Abstract
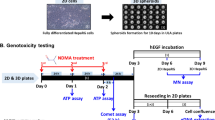
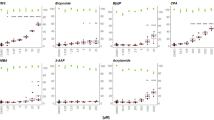
N-nitrosamine impurities have been increasingly detected in human drugs. This is a safety concern as many nitrosamines are mutagenic in bacteria and carcinogenic in rodent models. Typically, the mutagenic and carcinogenic activity of nitrosamines requires metabolic activation by cytochromes P450 enzymes (CYPs), which in many in vitro models are supplied exogenously using rodent liver homogenates. There are only limited data on the genotoxicity of nitrosamines in human cell systems. In this study, we used metabolically competent human HepaRG cells, whose metabolic capability is comparable to that of primary human hepatocytes, to evaluate the genotoxicity of eight nitrosamines [N-cyclopentyl-4-nitrosopiperazine (CPNP), N-nitrosodibutylamine (NDBA), N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA), N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), N-nitrosodiisopropylamine (NDIPA), N-nitrosoethylisopropylamine (NEIPA), N-nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutyric acid (NMBA), and N-nitrosomethylphenylamine (NMPA)]. Under the conditions we used to culture HepaRG cells, three-dimensional (3D) spheroids possessed higher levels of CYP activity compared to 2D monolayer cells; thus the genotoxicity of the eight nitrosamines was investigated using 3D HepaRG spheroids in addition to more conventional 2D cultures. Genotoxicity was assessed as DNA damage using the high-throughput CometChip assay and as aneugenicity/clastogenicity in the flow-cytometry-based micronucleus (MN) assay. Following a 24-h treatment, all the nitrosamines induced DNA damage in 3D spheroids, while only three nitrosamines, NDBA, NDEA, and NDMA, produced positive responses in 2D HepaRG cells. In addition, these three nitrosamines also caused significant increases in MN frequency in both 2D and 3D HepaRG models, while NMBA and NMPA were positive only in the 3D HepaRG MN assay. Overall, our results indicate that HepaRG spheroids may provide a sensitive, human-based cell system for evaluating the genotoxicity of nitrosamines.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Beard JC, Swager TM (2021) An organic chemist’s guide to n-nitrosamines: their structure, reactivity, and role as contaminants. J Org Chem 86(3):2037–2057. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.0c02774
Bharate SS (2021) Critical analysis of drug product recalls due to nitrosamine impurities. J Med Chem 64(6):2923–2936. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c02120
Bogovski P, Bogovski S (1981) Animal species in which N-Nitroso compounds induce cancer. Int J Cancer 27(4):471–474. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.2910270408
Bradley MO, Dysart G, Fitzsimmons K, Harbach P, Lewin J, Wolf G (1982) Measurements by filter elution of DNA single- and double-strand breaks in rat hepatocytes: effects of nitrosamines and gamma-irradiation. Cancer Res 42(7):2592–2597
Brambilla G, Cavanna M, Pino A, Robbiano L (1981) Quandtitative correlation among DNA damaging potency of six N-nitroso compounds and their potency in inducing tumor growth an bacterial mutations. Carcinogenesis 2(5):425–429. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/2.5.425
Camus AM, Geneste O, Honkakoski P et al (1993) High variability of nitrosamine metabolism among individuals: role of cytochromes P450 2A6 and 2E1 in the dealkylation of N-nitrosodimethylamine and N-nitrosodiethylamine in mice and humans. Mol Carcinog 7(4):268–275. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.2940070410
Cross KP, Ponting DJ (2021) Developing structure-activity relationships for N-nitrosamine activity. Comp Toxicol. 20:100186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comtox.2021.100186
Duivenvoorde LPM, Louisse J, Pinckaers NET, Nguyen T, van der Zande M (2021) Comparison of gene expression and biotransformation activity of HepaRG cells under static and dynamic culture conditions. Sci Rep 11(1):10327. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89710-6
ECHA (2023) C&L Inventory.https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals/cl-inventory-database Accessed 1 May 2023
FDA (2021) Control of nitrosamine impurities in human drugs. US Food and Drug Administration https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/control-nitrosamine-impurities-human-drugs Accessed 1 May 2023
Fujita K, Kamataki T (2001) Role of human cytochrome P450 (CYP) in the metabolic activation of N-alkylnitrosamines: application of genetically engineered Salmonella typhimurium YG7108 expressing each form of CYP together with human NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Mutat Res 483(1–2):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00223-8
Gold B, Farber J, Rogan E (1987) An investigation of the metabolism of N-nitroso-N-methylaniline by phenobarbital- and pyrazole-induced Sprague-Dawley rat liver and esophagus derived S-9. Chem Biol Interact 61(3):215–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2797(87)90002-0
