Abstract.
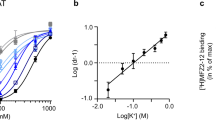
The uptake of norsalsolinol, a neurotoxin candidate causing parkinsonism-like symptoms, was studied in PC12 cells. The compound was actively taken up by the PC12 cells, with a K m value of 176.2±9.1 µM and a maximum velocity of 55.6±7.0 pmol/min per mg protein; norsalsolinol uptake was dependent on the presence of extracellular Na+. The uptake of norsalsolinol was sensitive to two dopamine transporter inhibitors, GBR-12909 and reserpine, but was less sensitive to desipramine, a noradrenaline transporter inhibitor. Dopamine competitively inhibited norsalsolinol uptake into PC12 cells with a K i value of 271.2±61.6 µM. These results suggest that norsalsolinol is taken up into PC12 cells mainly by the dopamine transporter.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruyama, .Y., Suzuki, .Y., Kazusaka, .A. et al. Uptake of the dopaminergic neurotoxin, norsalsolinol, into PC12 cells via dopamine transporter. Arch Toxicol 75, 209–213 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000202
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040000202