta Neuropathol 131:775–791. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-016-1541-5
Curtis MJ, Alexander S, Cirino G, Docherty JR, George CH, Giembycz MA, Hoyer D, Insel PA, Izzo AA, Ji Y, MacEwan DJ (2018) Experimental design and analysis and their reporting II: updated and simplified guidance for authors and peer reviewers. Br J Pharmacol 175:987–993. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14153
Derkach VA, Oh MC, Guire ES, Soderling TR (2007) Regulatory mechanisms of AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2055
Feigin VL, Stark BA, Johnson CO, Roth GA, Bisignano C, Abady GG, Abbasifard M, Abbasi-Kangevari M, Abd-Allah F, Abedi V, Abualhasan A (2021) Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol 20:795–820. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
Gerlai R, Henderson JT, Roder JC, Jia Z (1998) Multiple behavioral anomalies in GluR2 mutant mice exhibiting enhanced LTP. Behav Brain Res 95:37–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-4328(98)00002-3
Gupta YK, Briyal S, Sharma U, Jagannathan NR, Gulati A (2005) Effect of endothelin antagonist (TAK-044) on cerebral ischemic volume, oxidative stress markers and neurobehavioral parameters in the middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rats. Life Sci 77:15–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2004.11.025
Haupt M, Gerner ST, Bähr M, Doeppner TR (2023) Neuroprotective Strategies for Ischemic Stroke—Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 24:4334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054334
Helmer RA, Martinez-Zaguilan R, Kaur G, Smith LA, Dufour JM, Chilton BS (2021) Helicase-like transcription factor-deletion from the tumor microenvironment in a cell line-derived xenograft model of colorectal cancer reprogrammed the human transcriptome-S-nitroso-proteome to promote inflammation and redirect metastasis. PloS one 16:e0251132. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0251132
Hummel FC, Cohen LG (2006) Non-invasive brain stimulation: a new strategy to improve neurorehabilitation after stroke? Lancet Neurol 5:708–712. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70525-7
Hurn PD, Macrae IM (2000) Estrogen as a neuroprotectant in stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:631–652. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004647-200004000-00001
Ishikawa M, Takaseki S, Yoshitomi T, Covey DF, Zorumski CF, Izumi Y (2021) The neurosteroid allopregnanolone protects retinal neurons by effects on autophagy and GABRs/GABAA receptors in rat glaucoma models. Autophagy 17:743–760. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1731270
Jin W (2020) Regulation of BDNF-TrkB signaling and potential therapeutic strategies for Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Med 9:257. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9010257
Johnson CO, Nguyen M, Roth GA, Nichols E, Alam T, Abate D, Abd-Allah F, Abdelalim A, Abraha HN, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Adebayo OM (2019) Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol 18:439–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30034-1
Jourdi H, Hsu YT, Zhou M, Qin Q, Bi X, Baudry M (2009) Positive AMPA receptor modulation rapidly stimulates BDNF release and increases dendritic mRNA translation. J Neurosci 29:8688–8697. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6078-08.2009
Kale J, Osterlund EJ, Andrews DW (2018) BCL-2 family proteins: changing partners in the dance towards death. Cell Death Differ 25:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.186
Kyrylkova K, Kyryachenko S, Leid M, Kioussi C (2012) Detection of apoptosis by TUNEL assay. Methods Mol Biol 887:41–47. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61779-860-3_5
Lambertsen KL, Finsen B, Clausen BH (2019) Post-stroke inflammation—target or tool for therapy? Acta Neuropathol 137:693–714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-018-1930-z
Lees A, Fahn S, Eggert KM, Jankovic J, Lang A, Micheli F, Maral Mouradian M, Oertel WH, Olanow CW, Poewe W, Rascol O (2012) Perampanel, an AMPA antagonist, found to have no benefit in reducing “off” time in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 27:284–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.23983
Li Y, Zhang L, Li J, Wang C, Chen Y, Yuan Y, Xie K, Wang G, Yu Y (2021) A role for transmembrane protein 16C/Slack impairment in excitatory nociceptive synaptic plasticity in the pathogenesis of remifentanil-induced hyperalgesia in rats. Neurosci Bull 37:669–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-021-00652-5
Liguz-Lecznar M, Zakrzewska R, Kossut M (2015) Inhibition of Tnf-α R1 signaling can rescue functional cortical plasticity impaired in early post-stroke period. Neurobiol Aging 36:2877–2884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.06.015
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.20.1.84
