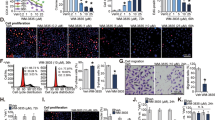
Abstract
Nm23-H1 is a metastasis suppressor gene whose overexpression is associated with both reduced cell motility in various cancers and increased metastatic potential in neuroblastomas, osteosarcomas, and hematological malignances. We previously reported that Nm23-H1 exerts tumor suppressor action in prostate cancer cells and that h-Prune, which is overexpressed in various tumor types, binds Nm23-H1. Moreover, blockage of the Nm23-H1/h-Prune interaction with a competitive permeable peptide (CPP) attenuates migration of breast and neuroblastoma cells. This series of events suggests that the Nm23-H1/h-Prune protein complex regulates cancer progression and that its specific impairment could be a new therapeutic strategy in oncology. We found that CPP leads to inhibition of the AKT/mTORv and NF-kBv signaling pathways and also activates apoptosis. To obtain a proof-of-concept of our hypothesis, we used a xenograft model of prostate cancer to evaluate whether impairment of this complex using CPP results in an anti-tumoral effect. Using a mouse orthotopic model with bioluminescent imaging, we show evidences that CPP reduces prostate cancer metastases formation. In conclusion, CPP being able to impair formation of the h-Prune/Nm23-H1 complex holds promise for the treatment of prostate cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andolfo I, De Martino D, Liguori L, Petrosino G, Troncone G, Tata N, Galasso A, Roma C, Chiancone F, Zarrilli S, Arrigoni G, Staibano S, Imbimbo C, Zollo M (2011) Correlation of NM23-H1 cytoplasmic expression with metastatic stage in human prostate cancer tissue. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 384:489–498
Bemis LT, Schedin P (2000) Reproductive state of rat mammary gland stroma modulates human breast cancer cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res 60:3414–3418
Bierhoff H, Dundr M, Michels AA, Grummt I (2008) Phosphorylation by casein kinase 2 facilitates rRNA gene transcription by promoting dissociation of TIF-IA from elongating RNA polymerase I. Mol Cell Biol 28:4988–4998
Biggs J, Hersperger E, Steeg PS, Liotta LA, Shearn A (1990) A Drosophila gene that is homologous to a mammalian gene associated with tumor metastasis codes for a nucleoside diphosphate kinase. Cell 63:933–940
Biondi RM, Engel M, Sauane M, Welter C, Issinger OG, Jimenez de Asua L, Passeron S (1996) Inhibition of nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity by in vitro phosphorylation by protein kinase CK2. Differential phosphorylation of NDP kinases in HeLa cells in culture. FEBS Lett 399:183–187
Carotenuto M, Pedone E, Diana D, de Antonellis P, Dzeroski S, Marino N, Navas L, Di Dato V, Scoppettuolo MN, Cimmino F, Correale S, Pirone L, Monti SM, Bruder E, Zenko B, Slavkov I, Pastorino F, Ponzoni M, Schulte JH, Schramm A, Eggert A, Westermann F, Arrigoni G, Accordi B, Basso G, Saviano M, Fattorusso R, Zollo M (2013) Neuroblastoma tumorigenesis is regulated through the Nm23-H1/h-Prune C-terminal interaction. Sci Rep 3:1351
Choo AY, Blenis J (2006) TORgeting oncogene addiction for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 9:77–79
Cuello F, Schulze RA, Heemeyer F, Meyer HE, Lutz S, Jakobs KH, Niroomand F, Wieland T (2003) Activation of heterotrimeric G proteins by a high energy phosphate transfer via nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) B and Gbeta subunits. Complex formation of NDPK B with Gbeta gamma dimers and phosphorylation of His-266 IN Gbeta. J Biol Chem 278:7220–7226
D’Angelo A, Garzia L, Andre A, Carotenuto P, Aglio V, Guardiola O, Arrigoni G, Cossu A, Palmieri G, Aravind L, Zollo M (2004) Prune cAMP phosphodiesterase binds nm23-H1 and promotes cancer metastasis. Cancer Cell 5:137–149
