Abstract
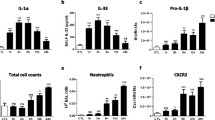
Inhalation exposure to fluoride compounds has been associated with respiratory failure. We have addressed effects of fluoride on alveolar macrophages and lung responses to intratracheally (i.t.) instilled fluoride in rats. I.t. instillation of fluoride at doses of 200 and 400 μg F/rat caused significant polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) infiltration in the rat lung at 20 h post-administration, while 100 μg fluoride did not recruit a significant number of PMNs in the alveolar space. Total RNA was extracted from the lung lavage cells obtained from 5 h post i.t. instillation and mRNA levels of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines were semi-quantitatively evaluated by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). I.t. instillation of fluoride significantly enhanced mRNA expression of cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor-α, cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant, and macrophage inflammatory proteins-1α and -2. Fluoride-induced augmentation in IL-1β mRNA expression was also examined by Northern hybridization following in vitro exposure of alveolar macrophages to fluoride. However, the enhancement of IL-1β mRNA expression following in vitro exposure to fluoride was observed only at 500 μM, a dose higher than the 50% lethal concentration (LC50). Non-specific adhesion of alveolar macrophages to the plastic dish was significantly increased following in vitro exposure to fluoride. The fluoride-induced non-specific adhesion was significantly reduced by anti-CD18, suggesting that β2 integrin played a role in the increase of adherence. Those results suggest that fluoride activates alveolar macrophages, enhances the production of chemokines and proinflammatory cytokines, and causes PMN infiltration in the lung.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 22 March 1999 / Accepted: 31 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirano, S., Ando, M. & Kanno, S. Inflammatory responses of rat alveolar macrophages following exposure to fluoride. Arch Toxicol 73, 310–315 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050624
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050624