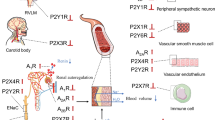
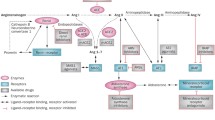
Abstract
Arterial hypertension is a considerable side effect that accompanies the clinical use of immunosuppressant drugs such as cyclosporine (CSA). In addition to promoting graft rejection, uncontrolled hypertension is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis, left ventricular hypertrophy, heart failure, and premature death. Most, if not all, reports that reviewed the hypertensive effect of CSA and underlying mechanisms focused on the roles of peripheral vasoactive machinaries, perhaps because of the limited capacity of CSA to diffuse to brain tissues and the lack of any appreciable effect for centrally administered CSA on blood pressure (BP) or central sympathetic outflow. This review focuses primarily on evidence that supports a modulatory role for central neural pathways, as go-between afferent and efferent sympathetic circuits, in the elicitation of the hypertensive action of CSA. Other areas covered briefly in the review include (1) an outline of peripheral mechanisms that contribute to the hypertensive action of CSA, and (2) comparisons of the BP effects of CSA and other calcineurin-dependent (tacrolimus) and independent (sirolimus) immunosuppressants. The knowledge of these mechanisms, central and peripheral, may permit the identification of new therapeutic strategies against CSA hypertension.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amundsen R, Åsberg A, Ohm IK, Christensen H (2012) Cyclosporine A- and tacrolimus-mediated inhibition of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in vitro. Drug Metab Dispos 40:655–661. doi:10.1124/dmd.111.043018
Asai A, Qiu J, Narita Y, Chi S, Saito N, Shinoura N, Hamada H, Kuchino Y, Kirino T (1999) High level calcineurin activity predisposes neuronal cells to apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:34450–34458
Bai JP, Lesko LJ, Burckart GJ (2010) Understanding the genetic basis for adverse drug effects: the calcineurin inhibitors. Pharmacotherapy 30:195–209. doi:10.1592/phco.30.2.195
Basset e-EA, Berthoux P, Cécillon S, Deprle C, Thibaudin D, De Filippis JP, Alamartin E, Berthou F (2002) Hypertension after renal transplantation and polymorphism of genes involved in essential hypertension: ACE, AGT, AT1 R and ecNOS. Clin Nephrol 57:192–200
Bellet M, Cabrol C, Sassano P, Léger P, Corvol P, Ménard J (1985) Systemic hypertension after cardiac transplantation: effect of cyclosporine on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Am J Cardiol 56:927–931
Bica L, Liddell JR, Donnelly PS, Duncan C, Caragounis A, Volitakis I, Paterson BM, Cappai R, Grubman A, Camakaris J, Crouch PJ, White AR (2014) Neuroprotective copper bis(thiosemicarbazonato) complexes promote neurite elongation. PLoS One 9:e90070. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090070
Bladen C, Vincent SR (1994) Characterization and localization of [3H] cyclosporin A binding sites in rat brain. Neuroreport 5:1386–1388
Borel JF, Feurer C, Gubler HU, Stähelin H (1976) Biological effects of cyclosporin A: a new antilymphocytic agent. Agents Actions 6:468–475
Borlongan CV, Fujisaki T, Watanabe S (1998) Chronic cyclosporine-A injection in rats with damaged blood–brain barrier does not impair retention of passive avoidance. Neurosci Res 32:195–200
Borlongan CV, Stahl CE, Fujisaki T, Sanberg PR, Watanabe S (1999) Cyclosporine A-induced hyperactivity in rats: is it mediated by immunosuppression, neurotrophism, or both? Cell Transplant 8:153–159
Canzanello VJ, Textor SC, Taler SJ, Schwartz LL, Porayko MK, Wiesner RH, Krom RA (1998) Late hypertension after liver transplantation: a comparison of cyclosporine and tacrolimus (FK 506). Liver Transpl Surg 4:328–334
Carlos TM, Clark RS, Franicola-Higgins D, Schiding JK, Kochanek PM (1997) Expression of endothelial adhesion molecules and recruitment of neutrophils after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Leukoc Biol 61:279–285
