Abstract
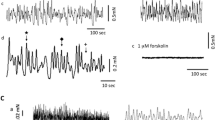
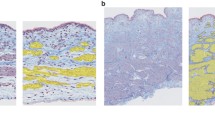
Human proximal and distal ureter tissues were studied to clarify whether the presence of mucosa affects contractile responses. In histological studies, human ureter was compared with urinary bladder (detrusor). Contractions in response to high KCl solution, phenylephrine, and carbachol were measured in intact and mucosa-denuded strips of human ureter. Tissue sections of human bladder and ureter were used for histological staining. Thirty-four percent of the ureter strips contracted spontaneously with highly variable patterns, and this was affected neither by mucosa nor by proximal or distal tissue origin. Upon stimulation with 40 mM KCl, ureter strips exhibited strong phasic and weak tonic contractions. In intact strips, normalized tonic force was lower than in denuded strips, but no consistent effect of mucosa was observed with phasic contractions. Absolute force values of phasic contractions were weaker in proximal than distal ureter strips, but similar when normalized to tissue wet weight. Stimulation with 80 mM KCl enhanced tonic contraction fourfold; phasic contractions occurred rarely. Phenylephrine produced no statistically significant stronger tonic contraction in distal compared with proximal ureter strips; nevertheless, in some strips, pre-existing spontaneous contractions increased. Carbachol did not influence ureter contractions. In the bladder, a suburothelial cell layer stained positive with α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA)-specific antibodies could be further differentiated with vimentin- and desmin-specific antibodies. α-SMA positive cells were absent in suburothelial ureter tissue. Like in detrusor, the mucosa inhibits KCl-stimulated tonic ureter contractions. The mucosa of detrusor and ureter tissue exhibits distinct staining patterns for α-SMA, vimentin, and desmin. This suggests a different distribution of smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and myofibroblasts, which could be a target for pharmacological therapy of pathologic contractile processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson K-E, McCloskey KD (2014) Lamina propria: the functional center of the bladder? Neurourol Urodyn 33:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22465
Birder L, Andersson K-E (2013) Urothelial signaling. Physiol Rev 93:653–680. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00030.2012
Canda AE, Turna B, Cinar GM, Nazli O (2007) Physiology and pharmacology of the human ureter: basis for current and future treatments. Urol Int 78:289–298. https://doi.org/10.1159/000100830
Dixon JS, Gosling JA (1983) Histology and fine structure of the muscularis mucosae of the human urinary bladder. J Anat 136:265–271
Drake MJ, Fry CH, Eyden B (2006) Structural characterization of myofibroblasts in the bladder. BJU Int 97:29–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2006.05818.x
Gevaert T, De Vos R, Van Der Aa F et al (2012) Identification of telocytes in the upper lamina propria of the human urinary tract. J Cell Mol Med 16:2085–2093. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01504.x
Gevaert T, Vanstreels E, Daelemans D, Franken J, van der Aa F, Roskams T, de Ridder D (2014) Identification of different phenotypes of interstitial cells in the upper and deep lamina propria of the human bladder dome. J Urol 192:1555–1563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.05.096
Hawthorn MH, Chapple CR, Cock M, Chess-Williams R (2000) Urothelium-derived inhibitory factor(s) influences on detrusor muscle contractility in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 129:416–419. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0703068
Jankovic SM, Jankovic SV, Stojanovic V et al (2011) Contractile effects of endothelins on isolated human ureter. Physiol Res Acad Sci Bohemoslov 60:933–939
Jerde TJ, Saban R, Nakada SY (1999) Evaluation of ureteric contraction: a comparison among ring, spiral-cut and longitudinal segments. BJU Int 83:95–100
Kasper M, Günthert U, Dall P, Kayser K, Schuh D, Haroske G, Müller M (1995) Distinct expression patterns of CD44 isoforms during human lung development and in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 13:648–656. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.13.6.7576702
Lang RJ, Tonta MA, Zoltkowski BZ, Meeker WF, Wendt I, Parkington HC (2006) Pyeloureteric peristalsis: role of atypical smooth muscle cells and interstitial cells of Cajal-like cells as pacemakers. J Physiol 576:695–705. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2006.116855
Langton P, Ward SM, Carl A, Norell MA, Sanders KM (1989) Spontaneous electrical activity of interstitial cells of Cajal isolated from canine proximal colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 86:7280–7284
Lee HW, Baak CH, Lee MY, Kim YC (2011) Spontaneous contractions augmented by cholinergic and adrenergic systems in the human ureter. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Off J Korean Physiol Soc Korean Soc Pharmacol 15:37–41. https://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2011.15.1.37
Mastrangelo D, Iselin CE (2007) Urothelium dependent inhibition of rat ureter contractile activity. J Urol 178:702–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2007.03.099
McCloskey KD (2010) Interstitial cells in the urinary bladder—localization and function. Neurourol Urodyn 29:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.20739
