Abstract
Hypertension is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally among all cardiovascular diseases. Purinergic signalling plays a crucial role in hypertension through the sympathetic nerve system, neurons in the brain stem, carotid body, endothelium, immune system, renin-angiotensin system, sodium excretion, epithelial sodium channel activity (ENaC), and renal autoregulation. Under hypertension, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is released as a cotransmitter from the sympathetic nerve. It mediates vascular tone mainly through P2X1R activation on smooth muscle cells and activation of P2X4R and P2YR on endothelial cells and also via interaction with other purinoceptors, showing dual effects. P2Y1R is linked to neurogenic hypertension. P2X7R and P2Y11R are potential targets for immune-related hypertension. P2X3R located on the carotid body is the most promising novel therapeutic target for hypertension. A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and P2X7R are all related to renal autoregulation, which contribute to both renal damage and hypertension. The main focus is on the evidence addressing the involvement of purinoceptors in hypertension and therapeutic interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Hypertension is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally among all cardiovascular diseases [1]. In 2020, 1.28 billion adults reportedly had hypertension, which made the health condition an issue of global concern [2, 3]. The pathophysiology of hypertension is complex. It involves the multi-interaction of the sympathetic nervous system, the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system, sodium homeostasis regulation, endothelium, and immune system. The drugs for controlling hypertension include β-receptor blocker, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin II receptor blocker, calcium-channel-blocker, and diuretics. However, despite the availability of multiple antihypertensive drugs, approximately 1 in 5 adults (21%) with hypertension is out of control due to side effects, intolerance, and poor efficacy. The poor efficacy might be that not all the pathophysiological mechanisms are neutralized by the conventional antihypertensive therapies currently available. Given the large population with uncontrolled hypertension and the complexity of pathogenesis, developing new antihypertensive agents to provide more choices for those people is vital.
Accumulating evidence indicates that purinergic signalling has shown great therapeutic potential for hypertension. Purinergic signalling, that is, ATP acting as an extracellular signalling molecule, was proposed as a cotransmitter in sympathetic nerves in 1972 by Dr. Burnstock [1]. It involves the activation of cell surface P1 and P2 receptors by extracellular nucleosides and nucleotides [1]. P1 receptors are classified into 4 subtypes, namely, A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and A3R, which can be activated by adenosine. P2 receptors include 7 P2X ion channel receptor subtypes (P2X1-7) and 8 P2Y G-protein-coupled receptor subtypes (P2Y1, P2Y2, P2Y4, P2Y6, P2Y11, P2Y12, P2Y13, and P2Y14), which can be activated by purine nucleotides (ATP, ADP) [1]. A previous review in 2017 by Dr. Burnstock [4] showed alteration of purinergic signalling contributes to hypertension in 6 different ways, including sympathetic nerve activities, endothelial cells, neurons in the brain stem, carotid body, inflammation, and renin-angiotensin system. Sympathetic nerve activities [5,6,7] and the renin-angiotensin system [5, 8, 9] directly control the BP by acting on peripheral resistance, blood volume, and cardiac output. Neurons in the brain stem [10] and carotid body [11] indirectly regulate the BP by triggering a systemic response. Endothelial cells [5] and inflammation [12] affect the BP mainly by regulation of peripheral resistance through releasing vasoactive cytokines. Apart from the aforementioned mechanisms, emerging evidences showed that purinergic signalling mediated hypertension via affecting sodium excretion [13], epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) [14] activity, and renal autoregulation [15, 16], which were associated with blood volume. This review summarizes important aspects of purine nucleotides and their receptors in the regulation of BP.
Purines in the regulation of blood pressure
Purines are released from the peripheral nerve fibres, endothelium in the local blood vessels, and the central nervous system (CNS), which play significant roles in the regulation of BP.
Purines in the peripheral nervous system
ATP is released as a cotransmitter from sympathetic nerves in the local blood vessels which significantly contributes to the constriction of the blood vessels. Under high pressure, ATP is the chief functional sympathetic neurotransmitter [17]. It is released from the vesicles with noradrenaline [18,19,20,21] and neuropeptide Y in peripheral sympathetic nerves. ATP binds to P2 receptors (mainly P2X1R, P2X2R, P2X4R, P2Y1R, P2Y2R, and P2Y6R) on the smooth muscle cells, leading to the constriction of the local blood vessels [22,23,24]. Higher levels of ATP and sympathetic nerve density were also observed in diet-induced obesity rats, which were susceptible to hypertension. This finding hints that purinergic hyperactivity is closely associated with hypertension [25]. Besides peripheral sympathetic nerves, ATP is also released from perivascular sensory-motor nerves as a cotransmitter, which leads to vasoconstriction by targeting P2XR. But the main neurotransmitter from perivascular sensory-motor nerves is calcitonin gene-related peptide, which mediate vasorelaxation. Thus, the vascular tone is an interaction between multi-neurotransmitters.
Purines in endothelium cells of blood vessels
ATP is released from endothelium cells besides sympathetic nerves and sensory-motor nerves in the local blood vessels. In lumen of blood vessels, shear stress- and hypoxia-induced ATP is released mainly from the endothelium and erythrocytes. ATP acted on P2X4R and P2YR to produce nitric oxide (NO) and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor, resulting in vasorelaxation [26,27,28]. This effect was abolished by degradation of ATP by ectonucleotidases. In the rat isolated mesenteric arterial bed, ATP acted on P2YR evoking the prolonged phase of endothelium-independent vasorelaxation and activating Na + /K + -ATPase and KATP channels [29]. In endothelial and smooth muscle cell surface, ATP, ADP, and UTP were hydrolyzed by ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase, and then ecto-5′-nucleotidase hydrolyzed AMP into adenosine. Adenosine is bound to A2AR and A2BR, leading to vasorelaxation [24]. At 10−5 mol/kg−1, adenosine could generate NO-dependent hypotensive activity [30]. Augmented contractile responses to UDP and UTP were seen in femoral arteries of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) than in those of Wistar-Kyoto [31]. The nucleotide uridine adenosine tetraphosphate (Up4A) is a dinucleotide comprising purine and pyrimidine moieties. It is proposed as a novel endothelium-derived vasoconstrictive factor. It binds mainly to P2X1R, and also P2Y2R and P2Y4R. Up4A induced hypertension by generating vasoconstriction and renal dysfunction [32]. The circulating level of Up4A was higher in juvenile hypertensives than in controls, thus indicating that Up4A was highly implicated with the onset of juvenile hypertension [33]. In the deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-salt rats, Up4A-induced contraction was enhanced in isolated renal arteries. This might be attributed to enhanced P2YR signalling and activation of the extracellular regulated protein kinases pathway [34]. However, different vascular beds responded differently to Up4A. Up4A-induced contraction was increased in renal but not in pulmonary arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats [35]. Also, different concentrations of Up4A resulted in different vascular responses. At a low concentration, Up4A induced vasoconstriction on the mouse aorta, but at a high concentration, it led to hypotension and electrolyte retention in rats [36]. When Up4A was applied for controlling hypertension, region- and concentration-specific effects should be cooperated.
Purines in central nervous system
In the CNS, ATP increased the central sympathetic drive, causing an increased systemic BP [37,38,39]. In the process, ATP activated the P2 receptors and thus increasing the firing activity of the hypothalamic sympathetic neurons [40]. In the commissural nucleus tractus solitarii (NTS), simultaneous blockade of ionotropic glutamate receptors and P2 receptors caused a remarkable decrease in the pressor and bradycardic responses [41]. In addition, ATP in the NTS mediated hindlimb vasodilation in response to alerting-defense [42]. These abnormal purinergic neurotransmissions and enhanced sympathetic activity are significant physiological processes which demonstrate that purinergic signalling in the CNS may be a potential target for hypertension.
Collectively, the effect of ATP on BP is a complex mechanism mainly involving P2XR and P2YR activation on peripheral sympathetic systems, CNS, and endothelial and smooth muscle cells, in addition, also involving the interaction among them. Similar dual effects on blood vessels are observed in ADP, adenosine, UTP, UDP, and Up4A. Region- and concentration-specific effects should be coordinated when referred to regulate BP. Purines are widely distributed and multifunctional, making it difficult to manipulate to reduce BP in clinical practice.
Purinoceptors in the regulation of blood pressure
P1 receptors in the regulation of blood pressure
All P1 purinoceptors, namely, A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and A3R, are found in smooth muscle and endothelial cells of arteries, as well as in the kidney [43,44,45], of which A2AR and A2BR are most commonly expressed in smooth muscle and endothelial cells [24]. Notably, the distribution of P1 receptors along the arteries varies [46].
