Abstract
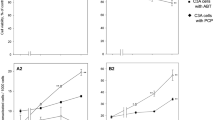
Cytochrome P450IA1 (CYP1A1) induction of Hepa-1 mouse and H4IIE rat hepatoma cell lines was compared using selected environmental samples. The results were in agreement for both cell lines: no induction was observed for the fly ash extract from peat combustion, an intermediate induction was found for the fly ash extract from biosludge combustion, and a strong induction was detected for natural peat extract. However, Hepa-1 responded to the samples more sensitively than did H4IIE: the half maximal induction (ED50) values for Hepa-1 were smaller than those for H4IIE. In a bacterial DNA repair assay without metabolic activation and in a mammalian sister chromatid exchange test in the presence of metabolic activation the samples were virtually non-genotoxic. Thus the CYP1A1-inducing potency and genotoxicity of the samples were not correlated. In light of these results, the CYP1A1 induction test might be a useful addition to conventional genotoxicity tests, which may fail to detect potentially harmful compounds/mixtures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborg UG, Brouwer A, Fingerhut MA, Jacobson JL, Jacobson SW, Kennedy SW, Kettrup AAF, Koeman JH, Poiger H, Rappe C, Safe SH, Seegal RF, Tuomisto J, van den Berg M (1992) Impact of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls on human and environmental health, with special emphasis on application of the toxic equivalency factor concept. Eur J Pharmacol 228: 179–199
Arey J, Harger WP, Helmig D, Atkinson R (1992) Bioassay-directed fractionation of mutagenic PAH atmospheric photooxidation products and ambient particulate extracts. Mutat Res 281: 67–76
Ashby J (1992) Use of short-term tests in determining the genotoxicity or nongenotoxicity of chemicals. In: Vainio H, Magee PN, McGregor DB, McMichael AJ (eds) Mechanism of carcinogenesis in risk identification. IARC Sci Publ, no 116, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 135–164
Bernhard HP, Darlington GJ, Ruddle FJ (1973) Expression of liver phenotypes in cultured mouse hepatoma cells: synthesis and secretion of serum albumin. Dev Biol 35: 83–96
Buser H-R (1975) Analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans in chlorinated phenols by mass fragmentography. J Chromatogr 107: 295–310
Carrier F, Owens RA, Nebert DW, Puga A (1992) Dioxin-dependent activation of murineCyp1a-1 gene transcription requires protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol 12: 1856–1863
Chou MW, Wang B, von Tungeln LS, Beland FA, Fu PP (1987) Induction of rat hepatic cytochromes P-450 by environmental nitropolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 2449–2454
Ewetz L, Camner P (1983) (eds) Health risks resulting from exposure to motor vehicle exhaust. A report to the Swedish Government Committee on Automotive Air Pollution, National Swedish Institute of Environmental Medicine, Stockholm, p 203
Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Imataka H, Sogawa K, Yasumoto K-I, Kikuchi Y (1992) Regulation ofCYP1A1 expression. FASEB J 6: 706–710
Goldstein JA, Safe S (1989) Mechanism of action and structure-activity relationships for the chlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and related compounds. In: Kimbrough RD, Jensen AA (eds) Halogenated biphenyls, terphenyls, naphthalenes, dibenzodioxins and related products. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 239–293.
