Abstract
Purpose
Cyclophosphamide is an alkylating agent with nephrotoxicity that constrains its clinical application. Berberine is an isoquinoline derivative alkaloid with biological functions like antioxidant and anti-inflammatory. The current research intended to examine the nephroprotective impacts of berberine against cyclophosphamide-stimulated nephrotoxicity.
Methods
Forty animal subjects were randomly separated into five categories of control (Group I), cyclophosphamide (200 mg/kg, i.p., on 7th day) (Group II), and groups III and IV that received berberine 50 and 100 mg/kg orally for seven days and a single injection of cyclophosphamide on 7th day. Group V as berberine (100 mg/kg, alone). On day 8, blood samples were drawn from the retro-orbital sinus to determine serum levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (Cr), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), and kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) as biomarkers for kidney injury. Nitric oxide (NO), malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH) levels, catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities as oxidative stress factors, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) levels as inflammatory mediators were assessed in kidney tissue.
Results
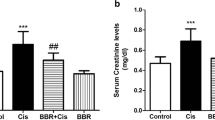
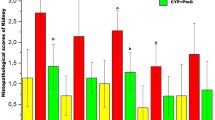
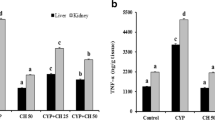
The results of this study demonstrated that berberine was able to protect remarkably the kidney from CP-induced injury through decreasing the level of BUN, Cr, NGAL, KIM-1, NO, MDA TNF-α, IL-1β and increasing the level of GSH, CAT, SOD, and GPx activities.
Conclusion
Berberine may be employed as a natural agent to prevent cyclophosphamide-induced nephrotoxicity through anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Bradford N (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation microgram quantities of a protein isolated from red cell membranes. Anal Biochem 72:e254
Chen X, Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Liu H, Guo H, Xiong C, Xie K, Zhang X, Su S (2016) Protective effect of berberine on doxorubicin-induced acute hepatorenal toxicity in rats. Mol Med Rep 13:3953–3960
Crivellari D, Bonetti M, Castiglione-Gertsch M, Gelber RD, Rudenstam C-M, Thürlimann B, Price KN, Coates AS, Hürny C, Bernhard J (2000) Burdens and benefits of adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil and tamoxifen for elderly patients with breast cancer: the International Breast Cancer Study Group Trial VII. J Clin Oncol 18:1412–1422
Edelstein CL (2017) Biomarkers in acute kidney injury. Biomarkers of Kidney Disease 241–315
El-Naggar SA, Alm-Eldeen AA, Germoush MO, El-Boray KF, Elgebaly HA (2015) Ameliorative effect of propolis against cyclophosphamide-induced toxicity in mice. Pharm Biol 53:235–241
Fraiser LH, Kanekal S, Kehrer JP (1991) Cyclophosphamide toxicity. Drugs 42:781–795
Goudarzi M, Khodayar MJ, Hosseini Tabatabaei SMT, Ghaznavi H, Fatemi I, Mehrzadi S (2017) Pretreatment with melatonin protects against cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress and renal damage in mice. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 31:625–635
Goudarzi M, Kalantar M, Sadeghi E, Karamallah MH, Kalantar H (2021) Protective effects of apigenin on altered lipid peroxidation, inflammation, and antioxidant factors in methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 394:523–531
Goudarzi M, Esmaeilizadeh M, Dolatshahi M, Kalantar H, Frouzandeh H, Kalantar M (2018) Protective effect of elaeagnus angustifolia L. Fruit hydroalcoholic extract on cyclophosphamide-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Shiraz E Med J 19
Goudarzi M, Karamallah MH, Malayeri A, Kalantar M, Mansouri E, Kalantar H (2020) Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid on di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced testicular toxicity in mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–9
Halliwell B (2001) Free radicals and other reactive species in disease. e LS
Hamsa T, Kuttan G (2011) Protective role of Ipomoea obscura (L.) on cyclophosphamide-induced uro-and nephrotoxicities by modulating antioxidant status and pro-inflammatory cytokine levels. Inflammopharmacology 19:155–167
Hasanein P, Ghafari-Vahed M, Khodadadi I (2017) Effects of isoquinoline alkaloid berberine on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant defense system, and liver damage induced by lead acetate in rats. Redox Rep 22:42–50
Hoitsma AJ, Wetzels JF, Koene RA (1991) Drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Drug Safety 6:131–147
Kalantar M, Houshmand G, Kalantar H, Asadi M, Goudarzi M (2016b) Protective effect of hydroalcoholic extract of Lavandula officinalis L. on gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J Babol Univ Med Sci 18:62–67
Kalantar H, Sabetkasaei M, Shahriari A, Haj Molla Hoseini M, Mansouri S, Kalantar M, Kalantari A, Khazaei Poul Y, Labibi F, Moini-Zanjani T (2016a) The effect of rapamycin on oxidative stress in MCF-7 and MDA MB-231 human breast cancer cell lines. Jundishapur J Nat Pharm Prod 11
Kuo C-L, Chi C-W, Liu T-Y (2004) The anti-inflammatory potential of berberine in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett 203:127–137
