Abstract
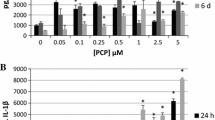
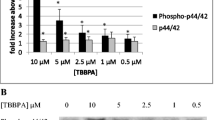
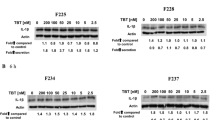
Environmental contaminant exposures occur due to the widespread use of synthetic chemicals. Tributyltin (TBT), dibutyltin (DBT), and pentachlorophenol (PCP) are each used in a variety of applications, including antifouling paints and stabilizers in certain plastics. Each of these compounds has been found in human blood, as well as other tissues, and they have been shown to stimulate pro-inflammatory cytokine production in human immune cells, Inflammatory cytokines mediate response to injury or infection. However, if their levels are increased in the absence of an appropriate stimulus, chronic inflammation can occur. Chronic inflammation is associated with a number of pathologies including cancer. Stimulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine production by these toxicants is dependent on activation of ERK 1/2 and/or p38 MAPK pathways. MAPK pathways have the capacity to regulate translation by increasing phosphorylation of key translation regulatory proteins. There have been no previous studies examining the effects of TBT, DBT, or PCP on translation. The current study shows that ribosomal protein S6 (S6), eukaryotic initiation factor 4B (eIF4B), and eIF4E are phosphorylated (activated) and/or their total levels are elevated in response to each of these compounds at concentrations found in human blood. Activation/increased levels of translational proteins occurred at concentrations of the compounds that have been shown to elevate pro-inflammatory cytokine production, but where there is no increase in mRNA for those proteins was seen. Compound-stimulated increases in translation appear to be part of the mechanism by which they elevate protein production in immune cells.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini L, Martinon F, Burns K, McDermott MF, Hawkins PN, Tschopp J (2004) NALP3 forms an IL-1β-processing inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle-Wells autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity 20(3):319–325
Antizar-Ladislao B (2008) Environmental levels, toxicity and human exposure to tributyltin (TBT)-contaminated marine environment. A review. Environ Int 34(2):292–308
ATSDR’s Toxicological Profiles (2002) Toxicological Profile for Pentachlorophenol. Atsdr’s Toxicol Profiles. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420061888_ch130
Avdulov S, Li S, Michalek V, Burrichter D, Peterson M, Perlman DM, Manivel JC, Sonenberg N, Yee D, Bitterman PB, Polunovsky VA (2004) Activation of translation complex eIF4F is essential for the genesis and maintenance of the malignant phenotype in human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Cell 5(6):553–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2004.05.024
Brown S, Whalen M (2015) Tributyltin alters secretion of interleukin 1 beta from human immune cells. J Appl Toxicol 35(8):895–908
Brown B, Loganathan B, Owen D (2005) Chlorophenol concentrations in sediment and mussel tissues from selected locations in Kentucky Lake. Chrysal Murray State Univ Undergr Res J 1:5–10
Brown S, Boules M, Hamza N, Wang X, Whalen M (2018a) Synthesis of interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 in human lymphocytes is stimulated by tributyltin. Arch Toxicol 92(8):2573–2586
Brown S, Wilburn W, Martin T, Whalen M (2018b) Butyltin compounds alter secretion of interleukin 6 from human immune cells. J Appl Toxicol 38(2):201–218
Cirelli DP (1978) Patterns of pentachlorophenol usage in the United States of America—an overview. Pentachlorophenol, pp 13–18
Cline RE, Hill RH, Phillips DL, Needham LL (1989) Pentachlorophenol measurements in body fluids of people in log homes and workplaces. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18(4):475–481
Dinarello CA (2011) Interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory diseases. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 117(14):3720–3732
Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Pankow JS, Ballantyne CM, Couper D, Vigo A, Hoogeveen R, Folsom AR, Heiss G (2003) Low-grade systemic inflammation and the development of type 2 diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes 52(7):1799–1805
Epstein RL, Phillippo ET, Harr R, Koscinski W, Vasco G (1991) Organotin residue determination in poultry and turkey sample survey in the United States. J Agric Food Chem 39(5):917–921
Forsyth D, Jay B (1997) Organotin leachates in drinking water from chlorinated poly (vinyl chloride)(CPVC) pipe. Appl Organomet Chem 11(7):551–558
