Abstract
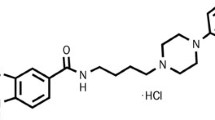
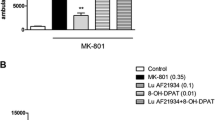
RG-15 (trans-N-{4-[2-[4-(3-cyano-5-trifluoromethyl-phenyl)-piperazine-1-yl]-ethyl]-cyclohexyl}-3-pyridinesulfonic amide dihydrochloride) displayed subnanomolar affinity to human and rat dopamine D3 receptors (pKi 10.49 and 9.42, respectively) and nanomolar affinity to human and rat D2 receptors (pKi 8.23 and 7.62, respectively). No apparent interactions were found with the other 44 receptors and four channel sites tested in this study. RG-15 inhibited dopamine-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in membranes from rat striatum, in murine A9 cells expressing human D2L receptors and in CHO cells expressing human D3 receptors (IC50 values were 21.2, 36.7 and 7.2 nM, respectively). In these tests RG-15 showed the highest affinity toward D3 receptors when compared to amisulpride, haloperidol and SB-277011. RG-15, similar to haloperidol and amisulpride, dose-dependently inhibited in vivo [3H]raclopride binding in mouse striatum, enhanced dopamine turnover and synthesis rate in mouse and rat striatum and olfactory tubercle. SB-277011 did not change [3H]raclopride binding in mouse striatum nor biosynthesis or turnover rates in either region in mice or rats. RG-15 and haloperidol, but not SB-277011, antagonised dopamine synthesis inhibition induced by the D3/D2 full agonist 7-OH-DPAT in GBL-treated mice. RG-15, but not SB-277011, elevated plasma prolactin levels. In vitro receptor binding and functional experiments demonstrated that RG-15 had an antagonist profile on both D3 and D2 receptors. with high selectivity for dopamine D3 receptors over D2 receptors. However, in vivo, its neurochemical actions were similar to those of D2 receptor antagonists. Neurochemical comparison of RG-15 with antagonists having a different affinity and selectivity toward D3 and D2 receptors indicate that D3 receptors have little, if any, role in the control of presynaptic dopamine biosynthesis/release in dopaminergic terminal regions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ágai-Csongor E, Nógrádi K, Galambos J, Vágó I, Bielik A, Magdó I, Ignácz-Szendrei G, Keserű GM, Greiner I, Laszlovszky I, Schmidt E, Kiss B, Sághy K, Laszy J, Gyertyán I, Zajer-Balázs, Gémesi L, Domány G (2007) Novel sulfonamides having dual dopamine D2 and D3 receptor affinity show in vivo antipsychotic efficacy with beneficial cognitive and EPS profile. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:5340–5344
Blagg J, Allerton CMN, Batchelor DVJ, Baxter AB, Burring DJ, Carr AS, Nichols CL, Phipps J, Sanderson VG, Verrier H, Wong S (2007) Design and synthesis of functionally selective D3 agonist and its in vivo delivery via intranasal route. Biorg Med Chem Lett 17:6691–6696
Carlsson A, Davis JN, Kehr W, Linqduist M, Atack CV (1972) Simultaneous measurement of tyrosine and tryptophan hydroxylase activities in brain in vivo using an inhibitor of the aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 275:153–168
Castelli MP, Mocci I, Sanna AM, Gessa GL, Pani L (2001) (-)S amisulpride bind with high affinity to cloned dopamine D3 and D2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 432:143–147
Cheng YC, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (KI) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition (IC50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108
Cussac D, Newman-Tancredi A, Sezgin L, Millan MJ (2000) [3H]S33084: a novel, selective and potent radioligand at cloned, human dopamine D3 receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 361:569–571
Daly SA, Waddington JL (1993) Behavioral effects of the putative D-3 dopamine receptor agonist 7-OH-DPAT in relation to other “D-2 like” agonists. Neuropharmacology 32:509–510
Gainetdinov RR, Sotnikova TD, Greghova TV, Rayevsky KG (1996) In vivo evidence for preferential role of dopamine D3 receptor in the presynaptic regulation of dopamine release but not synthesis. Eur J Pharmacol 308:261–269
Galloway MP, Wolf ME, Roth RH (1986) Regulation of dopamine synthesis in the medial prefrontal cortex is mediated by release modulating autoreceptors: studies in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 236:689–698
Gobert A, Rivet J-M, Audinot V, Cistarelli L, Spedding M, Vian J, Peglion J-L, Millan MJ (1995) Functional correlates of dopamine D3 receptor activation in the rat in vivo and their modulation by the selective antagonist, (+)-S 14297: II. Both D2 and “silent” D3 autoreceptors control synthesis and release in mesolimbic, mesocortical and nigrostriatal pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:899–913
Gyertyán I, Sághy K (2004) Effects of dopamine D3 receptor antagonists on spontaneous and agonist-reduced motor activity in NMRI mice and Wistar rats: comparative study with nafadotride, U99194A and SB 277011. Behav Pharmacol 15:253–262