P1 purinoceptors play an important role in cardiovascular responses [30] and renal sodium homeostasis. The activation of peripheral A1R decreased BP [47]. A1−/− mice showed an elevated BP [48,49,50], plasma renin [48, 49], and sodium excretion [49]. A higher BP in A1−/− mice attributed to a deficiency of A1R on the sympathetic innervation, thus causing more noradrenaline in the synaptic cleft to be released [51]. However, on a high-salt diet, the A1−/− mice showed a lower BP than wild-type (WT) [49, 52, 53]. During chronic salt loading, A1R was downregulated, leading to the insensitivity of the renal arterioles or tubules to adenosine. This process facilitated renal sodium and water excretion and maintained the fluid volume and arterial pressure [54]. The different responses of A1−/− mice to different diets could be explained by the lack of A1R on the renal afferent arteriole blunted tubuloglomerular feedback responses. Similarly, the hypertensive responses to NO inhibition [55] and angiotensin II (ANG II) mediated by tubuloglomerular feedback responses [55, 56] were blunted in A1−/− mice when compared with WT.
A2R include A2AR and A2BR subtypes. A2AR mediated vasodilation via producing NO in the endothelium [30, 57, 58]. Intraperitoneal injections of A2AR agonists decreased the BP in Sprague–Dawley rats [47]. A2A−/− Dahl salt-sensitive rats had a higher mean BP than WT [59]. Moreover, in never-treated essential hypertensive patients, lower affinity, higher density, and impaired function of A2AR were presented [60]. Besides, activation of A2AR led to hypotension through dilating the preglomerular microvessels mediated by epoxyeicosatrienoic acids [61, 62]. Activation of A2BR by adenosine also induced vasodilation, but the extent was much greater than A2AR in mesenteric arteries [50]. Of note, A2BR agonist showed either anti- or pro-hypertensive effects based on the various pathogenic mechanisms that induced BP. In Dahl salt-sensitive rats, the activation of A2BR caused diuresis and natriuresis. The dysfunctional A2BR impaired sodium excretion and resulted in elevated BP. In contrast, Dahl salt-sensitive rats with ANG II-induced hypertension activation of A2BR further released catecholamines. This triggered a proinflammatory state within the kidneys and/or the vasculature and thus contributing to high BP [63]. It was remarkable that A1−/− and A2A−/− displayed heterogeneity in gender. A1−/− and A2A−/− female rats rather than male rats revealed distinct lower BP than WT on a 4% salt diet [59].
A3R is abundantly expressed in afferent arterioles and participate in vasodilatation [43]. In the ANG II-supported circulation of the pithed rat, activation of A3R led to hypotension [64]. No BP elevation was observed in A3−/− mice, after uninephrectomy and chronic HS intake, but high BP was detected in WT mice [65]. The mechanism might be related to inhibiting Na+/H+ exchanger-3 by A3R, contributing to sodium and fluid balance [66]. A3R was upregulated significantly in the renal cortex and medulla in salt-loaded rats, which may be an intrarenal adaptive mechanism to chronic salt loading [54].
Adenosine receptors have been proven to improve some hypertension complications. Activation of A2AR improved cardiac dysfunction and decreased cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, cardiac inflammation, and fibrosis, possibly by increasing fibroblast growth factor 21 [67]. It suggests that A2AR may have great therapeutic potential for hypertensive heart disease. A2BR could ameliorate hypertension-induced social memory impairment in SHRs [68]. In uninephrectomy and chronic HS intake-induced hypertension models, severe pathological changes of heart and kidney were observed in WT mice, but not in A3−/− mice. In addition, A3R deficiency avoided oxidative stress in the renal [65].
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a life-threatening disease characterized by increased pulmonary arterial pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance. P1 receptors have been demonstrated to be a potential target in PAH. Nonselective P1 receptors antagonist aminophylline could attenuate the pulmonary vasodilation to adenosine in lamb model with hypoxia [69]. Among P1 receptors, A2AR is a promising target for PAH. In rats with monocrotaline-induced PAH, A2AR agonists, LASSBio-1386 [70] and LASSBio-1359 [71, 72], improved structural and functional alterations in heart and pulmonary artery, whereas A2A−/− mice showed PAH, pulmonary vascular constriction, and pulmonary artery remodelling compared to WT littermates [73, 74]. A2BR was also involved in the onset of pulmonary hypertension. In contrast to A2AR, A2BR expression was upregulated in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from idiopathic PAH. Activation of A2BR could aggravate pulmonary vascular remodelling [75]. A2BR antagonist GS-6201 and genetic removal A2BR alleviated bleomycin-induced pulmonary hypertension and vascular remodelling [76]. Currently, information regarding the role of A1R and A3R in PAH is limited.
P2 receptors in the regulation of blood pressure
P2X4R, P2Y1R, P2Y2R, and P2Y11R are the most expressed P2 receptors in endothelial cells [77] mediating pathways related to vasodilation via releasing NO, endothelium-dependent hyperpolarizing factor, and tissue-type plasminogen activator. In addition, P2 receptors, including P2X5R, P2Y1R, P2Y4R, P2Y6R, and P2Y14R, are responsible for human mesenchymal stem cells differentiation toward endothelial cells [78]. Moreover, P2Y2R is demonstrated to be associated with endothelial sprouting, vascular tube formation [79], and regulate shear stress-induced cytoskeletal alterations in human umbilical vein endothelial cells [80]. The dysfunction of above-mentioned purinoceptors may lead to abnormal vascular function, subsequently increasing the susceptibility to hypertension and hypertension-induced vascular damage. What’s more, P2XR-mediated neurogenic contractions are the predominant vasoconstrictor of small and medium arteries, namely, resistance artery [81].
P2 receptors play an important role in regulating of BP by acting on blood vessels and the CNS and participating in renal autoregulation. P2 receptors constricted afferent and efferent arterioles in ANG II-dependent hypertension [82] and triggered renal inflammation [83]. In inner medullary collecting duct cells, polycystin-2 and P2 receptors in response to flow might produce hypertension via Ca2+-dependent signalling pathways and thereby stimulating the synthesis of endothelin-1, an inhibitor of Na+ and water reabsorption [84]. ATP activated both P2XR and P2YR, modulating the activity of neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) [37]. Compared with the normotensive Wistar rats, SHRs showed a higher vascular tone of pial vessels on the RVLM region, indicating an augmented activity of sympathoexcitatory neurons, and a possible constant rise in the BP [85]. Brainstem P2 receptors mediated the hypothalamic defense area-NTS-RVLM pathway to regulate hindlimb vascular vasodilation. This process was achieved through attenuating sympathetic tone and increasing catecholamine release [42]. In addition, P2XR was expressed on the ventrolateral medulla projecting paraventricular nucleus neuron. These receptors might play a vital role in regulating sympathetic outflow [86]. Therefore, purinergic receptors may represent new avenues for treating hypertension resulting from over-activation of the sympathetic nervous in the CNS.
P2X1 receptors mediate vasoconstriction and renal injury
Stimulation of P2X1R mediated vasoconstriction in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) from human gastro-omental arteries [87]. In addition, P2X1R is activated by neurally released ATP mediated Ca2+ entering the smooth muscle cells, thus inducing the sympathetic neurogenic contraction. Arteries from P2X1−/− mice failed to contractions with the administration of P2XR agonist, whereas arteries from WT showed strong contractions [88].
Impaired P2X1R resulted in the dysfunction of autoregulation and microvascular reactivity. This impairment would lead to hypertension-induced renal injuries [89, 90]. Attenuated afferent arteriolar responses to P2X1R were observed in ANG II-infused rats on the HS diet [90]. The activation of normalized P2X1R averted lymphocyte infiltration, improved autoregulation [91], and protected renal autoregulation from inflammatory cascades induced by hypertension in DOCA-salt rats [92]. The plasma level of Up4A was elevated in hypertensive patients. Up4A activated P2X1R leading to hypertension, hence, the vascular P2X1R activity rather than plasma Up4A level might determine the role of Up4A in hypertension [93]. In summary, P2X1R shows great potential in regulating vascular tone in hypertension, mediating Ca2+ influx-caused vasoconstriction in VSMCs, and improving hypertension-induced renal injuries.