Lu ZG, Shen J, Yang J, Wang JW, Zhao RC, Zhang TL, Guo J, Zhang X (2023) Nucleic acid drug vectors for diagnosis and treatment of brain diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 8:39. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01298-z
Lynch G, Rex CS, Chen LY, Gall CM (2008) The substrates of memory: defects, treatments, and enhancement. Eur J Pharmacol 585:2–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.082
Mages B, Fuhs T, Aleithe S, Blietz A, Hobusch C, Härtig W, Schob S, Krueger M, Michalski D (2021) The cytoskeletal elements MAP2 and NF-L show substantial alterations in different stroke models while elevated serum levels highlight especially MAP2 as a sensitive biomarker in stroke patients. Mol Neurobiol 58:4051–4069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02372-3
Mallah K, Couch C, Borucki DM, Toutonji A, Alshareef M, Tomlinson S (2020) Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agents in clinical trials for CNS disease and injury: where do we go from here? Front Immunol 11:2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.02021
Moran PM, Higgins LS, Cordell B, Moser PC (1995) Age-related learning deficits in transgenic mice expressing the 751-amino acid isoform of human beta-amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5341–5345. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.12.5341
Nakajima M, Suda S, Sowa K, Sakamoto Y, Nito C, Nishiyama Y, Aoki J, Ueda M, Yokobori S, Yamada M, Yokota H (2018) AMPA Receptor Antagonist Perampanel Ameliorates Post-Stroke Functional and Cognitive Impairments. Neuroscience 386:256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.06.043
Nguyen TV, Frye JB, Zbesko JC, Stepanovic K, Hayes M, Urzua A, Serrano G, Beach TG, Doyle KP (2016) Multiplex immunoassay characterization and species comparison of inflammation in acute and non-acute ischemic infarcts in human and mouse brain tissue. Acta Neuropathol Commun 4:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-016-0371-y
Nito C, Ueda M, Inaba T, Katsura KI, Katayama Y (2011) FK506 ameliorates oxidative damage and protects rat brain following transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res 33:881–889. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743132811Y.0000000019
Niu HX, Wang JZ, Wang DL, Miao JJ, Li H, Liu ZG, Yuan X, Liu W, Zhou JR (2018) The Orally Active Noncompetitive AMPAR Antagonist Perampanel Attenuates Focal Cerebral Ischemia Injury in Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38:459–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0489-x
Ploughman M, Windle V, MacLellan CL, White N, Doré JJ, Corbett D (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor contributes to recovery of skilled reaching after focal ischemia in rats. Stroke 40:1490–1495. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.531806
Popiela TJ, Krzyściak W, Pilato F, Ligęzka A, Bystrowska B, Bukowska-Strakova K, Brzegowy P, Muthusamy K, Kozicz T (2022) The assessment of endovascular therapies in ischemic stroke: management, problems and future approaches. J Clin Med 11:1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11071864
Porter AG, Jänicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4400476
Qin C, Yang S, Chu YH, Zhang H, Pang XW, Chen L, Zhou LQ, Chen M, Tian DS, Wang W (2022) Signaling pathways involved in ischemic stroke: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7:215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01064-1
Rajah GB, Ding Y (2017) Experimental neuroprotection in ischemic stroke: a concise review. Neurosurg Focus 42:E2. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.1.FOCUS16497
Reeta KH, Singh D, Gupta YK (2017) Edaravone attenuates intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Eur J Neurosci 45:987–997. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13543
Rogers DC, Campbell CA, Stretton JL, Mackay KB (1997) Correlation between motor impairment and infarct volume after permanent and transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Stroke 28:2060–2065. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.28.10.2060
Sacco RL, Kasner SE, Broderick JP, Caplan LR, Connors JJ, Culebras A, Elkind MS, George MG, Hamdan AD, Higashida RT, Hoh BL (2013) An updated definition of stroke for the 21st century: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:2064–2089. https://doi.org/10.1161/STR.0b013e318296aeca
Schabitz WR, Berger C, Kollmar R, Seitz M, Tanay E, Kiessling M, Schwab S, Sommer C (2004) Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor treatment and forced arm use on functional motor recovery after small cortical ischemia. Stroke 35:992–997. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000119754.85848.0D
Siemonsen S, Löbel U, Sedlacik J, Forkert ND, Mouridsen K, Østergaard L, Thomalla G, Fiehler J (2012) Elevated T2-values in MRI of stroke patients shortly after symptom onset do not predict irreversible tissue infarction. Brain 135:1981–1989. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/aws079
Spronk E, Sykes G, Falcione S, Munsterman D, Joy T, Kamtchum-Tatuene J, Jickling GC (2021) Hemorrhagic transformation in ischemic stroke and the role of inflammation. Front Neurol 12:661955. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2021.661955