Cauduro RL, Costa C, Lhulier F, Garcia RG, Cabral RD, Gonçalves LF, Manfro RC (2005) Endothelin-1 plasma levels and hypertension in cyclosporine-treated renal transplant patients. Clin Transplant 19:470–474
Chiu PJ, Vemulapalli S, Sabin C, Rivelli M, Bernardino V, Sybertz EJ (1992) Sympathoadrenal stimulation, not endothelin, plays a role in acute pressor response to cyclosporine in anesthetized rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:994–999
Dai Y, Iwanaga K, Lin YS, Hebert MF, Davis CL, Huang W, Kharasch ED, Thummel KE (2004) In vitro metabolism of cyclosporine A by human kidney CYP3A5. Biochem Pharmacol 68:1889–1902
Denton MD, Magee CC, Sayegh MH (1999) Immunosuppressive strategies in transplantation. Lancet 353:1083–1091
Despas F, Detis N, Dumonteil N, Labrunee M, Bellon B, Franchitto N, Galinier M, Senard JM, Pathak A (2009) Excessive sympathetic activation in heart failure with chronic renal failure: role of chemoreflex activation. J Hypertens 27:1849–1854. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832e8d0f
Dohgu S, Nishioku T, Sumi N, Takata F, Nakagawa S, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Yamauchi A, Shuto H, Kataoka Y (2007) Adverse effect of cyclosporin A on barrier functions of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells after hypoxia-reoxygenation damage in vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:889–899
Dupont P, Warrens AN (2003) The evolving role of sirolimus in renal transplantation. QJM 96:401–409
El-Gowelli HM, Helmy MW, Ali RM, El-Mas MM (2014) Celecoxib offsets the negative renal influences of cyclosporine via modulation of the TGF-β1/IL-2/COX-2/endothelin ETB receptor cascade. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 275:88–95. doi:10.1097/FJC.0b013e318231166f
El-Gowilly SM (2011) Metoprolol ameliorates cyclosporine a-induced hypertension and nephrotoxicity in rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 58:639–646. doi:10.1097/FJC.0b013e318231166f
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (1995) Upregulation of imidazoline receptors in the medulla oblongata accounts for the enhanced hypotensive effect of clonidine in aortic barodenervated rats. Brain Res 691:195–204
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (1998) Estrogen enhances baroreflex control of heart rate in conscious ovariectomized rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 76:381–386
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (1999) Ethanol counteraction of II-imidazoline but not alpha-2 adrenergic receptor-mediated reduction in vascular resistance in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:455–462
El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (2009) Longitudinal assessment of the effects of estrogen on blood pressure and cardiovascular autonomic activity in female rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 36:1002–1009. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05192.x
El-Mas MM, Tao S, Carroll RG, Abdel-Rahman AA (1994) Ethanol-clonidine hemodynamic interaction in normotensive rats is modified by anesthesia. Alcohol 11:307–314
El-Mas MM, Afify EA, Omar AG, Sharabi FM (2002a) Cyclosporine adversely affects baroreflexes via inhibition of testosterone modulation of cardiac vagal control. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:346–354
El-Mas MM, Afify EA, Omar AG, Sharabi FM (2002b) Cyclosporine attenuates the autonomic modulation of reflex chronotropic responses in conscious rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80:766–776
El-Mas MM, Afify EA, Omar AG, Mohy El-Din MM, Sharabi FM (2003) Testosterone depletion contributes to cyclosporine-induced chronic impairment of acetylcholine renovascular relaxations. Eur J Pharmacol 468:217–224
El-Mas MM, Mohy El-Din MM, El-Gowilly SM, Sharabi FM (2004a) Relative roles of endothelial relaxing factors in cyclosporine-induced impairment of cholinergic and beta-adrenergic renal vasodilations. Eur J Pharmacol 487:149–158
