Abstract
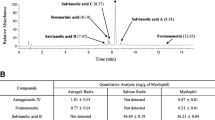
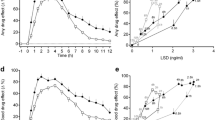
3-(Phenylamino)alanine (PAA), a newly discovered impurity in case-associated l-tryptophan tablets, has been investigated as a possible contributing factor in the etiology of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome (EMS). We have studied distribution and elimination of PAA in rats which were administered a single 5 mg/kg dose of PAA by gastric gavage. PAA concentrations in blood, brain, kidney and liver were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with electrochemical detection. The concentration of PAA in each tissue reached a maximum at 5 h, and then gradually declined. A high level of PAA still remained at 24 h, indicating gradual elimination. The concentration of PAA in brain at 5 h was 2139 ng/g tissue, demonstrating passage through the blood-brain barrier. Consecutive administration of PAA (5 mg/kg) for 4 days resulted in approximately double the concentration in all tissues. Chronic treatment using PAA incorporated into food pellets for 6 weeks resulted in similar accumulations in each tissue, and following 12 days on a PAA free diet, levels of this drug were still detectable in all tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Adachi J, Naito T, Ueno Y, Ogawa Y, Ninomiya I, Tatsuno Y (1993) Metabolism and distribution in the rat of peak E substance, a constituent in l-tryptophan product implicated in eosinophiliamyalgia syndrome. Arch Toxicol 67: 284–289
Adachi J, Mio T, Ueno Y, Naito T, Nishimura A, Fujiwara S, Sumino K, Tatsuno Y (1994) Identification of four metabolites of 3-(phenylamino)alanine, a constituent in l-tryptophan product implicated in eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome, in rats. Arch Toxicol 68: 500–505
Belongia EA, Hedberg CW, Gleich GJ, White KE, Mayeno AN, Loegering DA, Dunnette SL, Pirie PL, MacDonald KL, Osterholm MT (1990) An investigation of the cause of the eosinophiliamyalgia syndrome associated with tryptophan use. N Engl J Med 323: 357–365
Brady LS, Page SW, Thomas FS, Rader JI, Poltorak BM, Zelazowski E, Crofford LJ, Zelazowski P, Smith CC, Raybourne RB, Love LA, Gold PW, Sternberg EM (1994) 1,1′-Ethylidenebis[l-tryptophan], a contaminant implicated in l-tryptophan eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome, suppresses mRNA expression of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone in Lewis (LEW/N) rat brains. Neuroimmunomodulation 1: 59–65
Centers for Disease Control (1990) Analysis of l-tryptophan for the etiology of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. New Mexico MMWR 39: 589–591
Crofford LJ, Rader JI, Dalakas MC, Hill RH Jr, Page SW, Needham LL, Brady LS, Heyes MP, Wilder RL, Gold PW, Illa I, Smith CC, Sternberg EM (1990) l-Tryptophan implicated in human eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome causes fasciitis and perimyositis in the Lewis rat. J Clin Invest 86: 1757–1763
Goda Y, Suzuki J, Maitani T, Yoshihira K, Takeda M, Uchiyama M (1992) 3-Anilino-l-alanine, structural determination of UV-5, a contaminant in EMS-associated L-tryptophan samples. Chem Pharm Bull 40: 2236–2238
Hill RH Jr, Caudill SP, Philen RM, Bailey SL, Flanders WD, Driskell WJ (1993) Contaminants in l-tryptophan associated with eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome (EMS). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 25: 134–142
Love LA, Rader JI, Crofford LJ, Raybourne RB, Principato MA, Page SW, Trucksess MW, Dugen EM, Turner ML, Zelazowski E, Zelazowski P, Sternberg EM (1993) Pathological and immunological effects of ingesting l-tryptophan (l-TRP) and 1,1′-ethylidenebis(tryptophan) in Lewis rats. J Clin Invest 91: 804–811
Mayeno AN, Lin F, Foote CS, Loegering DA, Ames MM, Hedberg CW, Gleich GJ (1990) Characterization of “peak E”, a novel amino acid associated with eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. Science 250: 1707–1708
Mayeno AN, Belongia EA, Lin F, Lundy SK, Gleich GJ (1992) 3-(Phenylamino)alanine, a novel aniline-derived amino acid associated with the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome: a link to the toxic oil syndrome? Mayo Clin Proc 67: 1134–1139
Ogawa Y, Adachi J, Tatsuno Y (1993) Accumulation of 1-methyl-tetrahydro-β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid in blood and organs of rat. A possible causative substance of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with ingestion of l-tryptophan. Arch Toxicol 67: 290–293
Silver RM, Heyes MP, Maize JC, Quearry B, Vionnet-Fuasset M, Sternberg EM (1990) Sclerodermia, fasciitis, and eosinophilia associated with the ingestion of tryptophan. N Engl J Med 322: 874–881
Silver RM, Ludwicka A, Hampton M, Ohba T, Bingel SA, Smith T, Harley RA, Maize J, Heyes MP (1994) A murine model of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome induced by 1,1′-ethylidene-bis(tryptophan). J Clin Invest 93: 1473–1480
Slutsker L, Hoesly FC, Miller L, Williams LP, Watson JC, Fleming DW (1990) Eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with exposure to tryptophan from a single manufacturer. JAMA 264: 213–217
Smith MJ, Mazzola EP, Farrell TJ, Sphon JA, Page SW, Ashley D, Sirimanne SR, Hill RH, Needham LL (1991) 1−1′-Ethylidenebis(l-tryptophan), structure determination of contaminant “97”-Implicated in the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome (EMS). Tetrahedron Lett 32: 991–994
Toyo’oka T, Yamazaki T, Tanimoto T, Sato K, Sato M, Toyoda M, Ishibashi M, Yoshihira K, Uchiyama M (1991) Characterization of contaminants in EMS-associated l-tryptophan samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. Chem Pharm Bull 39: 820–822
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adachi, J., Gomez, M., Smith, C.C. et al. Accumulation of 3-(phenylamino)alanine, a constituent in l-tryptophan products implicated in eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome, in blood and organs of the Lewis rats. Arch Toxicol 69, 266–270 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050169
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050169