Lawson M, Vasilaras A, De Vries A, Mactaggart P, Nicol D (2008) Urological implications of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide. Scand J Urol Nephrol 42:309–317
Li Z, Geng Y-N, Jiang J-D, Kong W-J (2014) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of berberine in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Evid-Based Complement Alternat Med 2014
Lou T, Zhang Z, Xi Z, Liu K, Li L, Liu B, Huang F (2011) Berberine inhibits inflammatory response and ameliorates insulin resistance in hepatocytes. Inflammation 34:659–667
Mahmoud AM, Abdel-Rahman MM, Bastawy NA, Eissa HM (2017) Modulatory effect of berberine on adipose tissue PPARγ, adipocytokines and oxidative stress in high fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Appl Pharm Sci 7:1–10
Moore K, Roberts LJ (1998) Measurement of lipid peroxidation. Free Radical Res 28:659–671
Najafi H, Ashtiyani SC, Sayedzadeh SA (2015) Therapeutic effects of curcumin on the functional disturbances and oxidative stress induced by renal ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Avicenna J Phytomed 5:576
Neurath MF (2014) Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol 14:329–342
Oktem G, Uysal A, Oral O, Sezer ED, Olukman M, Erol A, Akgur SA, Bilir A (2012) Resveratrol attenuates doxorubicin-induced cellular damage by modulating nitric oxide and apoptosis. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:471–479
Perini P, Calabrese M, Rinaldi L, Gallo P (2007) The safety profile of cyclophosphamide in multiple sclerosis therapy. Expert Opin Drug Saf 6:183–190
Riddles PW, Blakeley RL, Zerner B (1979) Ellman’s reagent: 5, 5′-dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid)—a reexamination. Anal Biochem 94:75–81
Rodriguez-Antona C, Ingelman-Sundberg M (2006) Cytochrome P 450 pharmacogenetics and cancer. Oncogene 25:1679–1691
Salazar JH (2014) Overview of urea and creatinine. Lab Med 45:e19–e20
Stankiewicz A, Skrzydlewska E, Makiela M (2002) Effects of amifostine on liver oxidative stress caused by cyclophosphamide administration to rats. Drug Metab Drug Interact 19:67–82
Sun Y, Xun K, Wang Y, Chen X (2009) A systematic review of the anticancer properties of berberine, a natural product from Chinese herbs. Anticancer Drugs 20:757–769
Temel Y, Kucukler S, Yıldırım S, Caglayan C, Kandemir FM (2020) Protective effect of chrysin on cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity via the inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 393:325–337
Wadie W, Mohamed AH, Masoud MA, Rizk HA, Sayed HM (2021) Protective impact of lycopene on ethinylestradiol-induced cholestasis in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 394:447–455
Wahlang B, Falkner KC, Cave MC, Prough RA (2015) Role of cytochrome P450 monooxygenase in carcinogen and chemotherapeutic drug metabolism. Adv Pharmacol 74:1–33
Wang X, Feng S, Ding N, He Y, Li C, Li M, Ding X, Ding H, Li J, Wu J (2018) Anti-inflammatory effects of berberine hydrochloride in an LPS-induced murine model of mastitis. Evid-Based Complement Alternat Med 2018
Yu X, Wang Y, Dai F, Zhao J, Li P (2019) The protective effects of Berberine and Hesperidin on inflammatory factor-stimulating cardiac fibroblasts. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:5468–5476
Zhang S, Zhang B, Dai W, Zhang X (2011) Oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in Microcystis aeruginosa exposed to the allelochemical berberine isolated from golden thread. J Plant Physiol 168:639–643
Zhang X, He H, Liang D, Jiang Y, Liang W, Chi Z-H, Ma J (2016a) Protective effects of berberine on renal injury in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. Int J Mol Sci 17:1327
Zhang Z, Li X, Li F, An L (2016b) Berberine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing neuroinflammation in aged mice. Int Immunopharmacol 38:426–433
Zhou J-Y, Zhou S-W (2011) Protective effect of berberine on antioxidant enzymes and positive transcription elongation factor b expression in diabetic rat liver. Fitoterapia 82:184–189
Funding
This work was supported by Deputy of Research of Shoushtar University of Medical Sciences, Shoushtar, Iran (Grant number: TRC-9803) and Vice-Chancellor of Research, Toxicology Research Center, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MK and MAM conceived and designed the study. MAM, HK, and ES performed experiments. MAM, MG, and ES analyzed data. HK and HRK wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript and all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The investigation complies with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication no. 85–23, revised 1996). The investigation complies with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication no. 85–23, revised 1996). The Animal Ethics Committee of the Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences approved our research protocol (Ethic code: IR.BHN.REC.1397.033).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mombeini, M.A., Kalantar, H., Sadeghi, E. et al. Protective effects of berberine as a natural antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent against nephrotoxicity induced by cyclophosphamide in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 187–194 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02182-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02182-3