Guo X, Mei N (2018) Benchmark dose modeling of in vitro genotoxicity data: a reanalysis. Toxicol Res 34(4):303–310. https://doi.org/10.5487/TR.2018.34.4.303
Guo X, Seo JE, Li X, Mei N (2020a) Genetic toxicity assessment using liver cell models: past, present, and future. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 23(1):27–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2019.1692744
Guo X, Seo JE, Petibone D et al (2020b) Performance of HepaRG and HepG2 cells in the high-throughput micronucleus assay for in vitro genotoxicity assessment. J Toxicol Environ Health A 83(21–22):702–717. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2020.1822972
Gushgari AJ, Halden RU (2018) Critical review of major sources of human exposure to N-nitrosamines. Chemosphere 210:1124–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.07.098
Hammour MM, Othman A, Aspera-Werz R et al (2022) Optimisation of the HepaRG cell line model for drug toxicity studies using two different cultivation conditions: advantages and limitations. Arch Toxicol 96(9):2511–2521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03329-8
Hardy A, Benford D, EFSA SC et al (2017) Update: use of the benchmark dose approach in risk assessment. EFSA J 15(1):e04658. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4658
Horne S, Vera MD, Nagavelli LR et al (2023) Regulatory experiences with root causes and risk factors for nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals. J Pharm Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2022.12.022
IARC (1978) Some N-nitroso compounds. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 17:125–176. https://publications.iarc.fr/35 Accessed 1 May 2023
ICH (2023) M7(R2) Assessment and control of DNA reactive (mutagenic) impurities in pharmaceuticals to limit potential carcinogenic risk.:https://www.ich.org/page/multidisciplinary-guidelines#7-2 Accessed 1 May 2023
Inami K, Yasui H, Tsugumi H, Ishikawa S, Mochizuki M (2013) Oxidation of N-Alkyl-N-(3-carboxypropyl) nitrosamines by iron porphyrin and oxidant forms alkylating mutagens. Genes Environ 35(4):99–104. https://doi.org/10.3123/jemsge.2013.010
Janzowski C, Jacob D, Henn I, Zankl H, Poole-Zobel BL, Eisenbrand G (1989) Investigations on organ-specific metabolism and genotoxic effects of the urinary bladder carcinogen N-nitrosobutyl-3-carboxypropylamine (BCPN) and its analogs N-nitrosodibutylamine (NDBA) and N-nitrosobutyl-4-hydroxybutylamine (4-OH-NDBA). Toxicology 59(2):195–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/0300-483x(89)90057-7
Janzowski C, Landsiedel R, Gölzer P, Eisenbrand G (1994) Mitochondrial formation of beta-oxopropyl metabolites from bladder carcinogenic omega-carboxyalkylnitrosamines. Chem Biol Interact 90(1):23–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2797(94)90108-2
Johnson GE, Yamamoto M, Suzuki Y et al (2016) Measuring reproducibility of dose response data for the Pig-a assay using covariate benchmark dose analysis. Mutat Res, Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 811:135–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2016.04.004
Johnson GE, Dobo K, Gollapudi B et al (2021) Permitted daily exposure limits for noteworthy N-nitrosamines. Environ Mol Mutagen 62(5):293–305. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.22446
Kao YT, Wang SF, Wu MH et al (2022) A substructure-based screening approach to uncover N-nitrosamines in drug substances. J Food Drug Anal 30(1):150–162. https://doi.org/10.38212/2224-6614.3400
Krewski D, Acosta D Jr, Andersen M et al (2010) Toxicity testing in the 21st century: a vision and a strategy. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 13(2–4):51–138. https://doi.org/10.1080/10937404.2010.483176
Lee M, Ishizaki H, Brady JF, Yang CS (1989) Substrate specificity and alkyl group selectivity in the metabolism of N-nitrosodialkylamines. Cancer Res 49(6):1470–1474
Li Y, Hecht SS (2022) Metabolic activation and DNA interactions of carcinogenic N-nitrosamines to which humans are commonly exposed. Int J Mol Sci 23(9):4559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094559
Li X, He X, Le Y et al (2022) Genotoxicity evaluation of nitrosamine impurities using human TK6 cells transduced with cytochrome P450s. Arch Toxicol 96(11):3077–3089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03347-6
Lijinsky W, Taylor HW (1979) Carcinogenicity of methylated derivatives of N-nitrosodiethylamine and related compounds in sprague-dawley rats2. J Nat Cancer Inst. 62(2):407–410. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/62.2.407
Lijinsky W, Reuber MD, Saavedra JE, Singer GM (1983) Carcinogenesis in F344 rats by N-nitrosomethyl-n-propylamine derivatives. J Natl Cancer Inst 70(5):959–963
Marchetti F, Cardoso R, Chen CL et al (2023) Error-corrected next-generation sequencing to advance nonclinical genotoxicity and carcinogenicity testing. Nat Rev Drug Discov. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41573-023-00014-y
