Abstract
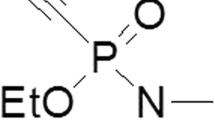
The efficiency of newly synthesized oxime derivatives of quinuclidinium were tested in vitro on soman inhibited acetylcholinesterase (AChE) of human erythrocytes and in vivo using soman poisoned mice. For this purpose, the inhibitory power of oximes (IC50), acute toxicity (LD50) as well as reactivating and protective capacities with respect to soman-inhibited AChE were determined for each of the oximes. All oximes tested were ineffective in vitro but protected mice very efficiently (BM-1 protects against 4LD50 of soman). The results indicate that the in vivo effectiveness of quinuclidinium oximes against soman poisoning may not be related to reactivation or protection of AChE but rather to some other mechanism of the cholinergic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 August 1996 / Accepted: 21 January 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lucić, A., Radić, B., Peraica, M. et al. Antidotal efficacy of quinuclidinium oximes against soman poisoning. Arch Toxicol 71, 467–470 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050413
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050413