Abstract
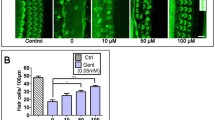
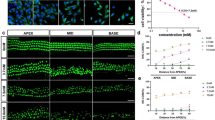
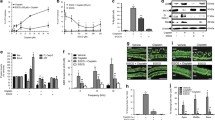
The ototoxic side effect of cisplatin is a main cause of sensorineural hearing loss. This side effect limits the clinical application of cisplatin and affects patients’ quality of life. This study was designed to investigate the effect of apelin-13 on cisplatin-induced C57BL/6 mice hearing loss model and explore the potential underlying molecular mechanisms. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with 100 μg/kg apelin-13 2 h before 3 mg/kg cisplatin injection for 7 consecutive days. Cochlear explants cultured in vitro were pretreated with 10 nM apelin-13 2 h prior to 30 μM cisplatin treatment for another 24 h. Hearing test and morphology results showed that apelin-13 attenuated cisplatin-induced mice hearing loss and protected cochlear hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons from damage. In vivo and in vitro experimental results showed that apelin-3 reduced cisplatin-induced apoptosis of hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons. In addition, apelin-3 preserved mitochondrial membrane potential and inhibited ROS production in cultured cochlear explants. Mechanistic studies showed that apelin-3 decreased cisplatin-induced cleaved caspase 3 expression but increased Bcl-2; inhibited the expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-a and IL-6; and increased STAT1 phosphorylation but decreased STAT3 phosphorylation. In conclusion, our results indicate that apelin-13 could be a potential otoprotective agent to prevent cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis, ROS production, TNF-α and IL-6 expression, and regulating phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3 transcription factors.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
Abbreviations
- STAT1:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- HCs:
-
Hair cells
- SGNs:
-
Spiral ganglion neurons
- ABR:
-
Auditory brainstem response
- HE:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin staining
- TUNEL:
-
TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- P-STAT1:
-
Phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 1
- P-STAT3:
-
Phosphorylated signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- MAPK/Akt:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase/ protein kinase B
References
Bhatta P, Dhukhwa A, Sheehan K et al (2019) Capsaicin protects against cisplatin ototoxicity by changing the STAT3/STAT1 ratio and activating cannabinoid (CB2) receptors in the cochlea. Sci Rep 9:4131. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40425-9
Bircan B, Cakir M, Kirbag S, Gul HF (2016) Effect of apelin hormone on renal ischemia/reperfusion induced oxidative damage in rats. Ren Fail 38:1122–1128. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2016.1184957
Borse V, Al Aameri RFH, Sheehan K et al (2017) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a prototypic chemopreventative agent for protection against cisplatin-based ototoxicity. Cell Death Dis 8:e2921. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.314
Butturini E, Cozzolino F, Boriero D et al (2018) S-glutathionylation exerts opposing roles in the regulation of STAT1 and STAT3 signaling in reactive microglia. Free Radic Biol Med 117:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.02.005
Butturini E, Carcereri de Prati A, Mariotto S (2020) Redox regulation of STAT1 and STAT3 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21197034
Dhillon S (2023) Sodium THIOSULFATE: PEDIATRIC FIRST APPROVAl. Paediatr Drugs 25:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-022-00550-x
Falcao-Pires I, Leite-Moreira AF (2005) Apelin: a novel neurohumoral modulator of the cardiovascular system. Pathophysiologic importance and potential use as a therapeutic target. Rev Port Cardiol 24:1263–1276
Febles NK, Bauer MA, Ding B, Zhu X, Gallant ND, Frisina RD (2022) A combinatorial approach to protect sensory tissue against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Hear Res 415:108430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2022.108430
Gentilin E, Simoni E, Candito M, Cazzador D, Astolfi L (2019) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: updates on molecular targets. Trends Mol Med 25:1123–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2019.08.002
Habata Y, Fujii R, Hosoya M et al (1999) Apelin, the natural ligand of the orphan receptor APJ, is abundantly secreted in the colostrum. Biochem Biophys Acta 1452:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-4889(99)00114-7
Huang Z, Wu L, Chen L (2018) Apelin/APJ system: a novel potential therapy target for kidney disease. J Cell Physiol 233:3892–3900. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26144