Gyertyán I, Sághy K (2007) The selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists, SB 277011-A and S33084 block haloperidol-induced catalepsy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 572:171–174
Hackling AE, Stark H (2002) Dopamine D3 receptor ligands with antagonist properties. ChemBioChem 3:946–961
Heidbreder CA, Baumann MH (2001) Autoregulation of dopamine synthesis in subregions of the rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Pharmacol 411:107–113
Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL, Xi Z-X, Thanos PK, Mugnaini M, Hagan JJ, Ashby CR (2005) The role of central dopamine D3 receptors in drug addiction: a review of pharmacological evidence. Brain Res Rev 49:77–105
Hillefors M, von Euler G (2001) Pharmacology of [3H]R(+)-7-OH-DPAT binding in the rat caudate-putamen. Neurochem Int 38:31–42
Hillefors M, von Euler M, Hedlund PB, von Euler G (1999) prominent binding of the dopamine D3 agonist [3H]PD128907 in the caudate-putamen of the adult rat. Brain Res 822:126–131
Joyce JN, Millan M (2005) Dopamine D3 receptor antagonists as therapeutic agents. Drug Discovery Today 10:917–925
Kapur S, Seeman P (2001) Does fast dissociation from the dopamine D2 receptor explain the action of atypical antipsychotics?: A new hypothesis. Am J Psychiatry 158:360–369
Kling-Petersen T, Ljung E, Svensson K (1995) Effects on locomotor activity after local application of D3 preferring compounds in discrete areas of the rat brain. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 102:209–220
Koeltzow TE, Xu M, Cooper DC, Tonegawa S, Wolf ME, White FJ (1998) Alterations in dopamine release but not dopamine autoreceptor function in dopamine D3 receptor mutant mice. J Neurosci 18:2231–2238
Köhler C, Hall H, Ögren S-O, Gawell L (1985) Specific in vitro and in vivo binding of 3H-raclopride a potent substituted benzamide drug with high affinity for dopamine D-2 receptors in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 34:2251–2259
Lacroix LP, Hows MEP, Shah AJ, Hagan J, Heidbreder CA (2003) Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors enhances monoaminergic and cholinergic neurotransmission in the rat anterior cingulate cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:839–849
Lacroix LP, Ceolin L, Zocchi A, Varnier G, Garzotti M, Curcuruto O, Heidbreder CA (2006) Dopamine D3 antagonists enhance cortical acetylcholine levels measured with high-performance chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry without anti-cholinesterases. J Neurosci Methods 157:25–31
Laszy J, Laszlovszky I, Gyertyán I (2005) Dopamine D3 receptor antagonists improve the learning performance in memory-impaired rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:567–575
Leopoldo M, Berardi F, Colabufo NA, De Giorgio P, Lacivita E, Perrone R, Tortorella V (2002) Structure-affinity relationship study on N-[4-(4-arylpiperazin-1-yl)butyl]arylcarboxamides as potent and selective D3 receptor ligands. J Med Chem 45:5727–5735
Levant B (1997) The D3 dopamine receptor: neurobiology and potential clinical relevance. Pharmacol Rev 49:231–252
Millan MJ, Gressier H, Brocco M (1997) The dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, (+)-S 14297, blocks the cataleptic properties of haloperidol in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 321:R7–R9
Millan MJ, Gobert A, Newman-Tancredi A, Lejeune F, Cussac D, Rivet J-M, Audinot V, Dubuffet T, Lavielle G (2000) S33084 a novel, potent, selective and competitive antagonist at dopamine D3 receptors: I Receptorial, electrophysiological and neurochemical profile compared with GR218,231 and L741,626. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:1048–1062
Millan MJ, Seguin L, Gobert A, Cussac D, Brocco M (2004) The role of dopamine D3 compared with D2 receptors in the control of locomotor activity: a combined behavioural and neurochemical analysis with novel, selective antagonists in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174:341–357
Millan MJ, Di Cara B, Dekeyne A, Panayi F, De Groote L, Sicard D, Cistarelli L, Billiras R, Gobert A (2007) Selective blockade of dopamine D3 versus D2 receptors enhances frontocortical cholinergic transmission and social memory in rats: a parallel neurochemical and behavioral analysis. J Neurochem 100:1047–1061
Missale C, Nash R, Robinson SW, Jaber M, Caron MG (1998) Dopamine receptors: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 78:189–225
Nyberg S, Nakashima Y, Nordström A-L, Halldin C, Farde L (1996) Positron emission tomography of in vivo binding characteristics of atypical antipsychotic drugs. Review of D2 and 5-HT2 receptor occupancy studies and clinical response. Br J Psychiatry 168:40–44