P2X3 receptors in the carotid body regulate blood pressure
The carotid body (CB) [11] is a potential novel target for hypertension. As a peripheral chemoreceptor located at the bifurcation of carotid arteries, CB is hypersensitive to arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, and blood pH levels. Thus, the reflex ventilation, cardiovascular system, and humoral response are regulated by CB. Researches during the past several decades on CB indicated that peripheral chemoreflex sensitivity of CB affected sympathetic activity and further influenced sympathetic-mediated diseases, such as hypertension. A significant increase of the CB reflex sensitivity was observed in SHRs [94] and hypertension patients [95]. Morphologically, CBs grew larger under the condition of hypertension in humans and rats [96, 97]. CB denervation effectively prevented the development and progression of hypertension in both hypertensive rats and patients [94, 95]. A clinical study found that hyperoxia-induced deactivation of CB chemoreceptors acutely lowered the BP in hypertensive patients [98]. Moreover, unilateral CB resection lowered the BP and sympathetic activity in 8 out of 15 patients with drug-resistant hypertension [99]. Interestingly, purinergic signalling is related to the functions of CB. It was demonstrated that P2X2R and P2X3R were expressed in petrosal neurons and were involved in ATP-mediated hypoxic chemo-transmission of CB in rats [100]. P2X3 mRNA expression was upregulated in the chemoreceptive petrosal sensory neurons of SHRs. Both tonic drive and hyperreflexia were normalized by local administration of a highly selective P2X3R antagonist. In conscious SHRs, blockade of P2X3R resulted in the reduction of arterial pressure and basal sympathetic activity, and the normalization of CB hyperreflexia. But, the P2X3R blocker did not affect normotensive Wistar [94]. More recently, canine models with P2X3R deficiency on CBs were created. This model showed a decreased BP and normalized the sympatho-vagal balance [101], thus suggesting the importance of P2X3R in CBs to control BP and sympathetic activity.
Taken together, antagonism of P2X3R in the CB lowers BP especially, and non-invasive targeted therapies will be more acceptable and needed by patients with neurogenic hypertension, refractory hypertension, or drug-resistant hypertension. Therefore, further researches should be the focus on those therapies.
P2X4 receptors regulate vasodilatation and ENaC activity
P2X4R is highly expressed in endothelial cells and VSMCs of human resistance arteries [87]. Similarly, P2X4–/– mice presented higher BP than WT mice [102, 103]. A clinical study found that the missense Y315C variant (rs28360472) in P2X4R was significantly related to increased pulse pressure, which might be attributed to a reduction in P2X4R-mediated vasodilation [104]. P2X4R has been proposed to be involved in lowering BP in two ways. Firstly, P2X4R in the endothelium was activated in response to shear stress, resulting in Ca2+ transients, NO formation, and thus inducing vasodilation [102, 103, 105,106,107,108]. Secondly, P2X4R was regarded as apical Na+ sensors to control Na+ balance and BP by modulating ENaC activity in the collecting duct [103, 109]. ENaC is relevant to the Na+ reabsorption at the distal nephron and is of great importance for BP regulation.
P2X7 receptors mediate renal injury and inflammation-related hypertension
A couple of genetic researches have proven that P2X7R is linked to night-time diastolic BP [110]. In addition, P2X7 non-synonymous rs3751143 polymorphism was linked to reduced susceptibility to essential hypertension and its estimated haplotypes in Chinese postmenopausal women [111]. However, another study revealed that, in untreated newly diagnosed essential hypertensive patients, two P2X7 gene SNPs 489C > T and 1513A > C were independent of altered endothelial function and arterial stiffness [112]. The mechanisms underlying the relation between P2X7 gene SNPs and hypertension are not fully understood, which deserves further investigation.
P2X7R may participate in the vicious cycle of salt-sensitive hypertension and renal injury in the Dahl salt-sensitive rats. In vivo, blockade of P2X7R could prevent and improve salt-sensitive hypertension and renal injury [113]. Likely, blockade and knockdown of P2X7R showed lower BP in ANG II-treated and DOCA-salt treatment rats [114]. In addition, a lower urinary albumin excretion, but a higher creatinine clearance was detected in P2X7−/− mice, suggesting the additional protective renal function of P2X7R [114]. Also, selective inhibitor of P2X7R reduced BP in the normotensive Fischer (F344) rats, which exerted vasodilation in renal vascular and a lower pressure diuresis threshold. This potent hypotension effect by P2X7R might be associated with sevenfold increased expression of preglomerular vasculature P2X7R gene in F344 rat vs. in Lewis rat in the endothelium [115].
Compared with WT mice, P2X7R-deficient mice showed lower BP, less renal interstitial fibrosis and infiltration of immune cells, and lower levels of interleukin-1 beta. In ren-2 transgenic hypertension rat model, the expression of P2X7R was upregulated in podocytes and endothelial and mesangial cells after glomerular injury [116]. This upregulation indicated that P2X7R might be related to renal vasoconstriction and tubulointerstitial inflammation [117].
P2X7R is highly expressed in immune cells, including antigen-presenting cells (APCs), T cells, mast cells, macrophages, and monocytes. Activation of P2X7R led to release of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-18, resulting in the inflammatory response [118, 119]. As we know, plasma ATP is higher in patients with hypertension than in normotensive controls. ATP acted on P2X7R of APCs and increased the expression of CD86. The action of ATP triggered the hyperactivation of T cells and contributed to the immune-mediated pathologic changes associated with hypertensive disease. Hydrolyzing ATP or blocking the P2X7R eliminated hypertension-induced T cells hyperactivation [120]. In addition, pharmacologic or genetic blockade of P2X7R suppressed the progression of hypertension. These findings support that P2X7R on APCs and T cells may be a potential target for immune-mediated hypertension.
P2Y2 receptors mediate endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation and suppress ENaC activity
P2Y2R acted on the vasculature and renal Na+ reabsorption, manifesting the great therapeutic potential in hypertension. Activation of P2Y2R contributed to an acute NO-independent reduction in BP and an increase in renal Na+ excretion [121]. P2Y2R was the major subtype leading to vasorelaxation in human endothelial cells [122]. ATP released from the perivascular nerves activated P2Y2-like receptors in the endothelium thus eliciting an endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor in small arteries [123]. P2Y2R and G proteins Gq/G11 is a vital endothelial mechano-signalling pathway needed for basal endothelial NO formation, vascular tone. This pathway mediated fluid shear stress-induced several endothelial responses, such as [Ca2+]i transients, and activation of the endothelial NO synthase [124]. However, another research reported P2Y2R activation resulted in a biphasic BP response mediated not by endothelial NO, but by endothelial-derived hyperpolarization, which required functional KCa3.1 (intermediate-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels) and connexin 37 [125].
The apical ATP/UTP-P2Y2-receptor system is a significant regulator to suppress the ENaC open probability in response to an increase in Na+ intake, thereby regulating NaCl homeostasis and BP [126,127,128,129,130]. Pharmacogenetic technology was used in the renal tubule, as compelling evidence to demonstrate that selective activation of the P2Y2R and Gq signalling was adequate to renal salt excretion in principal cells [131]. Hyperactivity of ENaC caused by an absence of P2Y2R [109, 126, 128] elicited an increase in BP [128]. P2Y2−/− mice showed salt-resistant hypertension, enhancing renal Na+ retention and water reabsorption [127]. However, the inhibition of ENaC was not mediated by P2Y2R in the intact rat [129]. This discrepancy between species should be considered.
Interestingly, in the absence of P2Y2R, P2Y2/4R agonist resulted in an acute increase in BP. It was possibly attributed to vasoconstriction mediated by P2Y4R. There seems to be a mutual antagonism of P2Y2R and P2Y4R [121].
Other purinoceptors, including P2Y1, P2Y11, and P2Y12 receptors, might regulate BP
P2Y1R within the CNS and peripheral nerves were implicated in BP modulation. The inhibition of P2Y1R in C1 neurons produced a decrease in peripheral chemoreceptor-mediated activation of phrenic nerve activity, sympathetic nerve activity, and BP [132]. In muscle afferents, inhibition of P2Y1R prevented increased mean BP induced by forced exercise in the ischemic injury mice. This antihypertensive effect might involve regulating membrane expression of acid-sensing ion channel 3 [133].
P2Y1R and P2Y2R were probably associated with salt-sensitive hypertension. On the HS diet, P2Y1R and P2Y2R in the inner medullary collecting duct cells participated in the adaptive mechanism for increasing urinary NaCl excretion [134].
Among the P2YR subtypes, P2Y6R is the highest expressed type in mouse resistance arteries [135]. Compared with WT, P2Y6−/− mice had a lower BP. In vitro studies, P2Y6R activated by UDP and UTP were responsible for arterial contraction in the rat model. P2Y6R also participated in myogenic tone via an autocrine/paracrine activation loop [135]. P2Y11R is closely linked with inflammation and may have therapeutic potential in immune system-related hypertension. P2Y11R activation improved the vasomotor function and decreased hydrogen peroxide release, indicating a heightened role for P2Y11R in inflammation-related endothelial dysfunction [136]. P2Y12R may regulate BP for participation in the balance of body fluid. It partly mediated ADP-induced antihypertensive effect via decreasing tubular water reabsorption and urine concentration [137].