Davies MA, Kim SJ, Parikh NU, Dong Z, Bucana CD, Gallick GE (2002) Adenoviral-mediated expression of MMAC/PTEN inhibits proliferation and metastasis of human prostate cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res:Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 8:1904–1914
de Antonellis P, Liguori L, Falanga A, Carotenuto M, Ferrucci V, Andolfo I, Marinaro F, Scognamiglio I, Virgilio A, De Rosa G, Galeone A, Galdiero S, Zollo M (2013) MicroRNA 199b-5p delivery through stable nucleic acid lipid particles (SNALPs) in tumorigenic cell lines. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 386:287–302
Fiano V, Ghimenti C, Imarisio S, Silengo L, Schiffer D (2004) PAkt, cyclin D1 and p27/Kip.1 in glioblastomas with and without EGFR amplification and PTEN mutation. Anticancer Res 24:2643–2647
Galasso A, Zollo M (2009) The Nm23-H1-h-Prune complex in cellular physiology: a ‘tip of the iceberg’ protein network perspective. Mol Cell Biochem 329:149–159
Garzia L, D’Angelo A, Amoresano A, Knauer SK, Cirulli C, Campanella C, Stauber RH, Steegborn C, Iolascon A, Zollo M (2008) Phosphorylation of nm23-H1 by CKI induces its complex formation with h-prune and promotes cell motility. Oncogene 27:1853–1864
Hockla A, Miller E, Salameh MA, Copland JA, Radisky DC, Radisky ES (2012) PRSS3/mesotrypsin is a therapeutic target for metastatic prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res: MCR 10:1555–1566
Igawa M, Rukstalis DB, Tanabe T, Chodak GW (1994) High levels of nm23 expression are related to cell proliferation in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res 54:1313–1318
Jessen BA, Lee L, Koudriakova T, Haines M, Lundgren K, Price S, Nonomiya J, Lewis C, Stevens GJ (2007) Peripheral white blood cell toxicity induced by broad spectrum cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. J Appl Toxicol: JAT 27:133–142
Korshunov AG, Sycheva RV, Golanov AV (1998) Immunohistochemical study of neoplasm-associated proteins in cerebellum medulloblastomas. Arkh Patol 60:8–14
Kozlowski JM, Fidler IJ, Campbell D, Xu ZL, Kaighn ME, Hart IR (1984) Metastatic behavior of human tumor cell lines grown in the nude mouse. Cancer Res 44:3522–3529
Lacombe ML, Milon L, Munier A, Mehus JG, Lambeth DO (2000) The human Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinases. J Bioenerg Biomembr 32:247–258
Lang CH, Frost RA (2005) Endotoxin disrupts the leucine-signaling pathway involving phosphorylation of mTOR, 4E-BP1, and S6K1 in skeletal muscle. J Cell Physiol 203:144–155
le Nguyen XT, Mitchell BS (2013) Akt activation enhances ribosomal RNA synthesis through casein kinase II and TIF-IA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:20681–20686
Leone A, Flatow U, VanHoutte K, Steeg PS (1993) Transfection of human nm23-H1 into the human MDA-MB-435 breast carcinoma cell line: effects on tumor metastatic potential, colonization and enzymatic activity. Oncogene 8:2325–2333
Marino N, Marshall JC, Steeg PS (2011) Protein-protein interactions: a mechanism regulating the anti-metastatic properties of Nm23-H1. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 384:351–362
Marino N, Marshall JC, Collins JW, Zhou M, Qian Y, Veenstra T, Steeg PS (2013) Nm23-h1 binds to gelsolin and inactivates its actin-severing capacity to promote tumor cell motility and metastasis. Cancer Res 73:5949–5962
Memmott RM, Dennis PA (2009) Akt-dependent and -independent mechanisms of mTOR regulation in cancer. Cell Signal 21:656–664
Molineux G (2003) Pegfilgrastim: using pegylation technology to improve neutropenia support in cancer patients. Anticancer Drugs 14:259–264
