Abstract
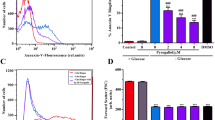
Osmotic shock, oxidative stress and Cl− removal activate a non-selective Ca2+-permeable cation conductance in human erythrocytes. The entry of Ca2+ leads to activation of a scramblase with subsequent exposure of phosphatidylserine at the cell surface. Phosphatidylserine mediates binding to phosphatidylserine receptors on macrophages which engulf and degrade phosphatidylserine exposing cells. Moreover, phosphatidylserine exposure may lead to adherence of erythrocytes to the vascular wall. In the present study, we explored whether activation of the non-selective cation conductance and subsequent phosphatidylserine exposure might be influenced by catecholamines. Phosphatidylserine exposure has been determined by FITC-annexin V binding while cell volume was estimated from forward scatter in FACS analysis. Removal of Cl− enhanced annexin binding and decreased forward scatter, an effect significantly blunted by the β agonist isoproterenol (IC50 approx. 1 μM). Fluo-3 fluorescence measurements revealed an increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity following Cl− removal, an effect again significantly blunted by isoproterenol exposure (10 μM). Whole-cell patch-clamp experiments performed in Cl− free bath solution indeed disclosed a time-dependent inactivation of a non-selective cation conductance following isoproterenol exposure (10 μM). Phenylephrine (IC50<10 μM), dobutamine (IC50 approx. 1 μM) and dopamine (IC50 approx. 3 μM) similarly inhibited the effect of Cl− removal on annexin binding and forward scatter. In conclusion, several catecholamines inhibit the Cl− removal-activated Ca2+ entry into erythrocytes, thus preventing increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity, subsequent cell shrinkage and activation of erythrocyte scramblase. The catecholamines thus counteract erythrocyte phosphatidylserine exposure and subsequent clearance of erythrocytes from circulating blood.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andree HA, Reutelingsperger CP, Hauptmann R, Hemker HC et al (1990) Binding of vascular anticoagulant alpha (VAC Alpha) to planar phospholipid bilayers. J Biol Chem 265:4923–4928
Andrews DA, Yang L, Low PS (2002) Phorbol ester stimulates a protein kinase C-mediated agatoxin-TK-sensitive calcium permeability pathway in human red blood cells. Blood 100:3392–3399
Barry PH, Lynch JW (1991) Liquid junction potentials and small cell effects in patch-clamp analysis. J Membr Biol 121:101–117
Benjamin LJ, Manning JM (1986) Enhanced survival of sickle erythrocytes upon treatment with glyceraldehyde. Blood 67:544–546
Berg CP, Engels IH, Rothbart A, Lauber K et al (2001) Human mature red blood cells express caspase-3 and caspase-8, but are devoid of mitochondrial regulators of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 8:1197–1206
Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD (2000) The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:11–21
Boas FE, Forman L, Beutler E (1998) Phosphatidylserine exposure and red cell viability in red cell aging and in hemolytic anemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3077–3081
Bonomini M, Sirolli V, Gizzi F, Di Stante S et al (2002) Enhanced adherence of human uremic erythrocytes to vascular endothelium: role of phosphatidylserine exposure. Kidney Int 62:1358–1363
Bosman GJCGM, Willekens FLA, Werre JM (2005) Erythrocyte aging: a more than superficial resemblance to apoptosis? Cell Physiol Biochem 16:1–8
Brand VB, Sandu CD, Duranton C, Tanneur V et al (2003) Dependence of plasmodium falciparum in vitro growth on the cation permeability of the human host erythrocyte. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:347–356
Bratosin D, Estaquier J, Petit F, Arnoult D et al (2001) Programmed cell death in mature erythrocytes: a model for investigating death effector pathways operating in the absence of mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 8:1143–1156
Cabado AG, Vieytes MR, Botana LM (1994) Effect of ion composition on the changes in membrane potential induced with several stimuli in rat mast cells. J Cell Physiol 158:309–316
Chan HC, Goldstein J, Nelson DJ (1992) Alternate pathways for chloride conductance activation in normal and cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 262:C1273–C1283