In addition, P2X1R, P2X7R, and AT1R seemed to share the same receptor or post-receptor signalling pathways [138]. In ANG II-dependent hypertension, P2XR and AT1R receptors mediated renal vasoconstriction, but P2XR was predominant [138, 139].
Altered P2 signalling also contributed to the development of PAH. In PAH, the protein of P2X1R, P2X4R, P2Y2R, P2Y11R, and P2Y12R were upregulated. P2X1R and P2Y12R mediated ATP-induced vasoconstriction, and P2Y6R mediated UDP-induced vasoconstriction in rat intrapulmonary arteries [140]. P2YR activated by Up4A resulted in pulmonary arteries contraction in rats [141, 142]. The P2 receptor-mediated Ca2+ signalosome of the human pulmonary endothelium, which was implications for PAH [143]. Shear stress modulated endothelial Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) through activation of P2X4R [144], and KLF2 mutation presented heritable PAH in clinical cases [145]. In addition, modulation of KLF2 showed therapeutic potential for pulmonary hypertension [146]. Thus, targeting P2X4R may be an option for modulating KLF2 in the PAH.
In the animal models with PAH, inhibition of P2X7R attenuated the inflammation [147, 148], pulmonary arteries remodelling [147, 149], and right ventricular function [147, 148]. The blockade effect of P2X7R on PAH and RV complications differed from current treatment options, where the significant improvements in pulmonary pressures ultimately do not prevent mortality due to RV failure [148]. Blockade of P2Y1R also decreased pulmonary arterial pressure in swine with acute hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension [150].
Overall, P2X4R and P2X7R may be therapeutic options in PAH. More studies are needed further to elucidate the involvement of P2X4R and P2X7R in PAH.
Conclusion and perspectives
Endogenous purines function as extracellular signalling molecules by activating purinoceptors. Purines and purinoceptors play a significant role in the regulation of BP. ATP mainly mediates vascular tone through the activation of P2X1R and P2X6R on the smooth muscle cells. ATP can also mediate vascular tone by activating A2AR, P2X4R, and P2Y2R on endothelial cells, and also by interacting with other purinoceptors, thereby showing dual effects. Similar dual effects are observed in ADP, adenosine, UTP, UDP, and Up4A.
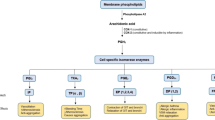
Purinoceptors play a crucial role in hypertension by modulating renin release, sodium excretion, ENaC activity and renal autoregulation, sympathetic nerve system, endothelium, CB, and immune system (Fig. 1). P2Y1R is demonstrated to be involved in neurogenic hypertension. P2X7R and P2Y11R are shown to be potential targets for immune-related hypertension. P2X3R located on CB is the most promising novel therapeutic target for hypertension. A1R, A2AR, A2BR, and P2X7R play significant roles in mediating renal autoregulation. The dysfunction of renal autoregulation eventually leads to renal damage and high BP. Purinergic signalling performs other roles which are similar to those of classic antihypertensive agents, including A1R, A2BR, A3R, P2X4R, P2Y1R, and P2Y2R mediated sodium excretion. A1R and P2X4R are related to NO formation. A1R activation induces renin release. Though numerous studies have demonstrated the effect of purines and purinoceptors on BP, none of the pharmacological tools targeting purinoceptors has entered clinical trials due to lower efficacy, complex kinetics issues, and adverse effect. Future studies are required to pinpoint purinoceptors and evaluate the purines and their receptors for potential treatment. More studies are needed to evaluate the purines and purinoceptors for the treatment of hypertension.
Purinoceptors in regulation of blood pressure. Activation or inhibition of purinoceptors can improve hypertension in 9 different ways, including sympathetic nerve activities, endothelial cells, neurons in the brain stem, carotid body, inflammation, renin-angiotensin system, sodium excretion, ENaC activity, and renal autoregulation. P2Y1R is involved in neurogenic hypertension. P2X3R located on the carotid body is the novel therapeutic target for hypertension. A1R activation induces renin release. A1R, A2BR, A3R, P2X4R, P2Y1R, and P2Y2R mediate sodium excretion. P2X1R and P2X6R on the smooth muscle cells, and A2AR, P2X4R, and P2Y2R on endothelial cells act on vessels to regulate vascular tone
Collectively, there is a complexity of purines- and purinoceptor-mediated effects in BP. Many aspects are still not fully understood due to many discrepant observations. The discrepancy arises from (1) purines concentration vs. purinoceptors sensitivity and (2) differences in purinoceptor expression and distribution in different blood vessels of different species. A better understanding of these aspects will help elucidate the role of purines and purinoceptors in the regulation of BP and the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Many questions remain from purinoceptors in the regulation of BP. Firstly, purines and purinoceptors are extensively distributed in the body. The BP regulation is a complex process mediated by purinoceptors in local blood vessels and the CNS. Thus, the assessment of drug safety and side effects should be of great concern. Secondly, heterogeneities in species, genders, and vascular beds should be taken into account. Lastly, the purinoceptors not mentioned above, including P2X2R, P2X5R, P2X6R, P2Y1R, P2Y3R, and P2Y13R, might have an impact on the regulation of BP.
Data availability
Not applicable.
Change history
18 February 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-023-09927-0
References
Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, Abdela J, Abdelalim A, Abdollahpour I, Abdulkader RS, Abebe HT, Abebe M, Abebe Z et al (2018) Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 392(10159):1736–1788
WHO (2021) Hypertension. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, Addolorato G, Ammirati E, Baddour LM, Barengo NC, Beaton AZ, Benjamin EJ, Benziger CP, Bonny A, Brauer M, Brodmann M, Cahill TJ, Carapetis J et al (2020) Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol 76(25):2982–3021
Burnstock G (2017) Purinergic signaling in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res 120(1):207–228
Oparil S, Acelajado MC, Bakris GL, Berlowitz DR, Cífková R, Dominiczak AF, Grassi G, Jordan J, Poulter NR, Rodgers A, Whelton PK (2018) Hypertension. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:18014
Hall JE, do Carmo JM, da Silva AA, Wang Z, Hall ME (2019) Obesity, kidney dysfunction and hypertension: mechanistic links. Nat Rev Nephrol 15(6):367–385
Fujita T (2014) Mechanism of salt-sensitive hypertension: focus on adrenal and sympathetic nervous systems. J Am Soc Nephrol 25(6):1148–1155
Patel S, Rauf A, Khan H, Abu-Izneid T (2017) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): the ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed Pharmacother 94:317–325
Manrique C, Lastra G, Gardner M, Sowers JR (2009) The renin angiotensin aldosterone system in hypertension: roles of insulin resistance and oxidative stress. Med Clin North Am 93(3):569–582
Guyenet PG, Stornetta RL, Holloway BB, Souza G, Abbott SBG (2018) Rostral ventrolateral medulla and hypertension. Hypertension 72(3):559–566
Iturriaga R, Alcayaga J, Chapleau MW, Somers VK (2021) Carotid body chemoreceptors: physiology, pathology, and implications for health and disease. Physiol Rev 101(3):1177–1235
Rucker AJ, Rudemiller NP, Crowley SD (2018) Salt, hypertension, and immunity. Annu Rev Physiol 80:283–307