Hanberg A, Ståhlberg M, Georgellis A, de Wit C, Ahlborg UG (1991) Swedish dioxin survey: evaluation of the H-4-II E bioassay for screening environmental samples for dioxin-like enzyme induction. Pharmacol Toxicol 69: 442–449
Hankinson O (1979) Single-step selection of clones of a mouse hepatoma line deficient in aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 373–376
Hankinson O (1980) Unstable aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase-deficient variants of a rat hepatoma line. Somat Cell Genet 6: 751–767
Hankinson O, Brooks BA, Weir-Brown KI, Hoffman EC, Johnson BS, Nanthur J, Reyes H, Watson AJ (1991) Genetic and molecular analysis of the Ah receptor andCyp1a1 gene expression. Biochimie 73: 61–66
Harris WR, Remsen JF, Chess EK, Later DW (1987) Correlation of nitroaromatic compounds with the mutagenic activity of coal fly ash. J Toxicol Environ Health 20: 81–103
Helmig D, Arey J, Harger WP, Atkinson R, Lopez-Cancio J (1992) Formation of mutagenic nitrobenzopyranones and their occurrence in ambient air. Environ Sci Technol 26: 622–624
Houk VS, Goto S, Endo O, Claxton LD, Lewtas J, Matsushita H (1992) Detection of direct-acting mutagens in ambient-air: a comparison of two highly sensitive mutagenicity assays. Environ Mol Mutagen 20: 19–28
Ioannides C (1990) Induction of cytochrome P450I and its influences in chemical carcinogenesis. Biochem Soc Trans 18: 32–34
Ioannides C, Parke DV (1987) The cytochromes P-448 — a unique family of enzymes involved in chemical toxicity and carcinogenesis. Biochem Pharmacol 36: 4197–4207
Kärenlampi S (1987) Mechanism of cytotoxicity of aflatoxin B1: role of cytochrome P1-450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 145: 854–860
Kärenlampi S, Törrönen R (1990) Induction of cytochrome P450IA1 in mouse hepatoma cells as a short-term bioassay. ATLA 17: 158–162
Kärenlampi SO, Tuomi K, Korkalainen M, Raunio H (1989) Induction of cytochrome P450IA1 in mouse hepatoma cells by several chemicals. Phenobarbital and TCDD induce the same form of cytochrome P450. Biochem Pharmacol 38: 1517–1525
Kopponen P, Törrönen R, Tarhanen J, Ruuskanen J, Kärenlampi S (1991) Cytochrome P450IA1 induction in mouse hepatoma cell culture as an indicator of polycyclic organic compounds in fly ash. Chemosphere 22: 895–904
Kopponen P, Mannila E, Kärenlampi S (1992a) Induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase AHH by two previously uncharacterized pentachlorinated biphenyls in a mouse and a rat hepatoma cell line. Chemosphere 24: 201–210
Kopponen P, Törrönen R, Ruuskanen J, Tarhanen J, Vartiainen T, Kärenlampi S (1992b) Comparison of cytochrome P450IA1 induction with the chemical composition of fly ash from combustion of chlorine containing material. Chemosphere 24: 391–401
Kopponen P, Tarhanen J, Ruuskanen J, Törrönen R, Kärenlampi S (1993) Peat induces cytochrome P450IA1 in Hepa-1 cell line. Comparison with fly ashes from combustion of peat, coal, heavy fuel oil and hazardous waste. Chemosphere 26: 1499–1506
Landers JP, Bunce NJ (1991) TheAh receptor and the mechanism of dioxin toxicity. Biochem J 276: 273–287
Lewtas J (1989) Emerging methodologies for assessment of complex mixtures: application of bioassays in the integrated air cancer project. Toxicol Ind Health 5: 839–850
Lipp H-P, Schrenk D, Wiesmüller T, Hagenmaier H, Bock KW (1992) Assessment of biological activities of mixtures of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (PCDDs) and their constituents in human HepG2 cells. Arch Toxicol 66: 220–223
Lucier GW (1992) Receptor-mediated carcinogenesis. In: Vainio H, Magee PN, McGregor DB, McMichael AJ (eds) Mechanisms of carcinogenesis in risk identification. IARC Sci Publ, vol 116, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 87–112
Löfroth G, Toftgård R, Nilsson L, Agurell E, Gustafsson J-Å (1984) Short-term bioassays of nitro derivates of benzo[a]pyrene and perylene. Carcinogenesis 5: 925–930
Maron DM, Ames BN (1983) Revised methods for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat Res 113: 173–215
Merchant M, Wang X, Kamps C, Rosengren R, Morrison V, Safe S (1992) Mechanism of benzo[a]pyrene-inducedCyp1a-1 gene expression in mouse Hepa 1c1c7 cells: role of the nuclear 6 s and 4 s proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys 292: 250–257