Stampanoni Bassi M, Iezzi E, Gilio L, Centonze D, Buttari F (2019) Synaptic plasticity shapes brain connectivity: implications for network topology. Int J Mol Sci 20:6193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246193
Stuckey SM, Ong LK, Collins-Praino LE, Turner RJ (2021) Neuroinflammation as a key driver of secondary neurodegeneration following stroke? Int J Mol Sci 22:13101. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222313101
Sun Y, Feng X, Ding Y, Li M, Yao J, Wang L, Gao Z (2019) Phased treatment strategies for cerebral ischemia based on glutamate receptors. Front Cell Neurosci 13:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2019.00168
Terashima A, Suh YH, Isaac JT (2019) The AMPA receptor subunit GluA1 is required for CA1 hippocampal long-term potentiation but is not essential for synaptic transmission. Neurochem Res 44:549–561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2425-3
Tourville A, Akbar D, Corti O, Prehn JH, Melki R, Hunot S, Michel PP (2022) Modelling α-Synuclein Aggregation and Neurodegeneration with Fibril Seeds in Primary Cultures of Mouse Dopaminergic Neurons. Cells 11:1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11101640
Valsecchi V, Boido M, Montarolo F, Guglielmotto M, Perga S, Martire S, Cutrupi S, Iannello A, Gionchiglia N, Signorino E, Calvo A (2020) The transcription factor Nurr1 is upregulated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients and SOD1-G93A mice. Dis Model Mech 13:p.dmm043513. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.043513
Wang H, Song G, Chuang H, Chiu C, Abdelmaksoud A, Ye Y, Zhao L (2018) Portrait of glial scar in neurological diseases. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 31:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/2058738418801406
Wang CS, Kavalali ET, Monteggia LM (2021) BDNF signaling in context: From synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders. Cell 185:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.003
Wasan H, Singh D, Joshi B, Sharma U, Dinda AK, Reeta KH (2021) Post stroke safinamide treatment attenuates neurological damage by modulating autophagy and apoptosis in experimental model of stroke in rats. Mol Neurobiol 58:6121–6135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02523-6
Yamada I, Miyasaka N, Kobayashi D, Wakana K, Oshima N, Wakabayashi A, Sakamoto J, Saida Y, Tateishi U, Eishi Y (2019) Endometrial carcinoma: texture analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient maps and its correlation with histopathologic findings and prognosis. Radiol Imaging Cancer 1:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1148/rycan.2019190054
Yang Z, Wang KK (2015) Glial fibrillary acidic protein: from intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci 38:364–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2015.04.003
Yrjänheikki J, Tikka T, Keinänen R, Goldsteins G, Chan PH, Koistinaho J (1999) Tetracycline derivative, minocycline, reduces inflammation and protects against focal cerebral ischemia with a wide therapeutic window. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13496–13500. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.23.13496
Zhang L, Schessl J, Werner M, Bonnemann C, Xiong G, Mojsilovic-Petrovic J, Zhou W, Cohen A, Seeburg P, Misawa H, Jayaram A (2008) Role of GluR1 in activity-dependent motor system development. J Neurosci 28:9953–9968. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0880-08.2008
Zhao H, Yenari MA, Cheng D, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (2003) Bcl-2 overexpression protects against neuron loss within the ischemic margin following experimental stroke and inhibits cytochrome c translocation and caspase-3 activity. J Neurochem 85:1026–1036. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01756.x
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial assistance from the Indian Council of Medical Research (58/06/2019/PHA/BMS) to Dr KH Reeta.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: H.S. and K.R. Methodology: H.S., K.R., U.S., V.S. and S.S. Validation: H.S., K.R., U.S. and V.S. Formal analysis: H.S., K.R., U.S., V.S. and S.S. Writing-original draft preparation: H.S. and K.R. Writing- review and editing: H.S. and K.R. Supervision: K.R. All authors have read and agreed to the final version of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was approved by Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India (150/IAEC-1/2019).
Competing interests
None to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, H., Reeta, K.H., Sharma, U. et al. AMPA receptor modulation through sequential treatment with perampanel and aniracetam mitigates post-stroke damage in experimental model of ischemic stroke. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 3529–3545 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02544-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02544-z