Abstract
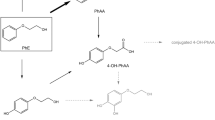
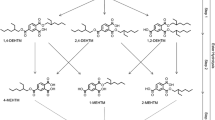
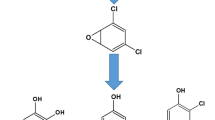
2,4,7,9-Tetramethyl-5-decyne-4,7-diol (TMDD) is a non-ionic surfactant with a wide range of applications. TMDD is considered a high-production chemical and, due to its low biodegradation rate, possesses a potentially high prevalence in the environment. However, despite its widespread use, toxicokinetic data and data on internal exposure to TMDD in the general population are completely lacking. Hence, we developed a human biomonitoring (HBM) method for TMDD. Our approach included a metabolism study with four subjects, who were administered an oral dose of 75 µg TMDD/kg body weight and a dermal dose of 750 µg/kg body weight. Terminal methyl-hydroxylated TMDD (1-OH-TMDD) was previously identified as the main urinary metabolite in our lab. The results of the oral and dermal applications were used to determine the toxicokinetic parameters of 1-OH-TMDD as a biomarker of exposure. Finally, the method was applied to 50 urine samples from non-occupationally exposed volunteers. Results show that TMDD was rapidly metabolized, with an average tmax of 1.7 h and a rapid and almost complete (96%) excretion of 1-OH-TMDD until 12 h after oral dosage. Elimination was bi-phasic, with half-lives of 0.75–1.6 h and 3.4–3.6 h for phases 1 and 2, respectively. The dermal application resulted in a delayed urinary excretion of this metabolite with a tmax of 12 h and complete excretion after about 48 h. The excreted amounts of 1-OH-TMDD represented 18% of the orally administered TMDD dose. The data of the metabolism study demonstrated a fast oral as well as substantial dermal resorption of TMDD. Moreover, the results indicated an effective metabolism of 1-OH-TMDD, which is excreted rapidly and completely via urine. Application of the method to 50 urine samples revealed a quantification rate of 90%, with an average concentration of 0.19 ng/mL (0.97 nmol/g creatinine). With the urinary excretion factor (Fue) derived from the metabolism study, we estimated an average daily intake of 1.65 µg TMDD from environmental and dietary sources. In conclusion, 1-OH-TMDD in urine is a suitable biomarker of exposure to TMDD and can be applied for biomonitoring of the general population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barr DB, Wilder LC, Caudill SP, Gonzalez AJ, Needham LL, Pirkle JL (2005) Urinary creatinine concentrations in the US population: implications for urinary biologic monitoring measurements. Environmental health perspectives:192–200
Blaszkewicz M, Liesenhoff-Henze K (2010) Creatinine in urine. In: (DFG) GRF (Eds) The MAK-Collection: Biomonitoring Methods. Volume 10 edn. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, p 169–184
Camacho-Munoz D, Martin J, Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2014) Occurrence of surfactants in wastewater: hourly and seasonal variations in urban and industrial wastewaters from Seville (Southern Spain). Sci Total Environ 468–469:977–984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.020
ECHA (2022) 2,4,7,9-tetramethyldec-5-yne-4,7-diol. In. https://echa.europa.eu/de/brief-profile/-/briefprofile/100.004.373
EPA (2006) Inert ingredient reassessment of 2,4,7,9-tetramethyl-5-decyne-4,7-diol (TMDD).