Feng W, Dell’Italia LJ, Sanders PW (2017) Novel paradigms of salt and hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol 28(5):1362–1369
Sagnella GA, Swift PA (2006) The renal epithelial sodium channel: genetic heterogeneity and implications for the treatment of high blood pressure. Curr Pharm Des 12(18):2221–2234
Guan Z, Makled MN, Inscho EW (2020) Purinoceptors, renal microvascular function and hypertension. Physiol Res 69(3):353–369
Persson PB (2002) Renal blood flow autoregulation in blood pressure control. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 11(1):67–72
Rummery NM, Brock JA, Pakdeechote P, Ralevic V, Dunn WR (2007) ATP is the predominant sympathetic neurotransmitter in rat mesenteric arteries at high pressure. J Physiol 582(2):745–754
Bulloch JM, Starke K (1990) Presynaptic alpha 2-autoinhibition in a vascular neuroeffector junction where ATP and noradrenaline act as co-transmitters. Br J Pharmacol 99(2):279–284
Shatarat A, Dunn WR, Ralevic V (2014) Raised tone reveals ATP as a sympathetic neurotransmitter in the porcine mesenteric arterial bed. Purinergic Signal 10(4):639–649
Sneddon P, Burnstock G (1984) ATP as a co-transmitter in rat tail artery. Eur J Pharmacol 106(1):149–152
Brock JA, Cunnane TC (1999) Effects of Ca2+ concentration and Ca2+ channel blockers on noradrenaline release and purinergic neuroeffector transmission in rat tail artery. Br J Pharmacol 126(1):11–18
Donoso MV, Steiner M, Huidobro-Toro JP (1997) BIBP 3226, suramin and prazosin identify neuropeptide Y, adenosine 5’-triphosphate and noradrenaline as sympathetic cotransmitters in the rat arterial mesenteric bed. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282(2):691–698
Racchi H, Irarrázabal MJ, Howard M, Morán S, Zalaquett R, Huidobro-Toro JP (1999) Adenosine 5’-triphosphate and neuropeptide Y are co-transmitters in conjunction with noradrenaline in the human saphenous vein. Br J Pharmacol 126(5):1175–1185
Burnstock G, Ralevic V (2014) Purinergic signaling and blood vessels in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 66(1):102–192
Haddock RE, Hill CE (2011) Sympathetic overdrive in obesity involves purinergic hyperactivity in the resistance vasculature. J Physiol 589(13):3289–3307
Bodin P, Bailey D, Burnstock G (1991) Increased flow-induced ATP release from isolated vascular endothelial cells but not smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol 103(1):1203–1205
Liu C, Mather S, Huang Y, Garland CJ, Yao X (2004) Extracellular ATP facilitates flow-induced vasodilatation in rat small mesenteric arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286(5):H1688–H1695
Alkayed F, Boudaka A, Shiina T, Takewaki T, Shimizu Y (2009) P2X purinoceptors mediate an endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization in longitudinal smooth muscle of anterior mesenteric artery in young chickens. Br J Pharmacol 158(3):888–895
Ralevic V (2001) Mechanism of prolonged vasorelaxation to ATP in the rat isolated mesenteric arterial bed. Br J Pharmacol 132(3):685–692
Nieri P, Martinotti E, Calderone V, Breschi MC (2001) Adenosine-mediated hypotension in in vivo guinea-pig: receptors involved and role of NO. Br J Pharmacol 134(4):745–752
Matsumoto T, Takayanagi K, Katome T, Kojima M, Taguchi K, Kobayashi T (2021) Extracellular uridine nucleotides-induced contractions were increased in femoral arteries of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pharmacology 106(7–8):435–445
Jankowski V, Tolle M, Vanholder R, Schonfelder G, van der Giet M, Henning L, Schluter H, Paul M, Zidek W, Jankowski J (2005) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate: a novel endothelium- derived vasoconstrictive factor. Nat Med 11(2):223–227
Jankowski V, Meyer AA, Schlattmann P, Gui Y, Zheng XL, Stamcou I, Radtke K, Tran TN, van der Giet M, Tolle M, Zidek W, Jankowski J (2007) Increased uridine adenosine tetraphosphate concentrations in plasma of juvenile hypertensives. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(8):1776–1781.
Matsumoto T, Tostes R C, Webb RC (2011) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced contraction is increased in renal but not pulmonary arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circulat Physiol 301(2):H409–417.
Matsumoto T, Tostes RC, Webb RC (2012) Alterations in vasoconstrictor responses to the endothelium-derived contracting factor uridine adenosine tetraphosphate are region specific in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Pharmacol Res 65(1):81–90
Hansen PB, Hristovska A, Wolff H, Vanhoutte P, Jensen BL, Bie P (2010) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate affects contractility of mouse aorta and decreases blood pressure in conscious rats and mice. Acta Physiol (Oxford, England) 200(2):171–179.
Ralevic V, Thomas T, Burnstock G, Spyer KM (1999) Characterization of P2 receptors modulating neural activity in rat rostral ventrolateral medulla. Neuroscience 94(3):867–878
Wu KLH, Hung CY, Chan JYH, Wu CW (2014) An increase in adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP) content in rostral ventrolateral medulla is engaged in the high fructose diet-induced hypertension. J Biomed Sci 21(1):8
Marina N, Ang R, Machhada A, Kasymov V, Karagiannis A, Hosford PS, Mosienko V, Teschemacher AG, Vihko P, Paton JF, Kasparov S, Gourine AV (2015) Brainstem hypoxia contributes to the development of hypertension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension 65(4):775–783
Ferreira-Neto HC, Antunes VR, Stern JE (2015) ATP stimulates rat hypothalamic sympathetic neurons by enhancing AMPA receptor-mediated currents. J Neurophysiol 114(1):159–169
Braga VA, Soriano RN, Braccialli AL, De Paula PM, Bonagamba LGH, Paton JFR, Machado BH (2007) Involvement ofl-glutamate and ATP in the neurotransmission of the sympathoexcitatory component of the chemoreflex in the commissural nucleus tractus solitarii of awake rats and in the working heart-brainstem preparation. J Physiol 581(3):1129–1145
Korim WS, Ferreira-Neto ML, Pedrino GR, Pilowsky PM, Cravo SL (2012) Interaction of medullary P2 and glutamate receptors mediates the vasodilation in the hindlimb of rat. Purinergic Signalling 8(4):715–728
Lu Y, Zhang R, Ge Y, Carlstrom M, Wang S, Fu Y, Cheng L, Wei J, Roman R J, Wang L, Gao X, Liu R (2015) Identification and function of adenosine A3 receptor in afferent arterioles. American journal of physiology. Renal Physiol 308(9):F1020–1025
Patinha D, Abreu C, Carvalho C, Cunha OM, Mota M, Afonso J, Sousa T, Albino-Teixeira A, Diniz C, Morato M (2020) Adenosine A2A and A3 receptors as targets for the treatment of hypertensive-diabetic nephropathy. Biomedicines 8(11):529
McCoy DE, Bhattacharya S, Olson BA, Levier DG, Arend LJ, Spielman WS (1993) The renal adenosine system: structure, function, and regulation. Semin Nephrol 13(1):31–40
Headrick JP, Ashton KJ, Rose'meyer RB, Peart JN (2013) Cardiovascular adenosine receptors: expression, actions and interactions. Pharmacol Therapeut 140(1):92–111
Schindler CW, Karcz-Kubicha M, Thorndike EB, Muller CE, Tella SR, Ferre S, Goldberg SR (2005) Role of central and peripheral adenosine receptors in the cardiovascular responses to intraperitoneal injections of adenosine A1 and A2A subtype receptor agonists. Brit J Pharmacol 144(5):642–650
Brown R, Ollerstam A, Johansson B, Skøtt O, Gebre-Medhin S, Fredholm B, Persson AE (2001) Abolished tubuloglomerular feedback and increased plasma renin in adenosine A1 receptor-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 281(5):R1362-R1367.