Niitsu N, Okabe-Kado J, Okamoto M, Takagi T, Yoshida T, Aoki S, Hirano M, Honma Y (2001) Serum nm23-H1 protein as a prognostic factor in aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 97:1202–1210
Noguchi T, Oue N, Wada S, Sentani K, Sakamoto N, Kikuchi A, Yasui W (2009) h-Prune is an independent prognostic marker for survival in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 16:1390–1396
Oda Y, Naka T, Takeshita M, Iwamoto Y, Tsuneyoshi M (2000) Comparison of histological changes and changes in nm23 and c-MET expression between primary and metastatic sites in osteosarcoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study. Hum Pathol 31:709–716
Oliveira LA, Artigiani-Neto R, Waisberg DR, Fernandes LC, Lima Fde O, Waisberg J (2010) NM23 protein expression in colorectal carcinoma using TMA (tissue microarray): association with metastases and survival. Arq Gastroenterol 47:361–367
Oue N, Yoshida K, Noguchi T, Sentani K, Kikuchi A, Yasui W (2007) Increased expression of h-prune is associated with tumor progression and poor survival in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 98:1198–1205
Palmieri D, Halverson DO, Ouatas T, Horak CE, Salerno M, Johnson J, Figg WD, Hollingshead M, Hursting S, Berrigan D, Steinberg SM, Merino MJ, Steeg PS (2005) Medroxyprogesterone acetate elevation of Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor expression in hormone receptor-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:632–642
Pettaway CA, Pathak S, Greene G, Ramirez E, Wilson MR, Killion JJ, Fidler IJ (1996) Selection of highly metastatic variants of different human prostatic carcinomas using orthotopic implantation in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 2:1627–1636
Reymond A, Volorio S, Merla G, Al-Maghtheh M, Zuffardi O, Bulfone A, Ballabio A, Zollo M (1999) Evidence for interaction between human PRUNE and nm23-H1 NDPKinase. Oncogene 18:7244–7252
Roymans D, Willems R, Vissenberg K, De Jonghe C, Grobben B, Claes P, Lascu I, Van Bockstaele D, Verbelen JP, Van Broeckhoven C, Slegers H (2000) Nucleoside diphosphate kinase beta (Nm23-R1/NDPKbeta) is associated with intermediate filaments and becomes upregulated upon cAMP-induced differentiation of rat C6 glioma. Exp Cell Res 261:127–138
Saffran DC, Raitano AB, Hubert RS, Witte ON, Reiter RE, Jakobovits A (2001) Anti-PSCA mAbs inhibit tumor growth and metastasis formation and prolong the survival of mice bearing human prostate cancer xenografts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:2658–2663
Steeg PS, Bevilacqua G, Pozzatti R, Liotta LA, Sobel ME (1988) Altered expression of NM23, a gene associated with low tumor metastatic potential, during adenovirus 2 Ela inhibition of experimental metastasis. Cancer Res 48:6550–6554
Stravodimos K, Constantinides C, Manousakas T, Pavlaki C, Pantazopoulos D, Giannopoulos A, Dimopoulos C (2000) Immunohistochemical expression of transforming growth factor beta 1 and nm-23 H1 antioncogene in prostate cancer: divergent correlation with clinicopathological parameters. Anticancer Res 20:3823–3828
Sugatani T, Alvarez U, Hruska KA (2003) PTEN regulates RANKL- and osteopontin-stimulated signal transduction during osteoclast differentiation and cell motility. J Biol Chem 278:5001–5008
Suzuki E, Ota T, Tsukuda K, Okita A, Matsuoka K, Murakami M, Doihara H, Shimizu N (2004) nm23-H1 reduces in vitro cell migration and the liver metastatic potential of colon cancer cells by regulating myosin light chain phosphorylation. Int J Cancer J Int Cancer 108:207–211
Tammenkoski M, Koivula K, Cusanelli E, Zollo M, Steegborn C, Baykov AA, Lahti R (2008) Human metastasis regulator protein H-prune is a short-chain exopolyphosphatase. Biochemistry 47:9707–9713