Closse C, Dachary-Prigent J, Boisseau MR (1999) Phosphatidylserine-related adhesion of human erythrocytes to vascular endothelium. Br J Haematol 107:300–302
Corash L, Spielberg S, Bartsocas C, Boxer L et al (1980) Reduced chronic hemolysis during high-dose Vitamin E administration in mediterranean-type glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. N Engl J Med 303:416–420
Damonte G, Guida L, Sdraffa A, Benatti U et al (1992) Mechanisms of perturbation of erythrocyte calcium homeostasis in favism. Cell Calcium 13:649–658
Daugas E, Cande C, Kroemer G (2001) Erythrocytes: death of a mummy. Cell Death Differ 8:1131–1133
Duranton C, Huber SM, Lang F (2002) Oxidation induces a Cl(-)-dependent cation conductance in human red blood cells. J Physiol 539:847–855
Duranton C, Huber S, Tanneur V, Lang K et al (2003) Electrophysiological properties of the plasmodium falciparum-induced cation conductance of human erythrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:189–198
Eda S, Sherman IW (2002) Cytoadherence of malaria-infected red blood cells involves exposure of phosphatidylserine. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:373–384
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Rose DM, Pearson A et al (2000) A receptor for phosphatidylserine-specific clearance of apoptotic cells. Nature 405:85–90
Gallagher PG, Chang SH, Rettig MP, Neely JE et al (2003) Altered erythrocyte endothelial adherence and membrane phospholipid asymmetry in hereditary hydrocytosis. Blood 101:4625–4627
Gamper N, Huber SM, Badawi K, Lang F (2000) Cell volume-sensitive sodium channels upregulated by glucocorticoids in U937 macrophages. Pflügers Archiv Eur J Physiol 441:281–286
Gulbins E, Jekle A, Ferlinz K, Grassme H et al (2000) Physiology of apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F605–F615
Harrison T, Samuel BU, Akompong T, Hamm H et al (2003) Erythrocyte G protein-coupled receptor signaling in malarial infection. Science 301:1734–1736
Hines PC, Zen Q, Burney SN, Shea DA et al (2003) Novel epinephrine and cyclic AMP-mediated activation of BCAM/Lu-Dependent Sickle (SS) RBC adhesion. Blood 101:3281–3287
Huber SM, Gamper N, Lang F (2001) Chloride conductance and volume-regulatory nonselective cation conductance in human red blood cell ghosts. Pflügers Archiv Eur J Physiol 441:551–558
Kiefer CR, Snyder LM (2000) Oxidation and erythrocyte senescence. Curr Opin Hematol 7:113–116
Koch J, Korbmacher C (1999) Osmotic shrinkage activates Nonselective Cation (NSC) channels in various cell types. J Membr Biol 168:131–139
Lang KS, Roll B, Myssina S, Schittenhelm M et al (2002) Enhanced erythrocyte apoptosis in sickle cell anemia, Thalassemia and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:365–372
Lang KS, Duranton C, Poehlmann H, Myssina S et al (2003a) Cation channels trigger apoptotic death of erythrocytes. Cell Death Differ 10:249–256
Lang KS, Myssina S, Tanneur V, Wieder T et al (2003b) Inhibition of erythrocyte cation channels and apoptosis by ethylisopropylamiloride. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 367:391–396
Lang PA, Kaiser S, Myssina S, Wieder T et al (2003c) Role of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in human erythrocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C1553–C1560
Lang PA, Warskulat U, Heller-Stilb B, Huang DY et al (2003d) Blunted apoptosis of erythrocytes from taurine transporter deficient mice. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:337–346
Lang KS, Myssina S, Brand V, Sandu C et al (2004a) Involvement of ceramide in hyperosmotic shock-induced death of erythrocytes. Cell Death Differ 11:231–243
Lang KS, Myssina S, Lang PA, Tanneur V et al (2004b) Inhibition of erythrocyte phosphatidylserine exposure by Urea and Cl-. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F1046–F1053
Lang KS, Lang PA, Bauer C, Duranton C et al (2005a) Mechanisms of suicidal erythrocyte death. Cell Physiol Biochem 15:195–202
Lang PA, Kempe DS, Myssina S, Tanneur V et al (2005b) PGE(2) in the regulation of programmed erythrocyte death. Cell Death Differ 12:415–428
Maeno E, Ishizaki Y, Kanaseki T, Hazama A et al (2000) Normotonic cell shrinkage because of disordered volume regulation is an early prerequisite to apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:9487–9492