Brown RD, Thoren P, Steege A, Mrowka R, Sallstrom J, Skott O, Fredholm BB, Persson AE (2006) Influence of the adenosine A1 receptor on blood pressure regulation and renin release. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290(5):R1324-1329
Wang Y, Yang JN, Arner A, Boels PJM, Fredholm BB (2010) Adenosine A(1) receptors and vascular reactivity. Acta Physiol (Oxford, England) 199(2):211–220
Rocha-Pereira C, Arribas SM, Fresco P, Gonzalez MC, Goncalves J, Diniz C (2013) Impaired inhibitory function of presynaptic A1-adenosine receptors in SHR mesenteric arteries. J Pharmacol Sci 122(2):59–70
Oberbauer R, Schreiner GF, Meyer TW (1998) Natriuretic effect of adenosine A1-receptor blockade in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 13(4):900–903
Gottlieb SS, Skettino SL, Wolff A, Beckman E, Fisher ML, Freudenberger R, Gladwell T, Marshall J, Cines M, Bennett D, Liittschwager EB (2000) Effects of BG9719 (CVT-124), an A1-adenosine receptor antagonist, and furosemide on glomerular filtration rate and natriuresis in patients with congestive heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 35(1):56–59
Zou AP, Wu F, Li PL, Cowley AW (1999) Effect of chronic salt loading on adenosine metabolism and receptor expression in renal cortex and medulla in rats. Hypertension 33(1 Pt 2):511–516
Gao X, Patzak A, Sendeski M, Scheffer PG, Teerlink T, Sallstrom J, Fredholm BB, Persson A E, Carlstrom M (2011) Adenosine A(1)-receptor deficiency diminishes afferent arteriolar and blood pressure responses during nitric oxide inhibition and angiotensin II treatment. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301(6):R1669–1681
Lee DL, Bell TD, Bhupatkar J, Solis G, Welch W J (2012) Adenosine A1-receptor knockout mice have a decreased blood pressure response to low-dose ANG II infusion. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 303(6):R683–688
Fahim M, Hussain T, Mustafa S J (2001) Role of endothelium in adenosine receptor-mediated vasorelaxation in hypertensive rats. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 15(5):325–334
Leal CM, Pereira S L, Kummerle AE, Leal DM, Tesch R, de Sant'Anna CM, Fraga A, Barreiro EJ, Sudo RT, Zapata-Sudo G (2012) Antihypertensive profile of 2-thienyl-3,4-methylenedioxybenzoylhydrazone is mediated by activation of the A2A adenosine receptor. Eur J Med Chem 55:49–57
Jackson EK, Gillespie DG, Mi Z, Cheng D (2018) Adenosine receptors influence hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats: dependence on receptor subtype, salt diet, and sex. Hypertension 72(2):511–521
Varani K, Manfredini R, Iannotta V, Pancaldi C, Cattabriga E, Uluoglu C, Borea PA, Portaluppi F (2002) Effects of doxazosin and propranolol on A2A adenosine receptors in essential hypertension. Hypertension 40(6):909–913
Carroll MA (2012) Role of the adenosine(2A) receptor-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 98(3–4):39–47
Liclican EL, McGiff JC, Falck JR, Carroll MA (2008) Failure to upregulate the adenosine2A receptor-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid pathway contributes to the development of hypertension in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295(6):F1696–1704
Nayak S, Khan MA, Wan TC, Pei H, Linden J, Dwinell MR, Geurts AM, Imig JD, Auchampach JA (2015) Characterization of Dahl salt-sensitive rats with genetic disruption of the A2B adenosine receptor gene: implications for A2B adenosine receptor signaling during hypertension. Purinergic signall 11(4):519–531
Fozard JR, Carruthers AM (1993) Adenosine A3 receptors mediate hypotension in the angiotensin II-supported circulation of the pithed rat. Brit J Pharmacol 109(1):3–5
Yang T, Zollbrecht C, Winerdal ME, Zhuge Z, Zhang XM, Terrando N, Checa A, Sallstrom J, Wheelock CE, Winqvist O, Harris RA, Larsson E, Persson AE, Fredholm BB, Carlstrom M (2016) Genetic abrogation of adenosine A3 receptor prevents uninephrectomy and high salt-induced hypertension. J Am Heart Assoc 5(7):e003868
Di Sole F, Cerull R, Babich V, Casavola V, Helmle-Roth C, Burckhardt G (2008) Short- and long-term A3 adenosine receptor activation inhibits the Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 activity and expression in opossum kidney cells. J Cellular Physiol 216(1):221–233
Zhou YP, Ruan CC, Kong LR, Gao PJ (2020) Adenosine A2A receptor activation prevents DOCA-salt induced hypertensive cardiac remodeling via iBAT. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 525(1):224–230
Prediger RD, Fernandes D, Takahashi RN (2005) Blockade of adenosine A2A receptors reverses short-term social memory impairments in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Behav Brain Res 159(2):197–205
Konduri GG, Woodard LL, Mukhopadhyay A, Deshmukh DR (1992) Adenosine is a pulmonary vasodilator in newborn lambs. Am Rev Respir Dis 146(3):670–676
Alencar AKN, Pereira SL, da Silva FE, Mendes LVP, Cunha V d MN, Lima LM, Montagnoli T L, Caruso-Neves C, Ferraz EB, Tesch R, Nascimento JHM, Sant'anna CMR, Fraga CAM, Barreiro EJ, Sudo RT, et al. (2014) N-acylhydrazone derivative ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension through the modulation of adenosine AA2R activity. Int J Cardiol 173(2):154–162
Alencar AKN, Pereira SL, Montagnoli TL, Maia C, Kümmerle AE, Landgraf SS, Caruso-Neves C, Ferraz EB, Tesch R, Nascimento JHM, de Sant'Anna CMR, Fraga CAM, Barreiro EJ, Sudo RT, Zapata-Sudo G (2013) Beneficial effects of a novel agonist of the adenosine A2A receptor on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Brit J Pharmacol 169(5):953–962
Alencar AK, Carvalho FI, Silva AM, Martinez ST, Calasans-Maia JA, Fraga CM, Barreiro EJ, Zapata-Sudo G, Sudo RT (2018) Synergistic interaction between a PDE5 inhibitor (sildenafil) and a new adenosine A2A receptor agonist (LASSBio-1359) improves pulmonary hypertension in rats. PLoS One.13(4):e0195047
Shang P, He ZY, Chen JF, Huang SY, Liu BH, Liu HX, Wang XT (2015) Absence of the adenosine A2A receptor confers pulmonary arterial hypertension through RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway in mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 66(6):569–575
Xu MH, Gong YS, Su MS, Dai ZY, Dai SS, Bao SZ, Li N, Zheng RY, He JC, Chen JF, Wang XT (2011) Absence of the adenosine A2A receptor confers pulmonary arterial hypertension and increased pulmonary vascular remodeling in mice. J Vasc Res 48(2):171–183
Mertens TCJ, Hanmandlu A, Tu L, Phan C, Collum SD, Chen NY, Weng T, Davies J, Liu C, Eltzschig HK, Jyothula SSK, Rajagopal K, Xia Y, Guha A, Bruckner BA et al (2018) Switching-off Adora2b in vascular smooth muscle cells halts the development of pulmonary hypertension. Front Physiol 9:555
Karmouty-Quintana H, Zhong H, Acero L, Weng T, Melicoff E, West JD, Hemnes A, Grenz A, Eltzschig HK, Blackwell TS, Xia Y, Johnston RA, Zeng D, Belardinelli L, Blackburn MR (2012) The A2B adenosine receptor modulates pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology 26(6):2546–2557
Wang L, Karlsson L, Moses S, Hultgårdh-Nilsson A, Andersson M, Borna C, Gudbjartsson T, Jern S, Erlinge D (2002) P2 receptor expression profiles in human vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 40(6):841–853
Zhang Y, Babczyk P, Pansky A, Kassack MU, Tobiasch E (2020) P2 Receptors influence hMSCs differentiation towards endothelial cell and smooth muscle cell lineages. Int J Mol Sci 21(17):6210
Muhleder S, Fuchs C, Basilio J, Szwarc D, Pill K, Labuda K, Slezak P, Siehs C, Proll J, Priglinger E, Hoffmann C, Junger WG, Redl H, Holnthoner W (2020) Purinergic P2Y2 receptors modulate endothelial sprouting. Cellular And Molecular Life Sciences 77(5):885–901
Sathanoori R, Bryl-Gorecka P, Muller CE, Erb L, Weisman GA, Olde B, Erlinge D (2017) P2Y2 receptor modulates shear stress-induced cell alignment and actin stress fibers in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cellular And Molecular Life Sciences 74(4):731–746
Gitterman DP, Evans RJ (2001) Nerve evoked P2X receptor contractions of rat mesenteric arteries; dependence on vessel size and lack of role of L-type calcium channels and calcium induced calcium release. Brit J Pharmacol 132(6):1201–1208
Franco M, Bautista R, Tapia E, Soto V, Santamaria J, Osorio H, Pacheco U, Sanchez-Lozada LG, Kobori H, Navar LG (2011) Contribution of renal purinergic receptors to renal vasoconstriction in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300(6):F1301-1309