Tripkovic A, Tripkovic I, Tomic S, Kovacic A, Grandic L, Capkun V (2012) The role of nm23 gene in colorectal carcinogenesis. Acta Clin Croat 51:43–49
Wagner PD, Vu ND (2000) Histidine to aspartate phosphotransferase activity of nm23 proteins: phosphorylation of aldolase C on Asp-319. Biochem J 346(Pt 3):623–630
Wallet V, Mutzel R, Troll H, Barzu O, Wurster B, Veron M, Lacombe ML (1990) Dictyostelium nucleoside diphosphate kinase highly homologous to Nm23 and Awd proteins involved in mammalian tumor metastasis and Drosophila development. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:1199–1202
Zamboni WC, D’Argenio DZ, Stewart CF, MacVittie T, Delauter BJ, Farese AM, Potter DM, Kubat NM, Tubergen D, Egorin MJ (2001) Pharmacodynamic model of topotecan-induced time course of neutropenia. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 7:2301–2308
Zhang Q, McCorkle JR, Novak M, Yang M, Kaetzel DM (2011) Metastasis suppressor function of NM23-H1 requires its 3′-5′ exonuclease activity. Int J Cancer 128:40–50
Zollo M, Andre A, Cossu A, Sini MC, D’Angelo A, Marino N, Budroni M, Tanda F, Arrigoni G, Palmieri G (2005) Overexpression of h-prune in breast cancer is correlated with advanced disease status. Clin Cancer Res: Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 11:199–205
Acknowledgments
We thank the Service Facilities of CEINGE and Jean Ann Gilder (Scientific Communication srl., Naples, Italy) for editing the text. Financial support for this study was provided by: PRIN (E5AZ5F) 2008 (MZ), Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC) 2011–2014 (MZ), FP6-EET pipeline LSH-CT-2006-037260 (MZ), FP7-Tumic HEALTH-F2-2008-201662 (MZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published as part of the Special issue on NDPK.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
(DOCX 12 kb)
Table S2
(DOCX 16 kb)
Table S3
(DOCX 13 kb)
Supplemental Fig. S1
(a) CPP mRNA expression detected by RT-PCR in DAOY and PC3 cells infected with AdV-MOCK or AdV-CPP. Data are expressed as mRNA expression (2–DCt) values. Data are means ± SD (n = 2) (*P< 0.05; ***P< 0.0005). (b) Representative images of PC3 cells after Adenovirus infection. Upper panels: GFP expression in transduced cells. PC3 cells were infected with Adenovirus Mock at MOI of 100 and visualized by fluorescence microscopy after 24 h. Lower panels: Phase contrast microscopy. (c) Analysis of caspase-3 activity, as measured with a fluorogenic substrate of caspase-3, in PC3 cells 50 hours after infection with AdV-MOCK or AdV-CPP. Caspase 3 activity was unchanged in AdV-CPP-treated PC3 cells compared to AdV-MOCK-infected counterparts. Data are means ±SD derived from triplicate measurements. (GIF 64 kb)
Supplemental fig. 2
(a) Intra-prostatic injection of PC3-Luc cells in two NOD/SCID mice groups that were treated with AdV-MOCK (5 mice) or AdV-CPP (5 mice). Tumorigenesis was followed by in-vivo bioluminescence photon emissions signals (IVIS Imaging System). Region of interest (ROI) analysis predominantly quantified light emission from peritumoral tissues. Gray boxes represent the animals that died during the trial. (b-d) Graphs showing lymphocytes, neutrophils (b), platelets (PLT; c) and red blood cells (RBC; d) counts in AdV-MOCK and AdV-CPP-treated mice. Data are means ±SD. (GIF 218 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carotenuto, M., de Antonellis, P., Chiarolla, C.M. et al. A therapeutic approach to treat prostate cancer by targeting Nm23-H1/h-Prune interaction. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 388, 257–269 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-1035-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-014-1035-8