El-Mas MM, Mohy El-Din MM, El-gowilly SM, Sharabi FM (2004b) Regional and endothelial differences in the cyclosporine attenuation of adenosine receptor-mediated vasorelaxations. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 43:562–573
El-Mas MM, Omar AG, Helmy MM, Mohy El-Din MM (2009) Interruption of central neuronal pathway of imidazoline I1 receptor mediates the hypertensive effect of cyclosporine in rats. Brain Res 1248:96–106. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.11.008
El-Mas MM, El-Gowelli HM, Abd-Elrahman KS, Saad EI, Abdel-Galil AG, Abdel-Rahman AA (2011) Pioglitazone abrogates cyclosporine-evoked hypertension via rectifying abnormalities in vascular endothelial function. Biochem Pharmacol 81:526–533. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2010.11.013
El-Mas MM, Mohy El-Din MM, Helmy MM, Omar AG (2012a) Redox imbalances incite the hypertensive, baroreflex, and autonomic effects of cyclosporine in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 694:82–88. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2012.08.021
El-Mas MM, Omar AG, Helmy MM, Mohy El-Din MM (2012b) Crosstalk between central pathways of nitric oxide and carbon monoxide in the hypertensive action of cyclosporine. Neuropharmacology 62:1890–1896. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.12.017
Ernsberger P, Damon TH, Graff LM, Schafer SG, Christen MO (1993) Moxonidine, a centrally acting antihypertensive agent, is a selective ligand for I1-imidazoline sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:172–182
Fadel PJ, Stromstad M, Wray DW, Smith SA, Raven PB, Secher NH (2003) New insights into differential baroreflex control of heart rate in humans. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 284:H735–H743
Fromm MF, Schmidt BM, Pahl A, Jacobi J, Schmieder RE (2005) CYP3A5 genotype is associated with elevated blood pressure. Pharmacogenet Genomics 15:737–741
Gaudet E, Godwin SJ, Head GA (2000) Effects of central infusion of ANG II and losartan on the cardiac baroreflex in rabbits. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278:H558–H566
Gerhardt U, Riedasch M, Hohage H (1999) Cyclosporine A modulates baroreceptor function in kidney transplant recipients. Int J Cardiol 68:203–208
Goto S, Matsukado Y, Mihara Y, Inoue N, Miyamoto E (1986) The distribution of calcineurin in rat brain by light and electron microscopic immunohistochemistry and enzyme-immunoassay. Brain Res 397:161–172
Gottschalk S, Cummins CL, Leibfritz D, Christians U, Benet LZ, Serkova NJ (2011) Age and sex differences in the effects of the immunosuppressants cyclosporine, sirolimus and everolimus on rat brain metabolism. Neurotoxicology 32:50–57. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2010.10.006
Handschumacher RE, Harding MW, Rice J, Drugge RJ, Speicher DW (1984) Cyclophilin: a specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science 226:544–547
Hardy G, Stanke-Labesque F, Deveaux G, Devillier P, Sessa C, Bessard G (2000) Cyclosporine A and cremophor EL induce contractions of human saphenous vein: involvement of thromboxane A2 receptor-dependent pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 36:693–698
Hirooka Y (2008) Role of reactive oxygen species in brainstem in neural mechanisms of hypertension. Auton Neurosci 142:20–24. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2008.06.001
Hirooka Y, Kishi T, Sakai K, Takeshita A, Sunagawa K (2011) Imbalance of central nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in the regulation of sympathetic activity and neural mechanisms of hypertension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300:R818–R826. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00426.2010
Honzíková N, Fiser B (2009) Baroreflex sensitivity and essential hypertension in adolescents. Physiol Res 58:605–612