Graciano ML, Nishiyama A, Jackson K, Seth DM, Ortiz RM, Prieto-Carrasquero MC, Kobori H, Navar LG (2008) Purinergic receptors contribute to early mesangial cell transformation and renal vessel hypertrophy during angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294(1):F161-169
Pandit MM, Inscho EW, Zhang S, Seki T, Rohatgi R, Gusella L, Kishore B, Kohan DE (2015) Flow regulation of endothelin-1 production in the inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 308(6):F541-552
Malheiros-Lima MR, Antunes VR, Takakura AC, Moreira TS (2020) Hypertension and sympathetic nervous system overactivity rely on the vascular tone of pial vessels of the rostral ventrolateral medulla in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Exp Physiol 105(1):65–74
Ferreira-Neto HC, Yao ST, Antunes VR (2013) Purinergic and glutamatergic interactions in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus modulate sympathetic outflow. Purinergic signall 9(3):337–349
Nichols CM, Povstyan OV, Albert AP, Gordienko DV, Khan O, Vasilikostas G, Khong TK, Wan A, Reddy M, Harhun MI (2014) Vascular smooth muscle cells from small human omental arteries express P2X1 and P2X4 receptor subunits. Purinergic signall 10(4):565–572
Lamont C, Vial C, Evans RJ, Wier WG (2006) P2X1 receptors mediate sympathetic postjunctional Ca2+ transients in mesenteric small arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circul Physiol 291(6):H3106-H3113
Guan Z, Fuller BS, Yamamoto T, Cook AK, Pollock JS, Inscho EW (2010) Pentosan polysulfate treatment preserves renal autoregulation in ANG II-infused hypertensive rats via normalization of P2X1 receptor activation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 298(5):F1276-1284
Inscho EW, Cook AK, Clarke A, Zhang S, Guan Z (2011) P2X1 receptor-mediated vasoconstriction of afferent arterioles in angiotensin II-infused hypertensive rats fed a high-salt diet. Hypertension 57(4):780–787
Guan Z, Giddens MI, Osmond DA, Cook AK, Hobbs JL, Zhang S, Yamamoto T, Pollock JS, Pollock DM, Inscho EW (2013) Immunosuppression preserves renal autoregulatory function and microvascular P2X(1) receptor reactivity in ANG II-hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 304(6):F801-807
Guan Z, Singletary ST, Cha H, Van Beusecum JP, Cook AK, Pollock JS, Pollock DM, Inscho E W (2016) Pentosan polysulfate preserves renal microvascular P2X1 receptor reactivity and autoregulatory behavior in DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 310(6):F456-F465
Zhou Z, Yadav VR, Sun C, Teng B, Mustafa JS (2017) Impaired aortic contractility to uridine adenosine tetraphosphate in angiotensin II-induced hypertensive mice: receptor desensitization? Am J Hypertens 30(3):304–312
Pijacka W, Moraes DJ, Ratcliffe LE, Nightingale AK, Hart EC, da Silva MP, Machado BH, McBryde FD, Abdala AP, Ford AP, Paton JF (2016) Purinergic receptors in the carotid body as a new drug target for controlling hypertension. Nat Med 22(10):1151–1159
Sinski M, Lewandowski J, Przybylski J, Bidiuk J, Abramczyk P, Ciarka A, Gaciong Z (2012) Tonic activity of carotid body chemoreceptors contributes to the increased sympathetic drive in essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 35(5):487–491
Heath D, Smith P, Fitch R, Harris P (1985) Comparative pathology of the enlarged carotid body. J Comparat Pathol 95(2):259–271
Nair S, Gupta A, Fudim M, Robinson C, Ravi V, Hurtado-Rua S, Engelman Z, Lee KS, Phillips CD, Sista AK (2013) CT angiography in the detection of carotid body enlargement in patients with hypertension and heart failure. Neuroradiology 55(11):1319–1322
Sinski M, Lewandowski J, Przybylski J, Zalewski P, Symonides B, Abramczyk P, Gaciong Z (2014) Deactivation of carotid body chemoreceptors by hyperoxia decreases blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 37(9):858–862
Narkiewicz K, Ratcliffe LE, Hart EC, Briant LJ, Chrostowska M, Wolf J, Szyndler A, Hering D, Abdala AP, Manghat N, Burchell AE, Durant C, Lobo MD, Sobotka PA, Patel NK et al (2016) Unilateral carotid body resection in resistant hypertension: a safety and feasibility trial. JACC-Basic to Translational Science 1(5):313–324
Prasad M, Fearon IM, Zhang M, Laing M, Vollmer C, Nurse CA (2001) Expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits in rat carotid body afferent neurons: role in chemosensory signalling. J Physiol 537(Pt 3):667–677
Xue Q, Wang R, Wang L, Xiong B, Li L, Qian J, Hao L, Wang Z, Liu D, Deng C, Rong S, Yao Y, Jiang Y, Zhu Q, Huang J (2021) Downregulating the P2X3 receptor in the carotid body to reduce blood pressure via acoustic gene delivery in canines. Transl Res 227:30–41
Yamamoto K, Sokabe T, Matsumoto T, Yoshimura K, Shibata M, Ohura N, Fukuda T, Sato T, Sekine K, Kato S, Isshiki M, Fujita T, Kobayashi M, Kawamura K, Masuda H et al (2006) Impaired flow-dependent control of vascular tone and remodeling in P2X4-deficient mice. Nat Med 12(1):133–137
Craigie E, Menzies RI, Larsen CK, Jacquillet G, Carrel M, Wildman SS, Loffing J, Leipziger J, Shirley DG, Bailey MA, Unwin RJ (2018) The renal and blood pressure response to low sodium diet in P2X4 receptor knockout mice. Physiol Rep 6(20):e13899
Stokes L, Scurrah K, Ellis JA, Cromer BA, Skarratt KK, Gu BJ, Harrap SB, Wiley JS (2011) A loss-of-function polymorphism in the human P2X4 receptor is associated with increased pulse pressure. Hypertension 58(6):1086–1092
Yamamoto K, Sokabe T, Ohura N, Nakatsuka H, Kamiya A, Ando J (2003) Endogenously released ATP mediates shear stress-induced Ca2+ influx into pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circulat Physiol 285(2):H793-H803
Yamamoto K, Furuya K, Nakamura M, Kobatake E, Sokabe M, Ando J (2011) Visualization of flow-induced ATP release and triggering of Ca2+ waves at caveolae in vascular endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 20):3477–3483
Li LF, Xiang C, Qin KR (2015) Modeling of TRPV(4)-C(1) -mediated calcium signaling in vascular endothelial cells induced by fluid shear stress and ATP. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 14(5):979–993
Yamamoto K, Korenaga R, Kamiya A, Ando J (2000) Fluid shear stress activates Ca(2+) influx into human endothelial cells via P2X4 purinoceptors. Circ Res 87(5):385–391
Wildman SS, Marks J, Turner CM, Yew-Booth L, Peppiatt-Wildman CM, King BF, Shirley DG, Wang W, Unwin RJ (2008) Sodium-dependent regulation of renal amiloride-sensitive currents by apical P2 receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(4):731–742
Palomino-Doza J, Rahman TJ, Avery PJ, Mayosi BM, Farrall M, Watkins H, Edwards CR, Keavney B (2008) Ambulatory blood pressure is associated with polymorphic variation in P2X receptor genes. Hypertension 52(5):980–985
Gong C, Liu X, Ding L, Liu Y, Li T, Wang S, Zhao J, Rao S, Xiong C, Yang Y, Liu C, Liang S, Xu H (2019) A non-synonymous polymorphism in purinergic P2X7 receptor gene confers reduced susceptibility to essential hypertension in Chinese postmenopausal women. Clin Exp Hypertens 41(6):558–563
Ghiadoni L, Rossi C, Duranti E, Santini E, Bruno RM, Salvati A, Taddei S, Solini A (2013) P2X7 receptor polymorphisms do not influence endothelial function and vascular tone in neo-diagnosed, treatment-naive essential hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 31(12):2362–2369
Ji X, Naito Y, Hirokawa G, Weng H, Hiura Y, Takahashi R, Iwai N (2012) P2X(7) receptor antagonism attenuates the hypertension and renal injury in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertens Res 35(2):173–179
Menzies RI, Howarth AR, Unwin RJ, Tam FW, Mullins JJ, Bailey MA (2015) Inhibition of the purinergic P2X7 receptor improves renal perfusion in angiotensin-II-infused rats. Kidney Int 88(5):1079–1087
Menzies RI, Unwin RJ, Dash RK, Beard DA, Cowley AW Jr, Carlson BE, Mullins JJ, Bailey MA (2013) Effect of P2X4 and P2X7 receptor antagonism on the pressure diuresis relationship in rats. Front Physiol 4:305
Vonend O, Turner CM, Chan CM, Loesch A, Dell'Anna GC, Srai KS, Burnstock G, Unwin R J (2004) Glomerular expression of the ATP-sensitive P2X receptor in diabetic and hypertensive rat models. Kidney Int 66(1):157–166
Bautista-Perez R, Perez-Mendez O, Cano-Martinez A, Pacheco U, Santamaria J, Rodriguez-Iturbe FRB, Navar L G, Franco M (2020) The role of P2X7 purinergic receptors in the renal inflammation associated with angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Int J Mol Sci 21(11)
Bracey NA, Beck PL, Muruve DA, Hirota SA, Guo J, Jabagi H, Wright JR, Macdonald JA, Lees-Miller JP, Roach D, Semeniuk LM, Duff HJ (2013) The Nlrp3 inflammasome promotes myocardial dysfunction in structural cardiomyopathy through interleukin-1β. Exp Physiol 98(2):462–472