Nebert DW (1989) TheAh locus: genetic differences in toxicity, cancer, mutation, and birth defects. Crit Rev Toxicol 20: 153–174
Perdew GH (1992) Chemical cross-linking of the cytosolic and nuclear forms of theAh receptor in hepatoma cell line 1c1c7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 182: 55–62
Pongratz I, Mason GGF, Poellinger L (1992) Dual roles of the 90-kDa heat shock protein hsp90 in modulating functional activities of the dioxin receptor. Evidence that the dioxin receptor functionally belongs to a subclass of nuclear receptors which require hsp90 both for ligand binding activity and repression of intrinsic DNA binding activity. J Biol Chem 267: 13728–13734
Rappe C, Buser HR (1989) Chemical and physical properties, analytical methods, sources and environmental levels of halogenated dibenzodioxins and dibenzofurans. In: Kimbrough RD, Jensen AA (eds) Halogenated biphenyls, terphenyls, naphthalenes, dibenzodioxins and related products. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 71–102
Safe S (1989) Risk assessment of PCDDs and PCDFs based on in vitro and in vivo bioassays. Chemosphere 19: 609–613
Safe S (1990) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBS), dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs), dibenzofurans (PCDFs), and related compounds: environmental and mechanistic considerations which support the development of toxic equivalency factors (TEFs). Crit Rev Toxicol 21: 51–88
Safe S, Mason G, Farrell K, Keys B, Piskorska-Pliszczynska J, Madge JA, Chittim B (1987) Validation of in vitro bioassays for 2,3,7,8-TCDD equivalents. Chemosphere 16: 1723–1728
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, Book 3, A. 3. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, USA
Schaefer EL, Au WW, Selkirk JK (1985) Differential induction of sister-chromatid exchanges by benzo[a]pyrene in variant mouse hepatoma cells. Mutat Res 143: 69–74
Schrenk D, Lipp H-P, Wiesmüller T, Hagenmaier H, Bock KW (1991) Assessment of biological activities of mixtures of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin: comparison between defined mixtures and their constituents. Arch Toxicol 65: 114–118
Silbergeld EK, Gasiewicz TA (1989) Dioxins and the Ah receptor. Am J Ind Med 16: 455–474
Silkowski MA, Smith SR, Plewa MJ (1992) Analysis of the genotoxicity of municipal solid waste incinerator ash. Sci Total Environ 111: 109–124
Skene SA, Dewhurst IC, Greenberg M (1989) Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans: the risks to human health. Hum Toxicol 8: 173–203
Tillitt DE, Giesy JP, Ankley GT (1991) Characterization of the H4IIE rat hepatoma cell bioassay as a tool for assessing toxic potency of planar halogenated hydrocarbons in environmental samples. Environ Sci Technol 25: 87–92
Turteltaub KW, Felton JS, Gledhill BL, Vogel JS, Southon JR, Caffee MW, Finkel RC, Nelson DE, Proctor ID, Davis JC (1990) Accelerator mass spectrometry in biomedical dosimetry: relationship between low-level exposure and covalent binding of heterocyclic amine carcinogens to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 5288–5292
Tweats DJ, Green HHL, Muriel W (1981) A differential killing assay for mutagens and carcinogens based on an improved repair-deficient strain ofEscherichia coli. Carcinogenesis 2: 189–194
Watson AJ, Hankinson O (1992) Dioxin- andAh receptor-dependent protein binding to xenobiotic responsive elements and G-rich DNA studied by in vivo footprinting. J Biol Chem 266: 6874–6878
von Wright A, Raatikainen O, Taipale H, Kärenlampi S, Mäki-Paakkanen J (1992) Directly acting geno- and cytotoxic agents from a wild mushroomDermocybe sanguinea. Mutat Res 269: 27–33
Wu L, Whitlock Jr JP (1992) Mechanism of dioxin action: Ah receptor-mediated increase in promoter accessibility in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89: 4811–4815
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopponen, P., Törrönen, R., Mäki-Paakkanen, J. et al. Comparison of CYP1A1 induction and genotoxicity in vitro as indicators of potentially harmful effects of environmental samples. Arch Toxicol 68, 167–173 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050050
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050050