Honzikova N, Labrova R, Fiser B, Maderova E, Novakova Z, Zavodna E, Semrad B (2006) Influence of age, body mass index, and blood pressure on the carotid intima-media thickness in normotensive and hypertensive patients. Biomed Tech (Berl) 51:159–162
Hoorn EJ, Walsh SB, McCormick JA, Fürstenberg A, Yang CL, Roeschel T, Paliege A, Howie AJ, Conley J, Bachmann S, Unwin RJ, Ellison DH (2011) The calcineurin inhibitor tacrolimus activates the renal sodium chloride cotransporter to cause hypertension. Nat Med 17:1304–1309. doi:10.1038/nm.2497
Hoorn EJ, Walsh SB, McCormick JA, Zietse R, Unwin RJ, Ellison DH (2012) Pathogenesis of calcineurin inhibitor-induced hypertension. J Nephrol 25:269–275. doi:10.5301/jn.5000174
Ingawale DK, Mandlik SK, Naik SR (2014) Models of hepatotoxicity and the underlying cellular, biochemical and immunological mechanism(s): a critical discussion. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:118–133. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.08.015
Issa N, Kukla A, Ibrahim HN (2013) Calcineurin inhibitor nephrotoxicity: a review and perspective of the evidence. Am J Nephrol 37:602–612. doi:10.1159/000351648
Ito S, Komatsu K, Tsukamoto K, Sved AF (2001) Tonic excitatory input to the rostral ventrolateral medulla in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension 37:687–691
Kasiske BL, Anjum S, Shah R, Skogen J, Kandaswamy C, Danielson B, O'Shaughnessy EA, Dahl DC, Silkensen JR, Sahadevan M, Snyder JJ (2004) Hypertension after kidney transplantation. Am J Kidney Dis 43:1071–1081
Klein IH, Abrahams AC, van Ede T, Oey PL, Ligtenberg G, Blankestijn PJ (2010) Differential effects of acute and sustained cyclosporine and tacrolimus on sympathetic nerve activity. J Hypertens 28:1928–1934. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e32833c20eb
Koomans HA, Ligtenberg G (2001) Mechanisms and consequences of arterial hypertension after renal transplantation. Transplantation 72(6 Suppl):S9–S12
Kubista H, Boehm S (2006) Molecular mechanisms underlying the modulation of exocytotic noradrenaline release via presynaptic receptors. Pharmacol Ther 112:213–242
Kumada M, Terui N, Kuwaki T (1990) Arterial baroreceptor reflex: its central and peripheral neural mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 35:331–361
Li YL (2013) Angiotensin II-superoxide signaling and arterial baroreceptor function in type-1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Suppl 12:1–6
Li DP, Fan ZZ, He RR (1998) Modulatory effects of endothelin on carotid baroreflex in anesthetized rats. Sheng Li Xue Bao 50:169–175
Li L, Hsu A, Moore PK (2009) Actions and interactions of nitric oxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulphide in the cardiovascular system and in inflammation–a tale of three gases! Pharmacol Ther 123:386–400. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.05.005
Lin G, Xiang Q, Fu X, Wang S, Wang S, Chen S, Shao L, Zhao Y, Wang T (2012) Heart rate variability biofeedback decreases blood pressure in prehypertensive subjects by improving autonomic function and baroreflex. J Altern Complement Med 18:143–152. doi:10.1089/acm.2010.0607
Liu J, Farmer JD Jr, Lane WS, Friedman J, Weissman I, Schreiber SL (1991) Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell 66:807–815
Liu H, Tu L, Wang Q, Sun Y, Ma Y, Cen J, Wei Q, Luo J (2013) Modulation of calcineurin activity in mouse brain by chronic oral administration of cyclosporine A. IUBMB Life 65:445–453. doi:10.1002/iub.1139
Lo Russo A, Passaquin AC, Cox C, Rüegg UT (1997) Cyclosporin A potentiates receptor-activated [Ca2+]c increase. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 17:149–461
Louhelainen M, Merasto S, Finckenberg P, Lapatto R, Cheng ZJ, Mervaala EM (2006) Lipoic acid supplementation prevents cyclosporine-induced hypertension and nephrotoxicity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 24:947–956