Ishimaru Y, Sumino A, Kajioka D et al (2017) Apelin protects against NMDA-induced retinal neuronal death via an APJ receptor by activating Akt and ERK1/2, and suppressing TNF-alpha expression in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 133:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2016.12.002
Jiang P, Ray A, Rybak LP, Brenner MJ (2016) Role of STAT1 and oxidative stress in gentamicin-induced hair cell death in organ of corti. Otol Neurotol 37:1449–1456. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000001192
Kalinec GM, Lomberk G, Urrutia RA, Kalinec F (2017) Resolution of cochlear inflammation: novel target for preventing or ameliorating drug-, noise- and age-related hearing loss. Front Cell Neurosci 11:192. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2017.00192
Kaur T, Mukherjea D, Sheehan K, Jajoo S, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V (2011) Short interfering RNA against STAT1 attenuates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in the rat by suppressing inflammation. Cell Death Dis 2:e180. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2011.63
Kaur T, Borse V, Sheth S et al (2016) Adenosine A1 receptor protects against cisplatin ototoxicity by suppressing the NOX3/STAT1 inflammatory pathway in the cochlea. J Neurosci 36:3962–3977. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3111-15.2016
Khoshsirat S, Abbaszadeh HA, Peyvandi AA et al (2021) Apelin-13 prevents apoptosis in the cochlear tissue of noise-exposed rat via Sirt-1 regulation. J Chem Neuroanat 114:101956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2021.101956
Kishimoto-Urata M, Urata S, Fujimoto C, Yamasoba T (2022) Role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in acquired inner ear disorders. Antioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11081469
Levano S, Bodmer D (2015) Loss of STAT1 protects hair cells from ototoxicity through modulation of STAT3, c-Jun, Akt, and autophagy factors. Cell Death Dis 6:e2019. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.362
Li R, Li X, Zhao J et al (2022) Mitochondrial STAT3 exacerbates LPS-induced sepsis by driving CPT1a-mediated fatty acid oxidation. Theranostics 12:976–998. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.63751
Liu J, Liu M, Chen L (2017) Novel pathogenesis: regulation of apoptosis by Apelin/APJ system. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (shanghai) 49:471–478. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmx035
Nan B, Zhao Z, Jiang K, Gu X, Li H, Huang X (2022) Astaxanthine attenuates cisplatin ototoxicity in vitro and protects against cisplatin-induced hearing loss in vivo. Acta Pharm Sin B 12:167–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.002
Niknazar S, Abbaszadeh HA, Peyvandi H et al (2019) Protective effect of [Pyr1]-apelin-13 on oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in hair cell-like cells derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol 853:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.012
Okur MN, Djalilian HR (2022) Approaches to mitigate mitochondrial dysfunction in sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Biomed Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-022-03103-y
Paken J, Govender CD, Pillay M, Sewram V (2019) A review of cisplatin-associated ototoxicity. Semin Hear 40:108–121. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1684041
Ramkumar V, Mukherjea D, Dhukhwa A, Rybak LP (2021) Oxidative stress and inflammation caused by cisplatin ototoxicity. Antioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10121919
Rosati R, Shahab M, Neumann WL, Jamesdaniel S (2019) Inhibition of protein nitration prevents cisplatin-induced inactivation of STAT3 and promotes anti-apoptotic signaling in organ of Corti cells. Exp Cell Res 381:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.05.008
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Ramkumar V (2019) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Semin Hear 40:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0039-1684048
Schmitt NC, Rubel EW, Nathanson NM (2009) Cisplatin-induced hair cell death requires STAT1 and is attenuated by epigallocatechin gallate. J Neurosci 29:3843–3851. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5842-08.2009
Shen X, Yuan G, Li B et al (2022) Apelin-13 attenuates early brain injury through inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis in rats after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol Biol Rep 49:2107–2118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-07028-y
So H, Kim H, Lee JH et al (2007) Cisplatin cytotoxicity of auditory cells requires secretions of proinflammatory cytokines via activation of ERK and NF-kappaB. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol JARO 8:338–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-007-0084-9