Stachon P, Heidenreich A, Merz J, Hilgendorf I, Wolf D, Willecke F, von Garlen S, Albrecht P, Härdtner C, Ehrat N, Hoppe N, Reinöhl J, von Zur MC, Bode C, Idzko M et al (2017) P2X deficiency blocks lesional inflammasome activity and ameliorates atherosclerosis in mice. Circulation 135(25):2524–2533
Zhao TV, Li Y, Liu X, Xia S, Shi P, Li L, Chen Z, Yin C, Eriguchi M, Chen Y, Bernstein EA, Giani JF, Bernstein KE, Shen XZ (2019) ATP release drives heightened immune responses associated with hypertension. Sci Immunol 4(36)
Rieg T, Gerasimova M, Boyer JL, Insel PA, Vallon V (2011) P2Y(2) receptor activation decreases blood pressure and increases renal Na(+) excretion. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301(2):R510–518
Raqeeb A, Sheng J, Ao N, Braun AP (2011) Purinergic P2Y2 receptors mediate rapid Ca(2+) mobilization, membrane hyperpolarization and nitric oxide production in human vascular endothelial cells. Cell Calcium 49(4):240–248
Thapaliya S, Matsuyama H, Takewaki T (1999) ATP released from perivascular nerves hyperpolarizes smooth muscle cells by releasing an endothelium-derived factor in hamster mesenteric arteries. J Physiol 521(Pt 1):191–199
Wang S, Iring A, Strilic B, Albarran Juarez J, Kaur H, Troidl K, Tonack S, Burbiel JC, Muller CE, Fleming I, Lundberg JO, Wettschureck N, Offermanns S (2015) P2Y(2) and Gq/G(1)(1) control blood pressure by mediating endothelial mechanotransduction. J Clin Investig 125(8):3077–3086
Dominguez Rieg JA, Burt JM, Ruth P, Rieg T (2015) P2Y(2) receptor activation decreases blood pressure via intermediate conductance potassium channels and connexin 37. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 213(3):628–641
Pochynyuk O, Rieg T, Bugaj V, Schroth J, Fridman A, Boss GR, Insel PA, Stockand JD, Vallon V (2010) Dietary Na+ inhibits the open probability of the epithelial sodium channel in the kidney by enhancing apical P2Y2-receptor tone. FASEB J 24(6):2056–2065
Rieg T, Bundey RA, Chen Y, Deschenes G, Junger W, Insel PA, Vallon V (2007) Mice lacking P2Y2 receptors have salt-resistant hypertension and facilitated renal Na+ and water reabsorption. FASEB J 21(13):3717–3726
Pochynyuk O, Bugaj V, Rieg T, Insel PA, Mironova E, Vallon V, Stockand JD (2008) Paracrine regulation of the epithelial Na+ channel in the mammalian collecting duct by purinergic P2Y2 receptor tone. J Biol Chem 283(52):36599–36607
Shirley DG, Bailey MA, Unwin RJ (2005) In vivo stimulation of apical P2 receptors in collecting ducts: evidence for inhibition of sodium reabsorption. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288(6):F1243-1248
Pochynyuk O, Bugaj V, Vandewalle A, Stockand JD (2008) Purinergic control of apical plasma membrane PI(4,5)P2 levels sets ENaC activity in principal cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294(1):F38-46
Mironova E, Suliman F, Stockand JD (2019) Renal Na(+) excretion consequent to pharmacogenetic activation of Gq-DREADD in principal cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 316(4):F758–F767
Wenker IC, Sobrinho CR, Takakura AC, Mulkey DK, Moreira TS (2013) P2Y1 receptors expressed by C1 neurons determine peripheral chemoreceptor modulation of breathing, sympathetic activity, and blood pressure. Hypertension 62(2):263–273
Queme LF, Ross JL, Lu P, Hudgins RC, Jankowski MP (2016) Dual modulation of nociception and cardiovascular reflexes during peripheral ischemia through P2Y1 receptor-dependent sensitization of muscle afferents. J Neurosci 36(1):19–30
Rajagopal M, Kathpalia PP, Thomas SV, Pao AC (2011) Activation of P2Y1 and P2Y2 receptors induces chloride secretion via calcium-activated chloride channels in kidney inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 301(3):F544-553
Kauffenstein G, Tamareille S, Prunier F, Roy C, Ayer A, Toutain B, Billaud M, Isakson BE, Grimaud L, Loufrani L, Rousseau P, Abraham P, Procaccio V, Monyer H, de Wit C et al (2016) Central role of P2Y6 UDP receptor in arteriolar myogenic tone. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36(8):1598–1606
Dănilă MD, Privistirescu A, Duicu OM, Raț iu CD, Angoulvant D, Muntean DM, Sturza A (2017) The effect of purinergic signaling via the P2Y11 receptor on vascular function in a rat model of acute inflammation. Mol Cell Biochem 431(1–2):37–44
Roszkowska-Chojecka MM, Walkowska A, Sadowski J, Dobrowolski L (2018) Clopidogrel partially counteracts adenosine-5’-diphosphate effects on blood pressure and renal hemodynamics and excretion in rats. Am J Med Sci 356(3):287–295
Kulthinee S, Shao W, Franco M, Navar LG (2020) Purinergic P2X1 receptor, purinergic P2X7 receptor, and angiotensin II type 1 receptor interactions in the regulation of renal afferent arterioles in angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 318(6):F1400–F1408
Franco M, Bautista-Perez R, Cano-Martinez A, Pacheco U, Santamaria J, Del Valle ML, Perez-Mendez O, Navar LG (2017) Physiopathological implications of P2X1 and P2X7 receptors in regulation of glomerular hemodynamics in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 313(1):F9–F19
Mitchell C, Syed NiH, Tengah A, Gurney AM, Kennedy C (2012) Identification of contractile P2Y1, P2Y6, and P2Y12 receptors in rat intrapulmonary artery using selective ligands. J Pharmacol Exp Therapeut 43(3):755–762
Matsumoto T, Tostes RC, Webb RC (2011) Uridine adenosine tetraphosphate-induced contraction is increased in renal but not pulmonary arteries from DOCA-salt hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circul Physiol 301(2):H409-H417
Gui Y, Walsh MP, Jankowski V, Jankowski J, Zheng XL (2008) Up4A stimulates endothelium-independent contraction of isolated rat pulmonary artery. American journal of physiology. Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294(4):L733-L738
Hennigs JK, Lüneburg N, Stage A, Schmitz M, Körbelin J, Harbaum L, Matuszcak C, Mienert J, Bokemeyer C, Böger R H, Kiefmann R, Klose H (2019) The P2-receptor-mediated Ca signalosome of the human pulmonary endothelium - implications for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Purinergic Signal 15(3):299–311
Sathanoori R, Rosi F, Gu BJ, Wiley JS, Muller CE, Olde B, Erlinge D (2015) Shear stress modulates endothelial KLF2 through activation of P2X4. Purinergic Signal 11(1):139–153
Eichstaedt CA, Song J, Viales RR, Pan Z, Benjamin N, Fischer C, Hoeper MM, Ulrich S, Hinderhofer K, Grunig E (2017) First identification of Kruppel-like factor 2 mutation in heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond,England) 131(8):689–698
Sindi HA, Russomanno G, Satta S, Abdul-Salam VB, Jo KB, Qazi-Chaudhry B, Ainscough AJ, Szulcek R, Jan Bogaard H, Morgan CC, Pullamsetti SS, Alzaydi MM, Rhodes CJ, Piva R, Eichstaedt CA et al (2020) Therapeutic potential of KLF2-induced exosomal microRNAs in pulmonary hypertension. Nat Commun 11(1):1185
Yin J, You S, Liu H, Chen L, Zhang C, Hu H, Xue M, Cheng W, Wang Y, Li X, Shi Y, Li N, Yan S, Li X (2017) Role of P2XR in the development and progression of pulmonary hypertension. Respir Res 18(1):127
Hansen T, Karimi Galougahi K, Besnier M, Genetzakis E, Tsang M, Finemore M, O'Brien-Brown J, Di Bartolo BA, Kassiou M, Bubb KJ, Figtree GA (2020) The novel P2X7 receptor antagonist PKT100 improves cardiac function and survival in pulmonary hypertension by direct targeting of the right ventricle. Am J Physiol Heart Circulat Physiol 319(1):H183-H191
Li X, Hu B, Wang L, Xia Q, Ni X (2021) P2X7 receptor-mediated phenotype switching of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells in hypoxia. Mol Biol Rep 48(3):2133–2142
Kylhammar D, Bune LT, Rådegran G (2014) P2Y1 and P2Y12 receptors in hypoxia- and adenosine diphosphate-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction in vivo in the pig. Eur J Appl Physiol 114(9):1995–2006
Funding
This work was supported by grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81904306) and Sichuan Science and Technology Program (2020YFH0115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Xuan Li declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Li-juan Zhu declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Jing Lv declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Xin Cao declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zhu, Lj., Lv, J. et al. Purinoceptor: a novel target for hypertension. Purinergic Signalling 19, 185–197 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-022-09852-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-022-09852-8