Lunde I, Bremer S, Midtvedt K, Mohebi B, Dahl M, Bergan S, Åsberg A, Christensen H (2014) The influence of CYP3A, PPARA, and POR genetic variants on the pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus and cyclosporine in renal transplant recipients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 70:685–693
Lyson T, McMullan DM, Ermel LD, Morgan BJ, Victor RG (1994) Mechanism of cyclosporine-induced sympathetic activation and acute hypertension in rats. Hypertension 23:667–675
Matsuda S, Koyasu S (2003) Regulation of MAPK signaling pathways through immunophilin-ligand complex. Curr Top Med Chem 3:1358–1367
Miller LW (2002) Cardiovascular toxicities of immunosuppressive agents. Am J Transplant 2:807–818
Moes DJ, Swen JJ, den Hartigh J, van der Straaten T, van der Heide JJ, Sanders JS, Bemelman FJ, de Fijter JW, Guchelaar HJ (2014) Effect of CYP3A4*22, CYP3A5*3, and CYP3A combined genotypes on cyclosporine, everolimus, and tacrolimus pharmacokinetics in renal transplantation. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 3:e100. doi:10.1038/psp.2013.78
Mohamed MK, El-Mas MM, Abdel-Rahman AA (1999) Estrogen enhancement of baroreflex sensitivity is centrally mediated. Am J Physiol 276(Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 45):R1030–R1037
Moreira TS, Takakura AC, Menani JV, Sato MA, Colombari E (2004) Central blockade of nitric oxide synthesis reduces moxonidine-induced hypotension. Br J Pharmacol 142:765–771
Morgan BJ, Lyson T, Scherrer U, Victor RG (1991) Cyclosporine causes sympathetically mediated elevations in arterial pressure in rats. Hypertension 18:458–466
Moss NG, Powell SL, Falk RJ (1985) Intravenous cyclosporine activates afferent and efferent renal nerves and causes sodium retention in innervated kidneys in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82:8222–8226
Nash EF, Stephenson A, Helm EJ, Durie PR, Tullis E, Singer LG, Chaparro C (2011) Impact of lung transplantation on serum lipids in adults with cystic fibrosis. J Heart Lung Transplant 30:188–193. doi:10.1016/j.healun.2010.08.024
Nasser SA, El-Mas MM (2014) Endothelin ETA receptor antagonism in cardiovascular disease. Eur J Pharmacol 737:210–213. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.05.046
Nasser SA, Elmallah AI, Sabra R, Khedr MM, El-Din MM, El-Mas MM (2014) Blockade of endothelin ET(A), but not thromboxane, receptors offsets the cyclosporine-evoked hypertension and interrelated baroreflex and vascular dysfunctions. Eur J Pharmacol 727:52–59. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.034
Navegantes LC, Mendes GE, Lira EC, Kettelhut Ido C, Baptista MA, Burdmann EA (2006) Effect of cyclosporine a on glucose interstitial concentration in renal cortex and medulla from rats. Am J Nephrol 26:163–169
Nishiyama A, Kobori H, Fukui T, Zhang GX, Yao L, Rahman M, Hitomi H, Kiyomoto H, Shokoji T, Kimura S, Kohno M, Abe Y (2003) Role of angiotensin II and reactive oxygen species in cyclosporine A-dependent hypertension. Hypertension 42:754–760
Niu T, Chen X, Xu X (2002) Angiotensin converting enzyme gene insertion/deletion polymorphism and cardiovascular disease: therapeutic implications. Drugs 62:977–993
Noè A, Cappelli B, Biffi A, Chiesa R, Frugnoli I, Biral E, Finizio V, Baldoli C, Vezzulli P, Minicucci F, Fanelli G, Fiori R, Ciceri F, Roncarolo MG, Marktel S (2010) High incidence of severe cyclosporine neurotoxicity in children affected by haemoglobinopaties undergoing myeloablative haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: early diagnosis and prompt intervention ameliorates neurological outcome. Ital J Pediatr 36:14. doi:10.1186/1824-7288-36-14
O'Donnell P (2013) Of mice and men: what physiological correlates of cognitive deficits in a mouse model of schizophrenia tell us about psychiatric disease. Neuron 80:265–266. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.012
Ogawa K, Hirooka Y, Shinohara K, Kishi T, Sunagawa K (2012) Inhibition of oxidative stress in rostral ventrolateral medulla improves impaired baroreflex sensitivity in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Int Heart J 53:193–198