European chemicals agency (ECHA) (2020) Substance information 2,4,7,9-tetramethyldec-5-yne-4,7-diol, TMDD. In. https://echa.europa.eu/de/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.004.373
European chemicals agency (ECHA) (2022) Substance information 2,4,7,9-tetramethyldec-5-yne-4,7-diol, TMDD. In. https://echa.europa.eu/de/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/14379/7/6/1
Félix JS, Isella F, Bosetti O, Nerín C (2012) Analytical tools for identification of non-intentionally added substances (NIAS) coming from polyurethane adhesives in multilayer packaging materials and their migration into food simulants. Anal Bioanal Chem 403(10):2869–2882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5965-z
Guedez AA, Püttmann W (2014) Printing ink and paper recycling sources of TMDD in wastewater and rivers. Sci Total Environ 468–469:671–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.046
Guedez AA, Frömmel S, Diehl P, Püttmann W (2010) Occurrence and temporal variations of TMDD in the river Rhine, Germany. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 17(2):321–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0191-8
Höllerer C, Becker G, Göen T, Eckert E (2018) Human metabolism and kinetics of tri-(2-ethylhexyl) trimellitate (TEHTM) after oral administration. Arch Toxicol 92(9):2793–2807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2264-2
Kessler W, Numtip W, Volkel W et al (2012) Kinetics of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) and mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in blood and of DEHP metabolites in urine of male volunteers after single ingestion of ring-deuterated DEHP. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 264(2):284–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2012.08.009
Klotz U (1978) Klinische pharmakokinetik von diazepam und seinen biologisch aktiven metaboliten. Klin Wochenschr 56(18):895–904. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01489215
Koch HM, Becker K, Wittassek M, Seiwert M, Angerer J, Kolossa-Gehring M (2006) Di-n-butylphthalate and butylbenzylphthalate - urinary metabolite levels and estimated daily intakes: pilot study for the German environmental survey on children. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 17:378–87
Lermen D, Bartel-Steinbach M, Gwinner F et al (2019) Trends in characteristics of 24-h urine samples and their relevance for human biomonitoring studies - 20years of experience in the German environmental specimen bank. Int J Hyg Environ Health 222(5):831–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2019.04.009
Otto A, du Plessis J, Wiechers JW (2009) Formulation effects of topical emulsions on transdermal and dermal delivery. Int J Cosmet Sci 31(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2494.2008.00467.x
Ringbeck B, Belov VN, Schmidtkunz C et al (2021) Human metabolism and urinary excretion kinetics of nonylphenol in three volunteers after a single oral dose. Chem Res Toxicol 34(11):2392–2403. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00301
Roegner N, Pluym N, Peschel O et al (2023) Determination of a specific metabolite for the non-ionic surfactant 2,4,7,9-tetramethyl-5-decyne-4,7-diol (TMDD) by UPLC-MS/MS. J chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 1216:123584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2022.123584
Sasso AF, Pirow R, Andra SS et al (2020) Pharmacokinetics of bisphenol a in humans following dermal administration. Environ Int 144:106031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106031
Scherer M, Koch HM, Schutze A et al (2016) Human metabolism and excretion kinetics of the fragrance lysmeral after a single oral dosage. Int J Hyg Environ Health 220(2):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2016.09.005
Stoeckelhuber M, Krnac D, Pluym N et al (2018) Human metabolism and excretion kinetics of the fragrance 7-hydroxycitronellal after a single oral or dermal dosage. Int J Hyg Environ Health 221(2):239–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2017.10.015
Stoeckelhuber M, Pluym N, Bracher F, Leibold E, Scherer G, Scherer M (2019) A validated UPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of urinary metabolites of Uvinul® A plus. Anal Bioanal Chem 411:8143–8152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-019-02201-6
Stoeckelhuber M, Scherer M, Bracher F et al (2020a) Development of a human biomonitoring method for assessing the exposure to ethoxyquin in the general population. Arch Toxicol 94(12):4209–4217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02871-7
Stoeckelhuber M, Scherer M, Peschel O et al (2020) Human metabolism and urinary excretion kinetics of the UV filter Uvinul A plus(R) after a single oral or dermal dosage. Int J Hyg Environ Health 227:113509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113509
Verband der chemischen Industrie e.V. (2016) Überblick zur Kooperation von BMUB und VCI beim Thema Human-Biomonitoring. In. https://www.vci.de/themen/chemikaliensicherheit/human-biomonitoring/ueberblick-kooperation-vci-bmub-human-biomonitoring-gesundheit-produktverantwortung.jsp Accessed 30.05.2017 2017
Vincze K, Gehring M, Braunbeck T (2014) (Eco)toxicological effects of 2,4,7,9-tetramethyl-5-decyne-4,7-diol (TMDD) in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and permanent fish cell cultures. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21(13):8233–8241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2806-y
Wiest L, Giroud B, Assoumani A, Lestremau F, Vulliet E (2021) A multi-family offline SPE LC-MS/MS analytical method for anionic, cationic and non-ionic surfactants quantification in surface water. Talanta 232:122441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122441
Funding
This study was funded by the Chemie Wirtschaftsförderungsgesellschaft, Frankfurt/Main, Germany. The method was developed as part of a 10-year human biomonitoring initiative between the Federal Ministry for Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) and the Verband der chemischen Industrie e.V. (German Chemical Industry Association (VCI)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Except for EL, the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. EL is working for a company using TMDD in part of their products in the past.
Ethical approval
Studies with human subjects were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Bayerische Landesärztekammer (registration number 17076), Munich, Germany in accordance with ethical standards laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki from 1964 and its later amendments. All subjects gave their informed written consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pluym, N., Roegner, N., Peschel, O. et al. Human metabolism and excretion kinetics of the surfactant 2,4,7,9-tetramethyl-5-decyne-4,7-diol (TMDD) after oral and dermal administration. Arch Toxicol 97, 2419–2428 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03547-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03547-8