Oka M, Noda Y, Ochi Y, Furukawa K, Une T, Kurumiya S, Hino K, Karasawa T (1992) Pharmacological profile of AD-5423, a novel antipsychotic with both potent dopamine-D2 and serotonin-S2 antagonist properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:158–165
Pilla M, Perachon S, Sautel F, Garrido F, Manni A, Wermuth CG, Schwartz JC, Everitt BJ, Sokoloff P (1999) Selective inhibition of cocaine seeking behavior by partial dopamine D3 receptor agonist. Nature 400:371–375
Pugsley TA, Davis MD, Akunne HC, Mackenzie RG, Shih YH, Damsma G, Wikstrom H, Whetzel SZ, Georgic LM, Cooke LW, Demattos SB, Corbin AE, Glase SA, Wise LD, Dijkstra D, Heffner TG (1995) Neurochemical and functional characterization of the preferentially selective dopamine D3 agonist PD 128907. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 275:1355–1366
Reavill C, Taylor SG, Wood MD, Ashmeade T, Austin NE, Avenell KY, Boyfield I, Branch CL, Cilia J, Coldwell MC, Hadley MS, Hunter AJ, Jeffrey P, Jewitt F, Johnson CN, Jones DN, Meadhearst AD, Middlemiss DN, Nash DJ, Riley GJ, Routledge C, Stemp G, Thewlis KM, Trainl B, Vong AK, Hagan JJ (2000) Pharmacological actions of a novel, high affinity, and selective human D3 receptor antagonist, SB-277011-A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:1154–1165
Ross SB, Jackson DM (1989) Kinetic properties of the accumulation of [3H]raclopride in the mouse brain in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 340:6–12
Schoemaker H, Claustre Y, Fage D, Rouquier DFL, Chergui K, Curet O, Oblin A, Carter C, Benavides J, Scatton B (1997) Neurochemical characteristics of amisulpride, an atypical dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with both presynaptic and limbic selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:83–97
Schotte A, Janssen PFM, Gommeren W, Luyten WHLM, Leysen J (1992) Autoradiographic evidence for the occlusion of rat brain dopamine D3 receptors in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 218:373–375
Schwartz J-C, Diaz J, Pilon C, Sokoloff P (2000) Possible implications of the dopamine D3 receptor in schizophrenia and in antipsychotic drug actions. Brain Res Rev 31:277–287
Seeman P (1983) Dopamine receptor measurement with [3H]ligands. In: Parvez S, Nagatsu T, Nagatsu I, Parvez H (eds) Methods in biogenic amine research. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 591–622
Seeman P (2001) Antipsychotic drugs, dopamine receptors and schizophrenia. Clin Neurosci Res 1:53–60
Sigala S, Missale C, Spano P (1997) Opposite effects of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors on learning and memory in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 336:107–112
Shafer R, Levant B (1998) The D3 dopamine receptor in cellular and organismal function. Psychopharmacology 135:1–16
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres MP, Bouthenet ML, Schwartz J-C (1990) Molecular cloning and characterisation of a novel dopamine receptor (D3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146–151
Sokoloff P, Diaz J, Levesque D, Pilon C, Dimitriadou V, Griffon N, Lammers CH, Martres MP, Schwartz J-C (1995) Novel dopamine receptor subtypes as targets for antipsychotic drugs. Ann NY Acad Sci USA 757:278–292
Sokoloff P, Diaz J, Le Foll B, Guillin O, Leriche L, Bezard E, Gross C (2006) The dopamine D3 receptor: A therapeutic target for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS & Neurological Disorder–Drug Targets 5:25–43
Toda M, Abi-Dargham A (2007) Dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: making sense of it all. Curr Psychiat Rep 9:329–336
Walters JR, Roth RH (1976) Dopaminergic neurons: an in vivo system for measuring drug interactions with presynaptic receptors. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 296:5–14
Waters N, Svensson K, Haadsma-Svensson SR, Smith MW, Carlsson A (1993) The dopamine D3 receptor: a postsynaptic receptor inhibitory on rat locomotor activity. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 94:11–19
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their thanks to K. Domján, Cs. Tóvári, E. Varga-Tilly, A. Vasadi for their expert technical assistance. We gratefully thank Klára Ihm-Varga (Institute for Experimental Medicine, Hungarian Academy of Science) for the prolactin determinations. We are grateful to Dr. Tony Ainsworth for his critical reading and comments on this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiss, B., Laszlovszky, I., Horváth, A. et al. Subnanomolar dopamine D3 receptor antagonism coupled to moderate D2 affinity results in favourable antipsychotic-like activity in rodent models: I. neurochemical characterisation of RG-15. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 378, 515–528 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0308-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-008-0308-5