Okonkwo DO, Melon DE, Pellicane AJ, Mutlu LK, Rubin DG, Stone JR, Helm GA (2003) Dose–response of cyclosporin A in attenuating traumatic axonal injury in rat. Neuroreport 14:463–466
Ouisuwan S, Buranakarl C (2005) Effects of cyclosporin A on blood pressure, baroreceptor reflex and renal function in dogs. Vet Res Commun 29:201–213
Pacheco-López G, Doenlen R, Krügel U, Arnold M, Wirth T, Riether C, Engler A, Niemi MB, Christians U, Engler H, Schedlowski M (2013) Neurobehavioural activation during peripheral immunosuppression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:137–149. doi:10.1017/S1461145711001799
Patsenker E, Schneider V, Ledermann M, Saegesser H, Dorn C, Hellerbrand C, Stickel F (2011) Potent antifibrotic activity of mTOR inhibitors sirolimus and everolimus but not of cyclosporine A and tacrolimus in experimental liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 55:388–398. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.10.044
Price CJ, Hoyda TD, Ferguson AV (2008) The area postrema: a brain monitor and integrator of systemic autonomic state. Neuroscientist 14:182–194
Robert N, Wong GW, Wright JM (2010) Effect of cyclosporine on blood pressure. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1, CD007893. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007893
Roberts DJ, Goralski KB (2008) A critical overview of the influence of inflammation and infection on P-glycoprotein expression and activity in the brain. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 4:1245–1264. doi:10.1517/17425255.4.10.1245
Ryuzaki M, Stahl LK, Lyson T, Victor RG, Bishop VS (1997) Sympathoexcitatory response to cyclosporin A and baroreflex resetting. Hypertension 29:576–582
Salgado MC, Justo SV, Joaquim LF, Fazan R Jr, Salgado HC (2006) Role of nitric oxide and prostanoids in attenuation of rapid baroreceptor resetting. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H1059–H1063
Schwartz RB, Bravo SM, Klufas RA, Hsu L, Barnes PD, Robson CD, Antin JH (1995) Cyclosporine neurotoxicity and its relationship to hypertensive encephalopathy: CT and MR findings in 16 cases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165:627–631
Seagard JL, Gallenberg LA, Hopp FA, Dean C (1992) Acute resetting in two functionally different types of carotid baroreceptors. Circ Res 70:559–565
Seibert F, Behrendt C, Schmidt S, van der Giet M, Zidek W, Westhoff TH (2011) Differential effects of cyclosporine and tacrolimus on arterial function. Transpl Int 24:708–715. doi:10.1111/j.1432-2277.2011.01265.x
Sereno J, Romão AM, Parada B, Lopes P, Carvalho E, Teixeira F, Reis F (2012) Cardiorenal benefits of early versus late cyclosporine to sirolimus conversion in a rat model. J Pharmacol Pharmacother 3:143–148. doi:10.4103/0976-500X.95513
Sereno J, Parada B, Rodrigues-Santos P, Lopes PC, Carvalho E, Vala H, Teixeira-Lemos E, Alves R, Figueiredo A, Mota A, Teixeira F, Reis F (2013) Serum and renal tissue markers of nephropathy in rats under immunosuppressive therapy: cyclosporine versus sirolimus. Transplant Proc 45:1149–1156. doi:10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.02.085
Shaltout HA, Abdel-Rahman AA (2003) Cyclosporine induces progressive attenuation of baroreceptor heart rate response and cumulative pressor response in conscious unrestrained rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:966–973
Sidharthan NP, Minchin RF, Butcher NJ (2013) Cytosolic sulfotransferase 1A3 is induced by dopamine and protects neuronal cells from dopamine toxicity: role of D1 receptor-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor coupling. J Biol Chem 288:34364–34374. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.493239
Siekierka-Harreis M, Kuhr N, Willers R, Ivens K, Grabensee B, Mondry A, Loh MC, Rump LC, Blume C (2009) Impact of genetic polymorphisms of the renin-angiotensin system and of non-genetic factors on kidney transplant function—a single-center experience. Clin Transplant 23:606–615. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0012.2009.01033.x