Manodori AB, Barabino GA, Lubin BH, Kuypers FA (2000) Adherence of phosphatidylserine-exposing erythrocytes to endothelial matrix thrombospondin. Blood 95:1293–1300
Michea L, Ferguson DR, Peters EM, Andrews PM et al (2000) Cell cycle delay and apoptosis are induced by high salt and urea in renal medullary cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278:F209–F218
Myssina S, Lang PA, Kempe DS, Kaiser S et al (2004) Cl- channel blockers NPPB and niflumic acid blunt Ca(2+)-induced erythrocyte ‘apoptosis’. Cell Physiol Biochem 14:241–248
Nicotera P, Orrenius S (1998) The role of calcium in apoptosis. Cell Calcium 23:173–180
Oonishi T, Sakashita K, Uyesaka N (1997) Regulation of red blood cell filterability by Ca2+ influx and CAMP-mediated signaling pathways. Am J Physiol 273:C1828–C1834
Pavoni V, Verri M, Ferraro L, Volta CA et al (1998) Plasma dopamine concentration and effects of low dopamine doses on urinary output after major vascular surgery. Kidney Int Suppl 66:S75–S80
Rice L, Alfrey CP (2005) The negative regulation of red cell mass by neocytolysis: physiologic and pathophysiologic manifestations. Cell Physiol Biochem 15:245–250
Roelofsen B (1991) Molecular architecture and dynamics of the plasma membrane lipid bilayer: the red blood cell as a model. Infection 19(Suppl 4):S206–S209
Roger F, Martin PY, Rousselot M, Favre H et al (1999) Cell shrinkage triggers the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by hypertonicity in the rat kidney medullary thick ascending limb of the henle's loop. Requirement of P38 kinase for the regulatory volume increase response. J Biol Chem 274:34103–34110
Romero PJ, Romero EA (1999) Effect of cell ageing on Ca2+ influx into human red cells. Cell Calcium 26:131–137
Rosette C, Karin M (1996) Ultraviolet light and osmotic stress: activation of the JNK cascade through multiple growth factor and cytokine receptors. Science 274:1194–1197
Ruymann FB, Popejoy LA, Brouillard RB (1978) Splenic sequestration and ineffective erythropoiesis in hemoglobin E-beta-Thalassemia disease. Pediatr Res 12:1020–1023
Sager G (1982) Receptor binding sites for beta-adrenergic ligands on human erythrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 31:99–104
Setty BN, Kulkarni S, Stuart MJ (2002) Role of erythrocyte phosphatidylserine in sickle red cell-endothelial adhesion. Blood 99:1564–1571
Sprague RS, Ellsworth ML, Stephenson AH, Lonigro AJ (2001) Participation of CAMP in a signal-transduction pathway relating erythrocyte deformation to ATP release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1158–C1164
Volk T, Fromter E, Korbmacher C (1995) Hypertonicity activates nonselective cation channels in mouse cortical collecting duct cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:8478–8482
Wali RK, Jaffe S, Kumar D, Kalra VK (1988) Alterations in organization of phospholipids in erythrocytes as factor in adherence to endothelial cells in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 37:104–111
Wehner F, Sauer H, Kinne RK (1995) Hypertonic stress increases the Na+ conductance of rat hepatocytes in primary culture. J Gen Physiol 105:507–535
Wehner F, Böhmer C, Heinzinger H, van den BF et al (2000) The hypertonicity-induced Na(+) conductance of rat hepatocytes: physiological significance and molecular correlate. Cell Physiol Biochem 10:335–340
Yang XY, Qu Q, Yang TY, Chan WC et al (1988) Treatment of the Thalassemia syndrome with splenectomy. Hemoglobin 12:601–608
Zhou Q, Zhao J, Wiedmer T, Sims PJ (2002) Normal hemostasis but defective hematopoietic response to growth factors in mice deficient in phospholipid scramblase 1. Blood 99:4030–4038
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the meticulous preparation of the manuscript by Tanja Loch. This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, No. La 315/4-3, La 315/13-1 and La 315/6-1, the Bundesministerium für Bildung, Wissenschaft, Forschung und Technologie (Center for Interdisciplinary Clinical Research) 01 KS 9602 and the Biomed program of the EU (BMH4-CT96-0602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lang, P.A., Kempe, D.S., Akel, A. et al. Inhibition of erythrocyte “apoptosis” by catecholamines. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol 372, 228–235 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-005-0009-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-005-0009-2