Abstract
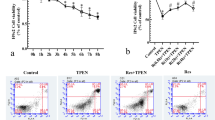
Excessive alcohol consumption provides risk to cardiomyopathy with unknown mechanisms. Resveratrol, a plant polyphenol, is widely reported for its cardiovascular benefits, while its effect on alcohol-induced impairments in cardiomyocytes largely remains unknown. Effects of resveratrol on the cardiomyocytes under ethanol insult were studied in vitro. Ethanol exposure in mouse neonatal cardiomyocytes increased cell death and induced a specific loss of tight junction protein, connexin 43. In spite of adverse effects at higher concentrations, resveratrol at 10 μM improved cell viability of cardiomyocytes in the presence of a deleterious dose of ethanol. Importantly, the co-treatment of resveratrol with ethanol exhibited the restoration of connexin 43 protein. Further assays showed that these effects were likely associated with the antioxidative actions of resveratrol, and correlated with the alleviation of MAP kinase activation in cultured cardiomyocytes in response to ethanol. Our data suggests a novel mechanism of cardiomyocyte cell loss under ethanol exposure and provides new evidence of protective effects of resveratrol in the cardiomyocytes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adermark L, Olsson T, Hansson E (2004) Ethanol acutely decreases astroglial gap junction permeability in primary cultures from defined brain regions. Neurochem Int 45:971–978. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2004.06.007
Blanc EM, Bruce-Keller AJ, Mattson MP (1998) Astrocytic gap junctional communication decreases neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress-induced disruption of Ca2+ homeostasis and cell death. J Neurochem 70:958–970
Delmar M, McKenna WJ (2010) The cardiac desmosome and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies: from gene to disease. Circ Res 107:700–714. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223412
Dupont E et al (2001) Altered connexin expression in human congestive heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:359–371. doi:10.1006/jmcc.2000.1308
Eckardt D et al (2004) Functional role of connexin43 gap junction channels in adult mouse heart assessed by inducible gene deletion. J Mol Cell Cardiol 36:101–110
Ehler E, Moore-Morris T, Lange S (2013) Isolation and culture of neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. J Vis Exp. doi:10.3791/50154
Fernandez-Sola J, Fatjo F, Sacanella E, Estruch R, Bosch X, Urbano-Marquez A, Nicolas JM (2006) Evidence of apoptosis in alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Hum Pathol 37:1100–1110. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2006.03.022
Fremont L (2000) Biological effects of resveratrol. Life Sci 66:663–673
Guan Z, Lui CY, Morkin E, Bahl JJ (2004) Oxidative stress and apoptosis in cardiomyocyte induced by high-dose alcohol. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 44:696–702
Gutstein DE et al (2001) Conduction slowing and sudden arrhythmic death in mice with cardiac-restricted inactivation of connexin43. Circ Res 88:333–339
Guzzo-Merello G, Cobo-Marcos M, Gallego-Delgado M, Garcia-Pavia P (2014) Alcoholic cardiomyopathy. World J Cardiol 6:771–781. doi:10.4330/wjc.v6.i8.771
Guzzo-Merello G et al (2015) Natural history and prognostic factors in alcoholic cardiomyopathy. JACC Heart Fail 3:78–86. doi:10.1016/j.jchf.2014.07.014
Hayashi T et al (2009) Three-dimensional electron microscopy reveals new details of membrane systems for Ca2+ signaling in the heart. J Cell Sci 122:1005–1013. doi:10.1242/jcs.028175
Huang LH, Shiao NH, Hsuuw YD, Chan WH (2007) Protective effects of resveratrol on ethanol-induced apoptosis in embryonic stem cells and disruption of embryonic development in mouse blastocysts. Toxicology 242:109–122. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2007.09.015
Kasdallah-Grissa A, Mornagui B, Aouani E, Hammami M, Gharbi N, Kamoun A, El-Fazaa S (2006) Protective effect of resveratrol on ethanol-induced lipid peroxidation in rats. Alcohol Alcohol 41:236–239. doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh256
Lai YJ et al (2011) Slow conduction and gap junction remodeling in murine ventricle after chronic alcohol ingestion. J Biomed Sci 18:72. doi:10.1186/1423-0127-18-72