Wakabayashi K, Fujioka M, Kanzaki S et al (2010) Blockade of interleukin-6 signaling suppressed cochlear inflammatory response and improved hearing impairment in noise-damaged mice cochlea. Neurosci Res 66:345–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2009.12.008
Wan T, Fu M, Jiang Y, Jiang W, Li P, Zhou S (2022) Research progress on mechanism of neuroprotective roles of Apelin-13 in prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 47:205–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03448-1
Wang X, Zhou Y, Wang D et al (2022) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: From signaling network to therapeutic targets. Biomed Pharmacother Biomed Pharmacother 157:114045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114045
Wu X, Li X, Song Y et al (2017) Allicin protects auditory hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons from cisplatin—induced apoptosis. Neuropharmacology 116:429–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.001
Xia F, Chen H, Jin Z, Fu Z (2021) Apelin-13 protects the lungs from ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuating inflammatory and oxidative stress. Hum Exp Toxicol 40:685–694. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327120961436
Xu W, Li T, Gao L et al (2019) Apelin-13/APJ system attenuates early brain injury via suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and oxidative stress in a AMPK-dependent manner after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Neuroinflamm 16:247. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1620-3
Yang S, Li H, Tang L et al (2015) Apelin-13 protects the heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury through the RISK-GSK-3beta-mPTP pathway. Arch Med Sci AMS 11:1065–1073. https://doi.org/10.5114/aoms.2015.54863
Ye Y, Cai Y, Xia E et al (2021) Apelin-13 reverses bupivacaine-induced cardiotoxicity via the adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase pathway. Anesth Analg 133:1048–1059. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000005692
Yin H, Sun G, Yang Q et al (2017) NLRX1 accelerates cisplatin-induced ototoxity in HEI-OC1 cells via promoting generation of ROS and activation of JNK signaling pathway. Sci Rep 7:44311. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44311
Yin H, Zhang H, Kong Y et al (2020) Apelin protects auditory cells from cisplatin-induced toxicity in vitro by inhibiting ROS and apoptosis. Neurosci Lett 728:134948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134948
Yu X, Man R, Li Y et al (2019) Paeoniflorin protects spiral ganglion neurons from cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: possible relation to PINK1/BAD pathway. J Cell Mol Med 23:5098–5107. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14379
Zhang P, Yi LH, Meng GY, Zhang HY, Sun HH, Cui LQ (2017) Apelin-13 attenuates cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity through inhibition of ROS-mediated DNA damage and regulation of MAPKs and AKT pathways. Free Radic Res 51:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2017.1313414
Zhang L, Li F, Su X et al (2019) Melatonin prevents lung injury by regulating apelin 13 to improve mitochondrial dysfunction. Exp Mol Med 51:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-019-0273-8
Zhou Q, Cao J, Chen L (2016) Apelin/APJ system: a novel therapeutic target for oxidative stress-related inflammatory diseases (Review). Int J Mol Med 37:1159–1169. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2544
Zhou S, Guo X, Chen S, Xu Z, Duan W, Zeng B (2019) Apelin-13 regulates LPS-induced N9 microglia polarization involving STAT3 signaling pathway. Neuropeptides 76:101938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2019.101938
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant number 82000979, 82101215]; the Fund of Lin He Academician Workstation of Jining Medical University [Grant number JYHL2019MS13]; National College Students' innovation and entrepreneurship training program [Grant number 202110443040]; the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province [grant number BK20200201].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY: experimental design, methodology, writing—original draft. QY: writing—reviewing and editing. YS and BY: conducted experimental procedures, data collecting and analyzing. HZ and FW: software, investigation. YG, LZ, and WZ: conceptualization, data analyzing, validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Jining Medical University (2019-JC-001).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, H., Sun, Y., Ya, B. et al. Apelin-13 protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis and regulating STAT1 and STAT3. Arch Toxicol 97, 2477–2493 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03544-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03544-x