Michel MC, Igawa Y (2015) Therapeutic targets for overactive bladder other than smooth muscle. Expert Opin Ther Targets 19:687–705. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2015.1009447
Popescu LM, Faussone-Pellegrini M-S (2010) TELOCYTES—a case of serendipity: the winding way from interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC), via interstitial Cajal-like cells (ICLC) to TELOCYTES. J Cell Mol Med 14:729–740. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01059.x
Propping S, Wuest M, Eichhorn B, Wirth MP, Kaumann AJ, Ravens U (2013) Mucosa of human detrusor impairs contraction and β-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation. BJU Int 112:1215–1222. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.12267
Propping S, Roedel M, Wirth MP, Ravens U (2015) Pharmacological modulation of mucosa-related impairment of β-adrenoceptor-mediated relaxation in human detrusor. Urol Int 95:300–308. https://doi.org/10.1159/000431260
Roshani H, Dabhoiwala NF, Dijkhuis T et al (2003) Pharmacological modulation of ureteral peristalsis in a chronically instrumented conscious pig model. I: effect of cholinergic stimulation and inhibition. J Urol 170:264–267. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000071964.04804.e4
Sadananda P, Chess-Williams R, Burcher E (2008) Contractile properties of the pig bladder mucosa in response to neurokinin A: a role for myofibroblasts? Br J Pharmacol 153:1465–1473. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjp.2008.29
Sakamoto K, Suri D, Rajasekaran M (2006) Characterization of muscarinic receptor subtypes in human ureter. J Endourol Endourol Soc 20:939–942. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2006.20.939
Sasaki S, Tomiyama Y, Kobayashi S, Kojima Y, Kubota Y, Kohri K (2011) Characterization of α1-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating contraction in human isolated ureters. Urology 77:762.e13–762.e17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2010.09.034
Sui GP, Rothery S, Dupont E, Fry CH, Severs NJ (2002) Gap junctions and connexin expression in human suburothelial interstitial cells. BJU Int 90:118–129
Sui GP, Wu C, Fry CH (2004) Electrical characteristics of suburothelial cells isolated from the human bladder. J Urol 171:938–943. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000108120.28291.eb
Tomiyama Y, Wanajo I, Yamazaki Y, Murakami M, Kojima M, Shibata N (2003) Functional muscarinic cholinoceptors in the isolated canine ureter. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 367:348–352. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0697-4
Vannucchi M-G, Traini C, Guasti D, Giulio DP, Faussone-Pellegrini MS (2014) Telocytes subtypes in human urinary bladder. J Cell Mol Med 18:2000–2008. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12375
Weaver MG, Abdul-Karim FW (1990) The prevalence and character of the muscularis mucosae of the human urinary bladder. Histopathology 17:563–566
Wiseman OJ, Fowler CJ, Landon DN (2003) The role of the human bladder lamina propria myofibroblast. BJU Int 91:89–93
Wuest M, Morgenstern K, Graf E-M et al (2005) Cholinergic and purinergic responses in isolated human detrusor in relation to age. J Urol 173:2182–2189. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000158126.53702.e4
Wuest M, Eichhorn B, Grimm MO, Wirth MP, Ravens U, Kaumann AJ (2009) Catecholamines relax detrusor through beta 2-adrenoceptors in mouse and beta 3-adrenoceptors in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.142562
Yu W, Zeidel ML, Hill WG (2012) Cellular expression profile for interstitial cells of cajal in bladder—a cell often misidentified as myocyte or myofibroblast. PLoS One 7:e48897. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0048897
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the team of the Clinic of Urology, University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden for providing the tissue samples used for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Fig. 1
A: Distal ureteral strip, cut open longitudinally. B: Larger magnification on the right side showing fine spider-like vessels of the mucosa. Scale bar, left 4 mm, right 1 mm. C and D: Hematoxylin-Eosin staining of distal ureter strips, intact (C) and without mucosa (D). 1: Urothelium; 2: Lamina propria, 2a: transition from lower rim of lamina propria and smooth muscle; 3: smooth muscle. (PNG 767 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Correlation between wet weight (mg) of ureteral strips and maximum phasic and tonic force in response to 40 mM KCl. All values for phasic force ≥1.0 mN and tonic force ≥0.5 mN included. Correlation coefficient (r2) and P value for significantly difference from slope zero is given for each group. A + C: Proximal strips (with and without mucosa); B + D: Distal strips (with and without mucosa). (PNG 47 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Maximum phasic and tonic force development of human ureteral strips exposed to 40 mM KCl. A: Bar graphs (means ± SD): same values as for Fig. 2, but P values given for difference between proximal and distal strips. B: Scatter plots contain all values for phasic force ≥1 mN and tonic force ≥0.5 mN. P values for comparison of proximal versus distal strips. (PNG 115 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roedel, M., Ravens, U., Kasper, M. et al. Contractile responses in intact and mucosa-denuded human ureter—a comparison with urinary bladder detrusor preparations. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 391, 773–782 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1505-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1505-5