OECD (2015) Guidance document on revisions to OECD genetic toxicology test guidelines. OECD Workgroup of National Coordinators for Test 42 Guidelines (WNT) https://www.oecd.org/env/ehs/testing/Draft%20Guidance%20Document%20on%20OECD%20Genetic%20Toxicology%20Test%20Guidelines.pdf Accessed 1 May 2023
OECD (2016) Test No. 487: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4, OECD Publishing, Paris https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264264861-en: Accessed 1 May 2023
Peto R, Gray R, Brantom P, Grasso P (1991) Effects on 4080 rats of chronic ingestion of N-nitrosodiethylamine or N-nitrosodimethylamine: a detailed dose-response study. Cancer Res 51(23):6415–6451
Schmidtsdorff S, Neumann J, Schmidt AH, Parr MK (2022) Risk assessment for nitrosated pharmaceuticals: a future perspective in drug development. Arch Pharm 355(4):e2100435. https://doi.org/10.1002/ardp.202100435
Schrenk D, Bignami M, Bodin L et al (2023) Risk assessment of N-nitrosamines in food. Efsa J 21(3):e07884. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2023.7884
Seo JE, Tryndyak V, Wu Q et al (2019) Quantitative comparison of in vitro genotoxicity between metabolically competent HepaRG cells and HepG2 cells using the high-throughput high-content CometChip assay. Arch Toxicol 93(5):1433–1448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02406-9
Seo JE, Wu Q, Bryant M et al (2020) Performance of high-throughput CometChip assay using primary human hepatocytes: a comparison of DNA damage responses with in vitro human hepatoma cell lines. Arch Toxicol 94(6):2207–2224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02736-z
Seo JE, He X, Muskhelishvili L et al (2022) Evaluation of an in vitro three-dimensional HepaRG spheroid model for genotoxicity testing using the high-throughput CometChip platform. Altex 39(4):583–604. https://doi.org/10.14573/altex.2201121
Seo JE, Li X, Le Y, Mei N, Zhou T, Guo X (2023) High-throughput micronucleus assay using three-dimensional HepaRG spheroids for in vitro genotoxicity testing. Arch Toxicol 97(4):1163–1175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03461-z
Shu L, Hollenberg PF (1996) Identification of the cytochrome P450 isozymes involved in the metabolism of N-nitrosodipropyl-, N-nitrosodibutyl- and N-nitroso-n-butyl-n-propylamine. Carcinogenesis 17(4):839–848. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/17.4.839
Thresher A, Foster R, Ponting DJ, Stalford SA, Tennant RE, Thomas R (2020) Are all nitrosamines concerning? A review of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity data. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 116:104749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104749
Vanoye-Carlo A, Gutiérrez-Ospina G, Marcial-Quino J et al (2015) Analysis of Cyp2b1 gene expression in the rat liver and brain by multiplex PCR. Mol Cell Toxicol 11(4):407–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-015-0043-1
WHO (2019) Update on nitrosamine impurities. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/news/item/20-11-2019-information-note-nitrosamine-impurities: Accessed 1 May 2023
WHO (2022) Nitrosamine concerns in rifapentine products - Update. https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/news/nitrosamine-concerns-rifapentine-products-update Accessed 1 May 2023
Yamazaki H, Inui Y, Yun CH, Guengerich FP, Shimada T (1992) Cytochrome P450 2E1 and 2A6 enzymes as major catalysts for metabolic activation of N-nitrosodialkylamines and tobacco-related nitrosamines in human liver microsomes. Carcinogenesis 13(10):1789–1794. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/13.10.1789
Zielenska M, Guttenplan JB (1988) Mutagenic activity and specificity of N-nitrosomethylaniline and N-nitrosodiphenylamine in Salmonella. Mutat Res 202(1):269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/0027-5107(88)90189-3
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by funding from the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Regulatory Science Research program. HX was supported by an appointment to the Postgraduate Research Program and JY was supported by an appointment to the Summer Student Research Program; both programs are administered for CDER by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science Education through an interagency agreement between the U.S. Department of Energy and the U.S. FDA. We thank Drs. David Keire, Robert Dorsam, Sruthi King, Naomi Kruhlak from CDER for their valuable comments regarding nitrosamine impurities and Drs. Tao Chen and Li-Rong Yu from NCTR for their critical review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article reflects the views of the authors and does not necessarily reflect those of the US. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Any mention of commercial products is for clarification only and is not intended as approval, endorsement, or recommendation.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, JE., Yu, J.Z., Xu, H. et al. Genotoxicity assessment of eight nitrosamines using 2D and 3D HepaRG cell models. Arch Toxicol 97, 2785–2798 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03560-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03560-x