Laird DW (2005) Connexin phosphorylation as a regulatory event linked to gap junction internalization and degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1711:172–182. doi:10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.09.009
Lyon RC et al (2014) Connexin defects underlie arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy in a novel mouse model. Hum Mol Genet 23:1134–1150. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddt508
Magyar K et al (2012) Cardioprotection by resveratrol: a human clinical trial in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 50:179–187. doi:10.3233/CH-2011-1424
Matsuyama D, Kawahara K (2011) Oxidative stress-induced formation of a positive-feedback loop for the sustained activation of p38 MAPK leading to the loss of cell division in cardiomyocytes soon after birth. Basic Res Cardiol 106:815–828. doi:10.1007/s00395-011-0178-8
Noritake K, Aki T, Funakoshi T, Unuma K, Uemura K (2015) Direct exposure to ethanol disrupts junctional cell-cell contact and hippo-YAP signaling in HL-1 murine atrial cardiomyocytes. PLoS One 10:e0136952. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0136952
Oxford EM et al (2007) Molecular composition of the intercalated disc in a spontaneous canine animal model of arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm 4:1196–1205. doi:10.1016/j.hrthm.2007.05.025
Penumathsa SV, Maulik N (2009) Resveratrol: a promising agent in promoting cardioprotection against coronary heart disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 87:275–286. doi:10.1139/Y09-013
Perriard JC, Hirschy A, Ehler E (2003) Dilated cardiomyopathy: a disease of the intercalated disc? Trends Cardiovasc Med 13:30–38
Piano MR, Phillips SA (2014) Alcoholic cardiomyopathy: pathophysiologic insights. Cardiovasc Toxicol 14:291–308. doi:10.1007/s12012-014-9252-4
Ramachandran S, Xie LH, John SA, Subramaniam S, Lal R (2007) A novel role for connexin hemichannel in oxidative stress and smoking-induced cell injury. PLoS One 2:e712. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000712
Ren J, Wold LE (2008) Mechanisms of alcoholic heart disease. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 2:497–506. doi:10.1177/1753944708095137
Runchel C, Matsuzawa A, Ichijo H (2011) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in mammalian oxidative stress responses. Antioxid Redox Signal 15:205–218. doi:10.1089/ars.2010.3733
Severs NJ et al (2006) Alterations in cardiac connexin expression in cardiomyopathies. Adv Cardiol 42:228–242. doi:10.1159/000092572
Severs NJ, Bruce AF, Dupont E, Rothery S (2008) Remodelling of gap junctions and connexin expression in diseased myocardium. Cardiovasc Res 80:9–19. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvn133
Smyth JW et al (2010) Limited forward trafficking of connexin 43 reduces cell-cell coupling in stressed human and mouse myocardium. J Clin Invest 120:266–279. doi:10.1172/JCI39740
Sun LP, Wang L, Wang H, Zhang YH, Pu JL (2010) Connexin 43 remodeling induced by LMNA gene mutation Glu82Lys in familial dilated cardiomyopathy with atrial ventricular block. Chin Med J 123:1058–1062
Tome-Carneiro J et al (2012) One-year consumption of a grape nutraceutical containing resveratrol improves the inflammatory and fibrinolytic status of patients in primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol 110:356–363. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.03.030
Zhang X, Li SY, Brown RA, Ren J (2004) Ethanol and acetaldehyde in alcoholic cardiomyopathy: from bad to ugly en route to oxidative stress. Alcohol 32:175–186. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2004.01.005
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The procedure regarding mouse handling and dissection was performed in accordance with the animal protocol approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of Wuxi No. 2 People’s Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University.
Funding
This study was supported by Science and Technology Development Fund of Nanjing Medical University (2014NJMU2D 037).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 712 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, S., Cao, Ft., Fan, Xc. et al. Resveratrol protects the loss of connexin 43 induced by ethanol exposure in neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 651–660 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1368-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1368-1