Smit AA, Timmers HJ, Wieling W, Wagenaar M, Marres HA, Lenders JW, van Montfrans GA, Karemaker JM (2002) Long-term effects of carotid sinus denervation on arterial blood pressure in humans. Circulation 105:1329–1335
Stepkowski SM (2000) Molecular targets for existing and novel immunosuppressive drugs. Expert Rev Mol Med 2:1–23
Taler SJ, Textor SC, Canzanello VJ, Schwartz L (1999) Cyclosporin-induced hypertension: incidence, pathogenesis and management. Drug Saf 20:437–449
Taylor DO, Barr ML, Radovancevic B, Renlund DG, Mentzer RM Jr, Smart FW, Tolman DE, Frazier OH, Young JB, VanVeldhuisen P (1999) A randomized, multicenter comparison of tacrolimus and cyclosporine immunosuppressive regimens in cardiac transplantation: decreased hyperlipidemia and hypertension with tacrolimus. J Heart Lung Transplant 18:336–345
Timmers HJ, Wieling W, Karemaker JM, Lenders JW (2004) Cardiovascular responses to stress after carotid baroreceptor denervation in humans. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1018:515–519
Tkaczyszyn M, Rydlewska A, Ponikowska B, Borodulin-Nadzieja L, Banasiak W, Ponikowski P, Jankowska EA (2013) Arterial baroreflex–physiological role and assessment of functioning. Pol Merkur Lekarski 35:104–110
Tocci MJ, Sigal NH (1992) Recent advances in the mechanism of action of cyclosporine and FK506. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 1:236–242
Totola LT, Alves TB, Takakura AC, Ferreira-Neto HC, Antunes VR, Menani JV, Colombari E, Moreira TS (2013) Commissural nucleus of the solitary tract regulates the antihypertensive effects elicited by moxonidine. Neuroscience 250:80–91
Wang Y, Golledge J (2013) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and sympathetic nerve activity in neurovascular and metabolic systems. Curr Neurovasc Res 10:81–89
Wang A, Chi Z, Wang S, Wang S, Sun Q (2009) Calcineurin-mediated GABA(A) receptor dephosphorylation in rats after kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Seizure 18:519–523. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2009.05.001
Wispelwey B, Lesse AJ, Hansen EJ, Scheld WM (1988) Haemophilus influenzae lipopolysaccharide-induced blood brain barrier permeability during experimental meningitis in the rat. J Clin Invest 82:1339–1346
Yanagimachi M, Naruto T, Tanoshima R, Kato H, Yokosuka T, Kajiwara R, Fujii H, Tanaka F, Goto H, Yagihashi T, Kosaki K, Yokota S (2010) Influence of CYP3A5 and ABCB1 gene polymorphisms on calcineurin inhibitor-related neurotoxicity after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Transplant 24:855–861. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0012.2009.01181.x
Ye S, Ozgur B, Campese VM (1997) Renal afferent impulses, the posterior hypothalamus, and hypertension in rats with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 51:722–727
Ye S, Zhong H, Yanamadala V, Campese VM (2002) Renal injury caused by intrarenal injection of phenol increases afferent and efferent renal sympathetic nerve activity. Am J Hypertens 15:717–724
Zeier M, Van Der Giet M (2011) Calcineurin inhibitor sparing regimens using m-target of rapamycin inhibitors: an opportunity to improve cardiovascular risk following kidney transplantation? Transpl Int 24:30–42. doi:10.1111/j.1432-2277.2010.01140.x
Zhang W, Victor RG (2000) Calcineurin inhibitors cause renal afferent activation in rats: a novel mechanism of cyclosporine-induced hypertension. Am J Hypertens 13:999–1004
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant HLTH-13-01 from the Research Enhancement Program of Alexandria University (ALEX-REP), Egypt.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Gowelli, H.M., El-Mas, M.M. Central modulation of cyclosporine-induced hypertension. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388, 351–361 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-1074-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-1074-1