Forsyth D, Weber D, Cleroux C (1992) Determination of butyltin, cyclohexyltin and phenyltin compounds in beers and wines. Food Addit Contam 9(2):161–169
Gabay C (2006) Interleukin-6 and chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther 8(2):1–6
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N (1999) eIF4 initiation factors: Effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem 68:913–963. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.913
Gipperth L (2009) The legal design of the international and European Union ban on tributyltin antifouling paint: Direct and indirect effects. J Environ Manag 90:S86–S95
Godet A-C, David F, Hantelys F, Tatin F, Lacazette E, Garmy-Susini B, Prats A-C (2019) IRES trans-acting factors, key actors of the stress response. Int J Mol Sci 20(4):924
Harms U, Andreou AZ, Gubaev A, Klostermeier D (2014) EIF4B, eIF4G and RNA regulate eIF4A activity in translation initiation by modulating the eIF4A conformational cycle. Nucleic Acids Res 42(12):7911–7922. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku440
Holland EC, Sonenberg N, Pandolfi PP, Thomas G (2004) Signaling control of mRNA translation in cancer pathogenesis. Oncogene 23(18):3138–3144. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207590
Holz MK, Ballif BA, Gygi SP, Blenis J (2005) MTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 123(4):569–580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.024
Kannan K, Tanabe S, Tatsukawa R (1995) Occurrence of butyltin residues in certain foodstuffs. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 55(4):510–516
Kannan K, Senthilkumar K, Giesy JP (1999) Occurrence of butyltin compounds in human blood. Environ Sci Technol 33(10):1776–1779
Kosciuczuk EM, Saleiro D, Platanias LC (2017) Dual targeting of eIF4E by blocking MNK and mTOR pathways in leukemia. Cytokine 89:116–121
Lawrence S, Reid J, Whalen M (2015) Secretion of interferon gamma from human immune cells is altered by exposure to tributyltin and dibutyltin. Environ Toxicol 30(5):559–571. https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.21932
Lawrence S, Ismail F, Jamal SZ, Whalen MM (2018) Tributyltin stimulates synthesis of interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha in human lymphocytes. J Appl Toxicol JAT 38(8):1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3617
Mamane Y, Petroulakis E, LeBacquer O, Sonenberg N (2006) MTOR, translation initiation and cancer. Oncogene 25(48):6416–6422. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209888
Martin TJ, Gabure S, Maise J, Snipes S, Peete M, Whalen MM (2019a) The organochlorine pesticides pentachlorophenol and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane increase secretion and production of interleukin 6 by human immune cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 72:103263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.103263
Martin TJ, Maise J, Gabure S, Whalen MM (2019b) Exposures to the environmental contaminants pentachlorophenol and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane increase production of the proinflammatory cytokine, interleukin-1β, in human immune cells. J Appl Toxicol 39(8):1132–1142
Meyer TPH, Zehnter I, Hofmann B, Zaisserer J, Burkhart J, Rapp S, Weinauer F, Schmitz J, Illert WE (2005) Filter Buffy Coats (FBC): a source of peripheral blood leukocytes recovered from leukocyte depletion filters. J Immunol Methods 307(1–2):150–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jim.2005.10.004
Morley SJ, Traugh JA (1989) Phorbol esters stimulate phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factors 3, 4B, and 4F. J Biol Chem 264(5):2401–2404
Pyronnet S, Imataka H, Gingras AC, Fukunaga R, Hunter T, Sonenberg N (1999) Human eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) recruits Mnk1 to phosphorylate eIF4E. EMBO J 18(1):270–279. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.1.270
Roper WL (1992) Toxicological profile for tin. US Department of Health and Human Services, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
Roux PP, Topisirovic I (2012) Regulation of mRNA translation by signaling pathways. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(11):a012252
Ruvinsky I, Meyuhas O (2006) Ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation: From protein synthesis to cell size. Trends Biochem Sci 31(6):342–348
Sadiki A-I, Williams DT (1999) A study on organotin levels in Canadian drinking water distributed through PVC pipesa. Chemosphere 38(7):1541–1548
Sadiki A-I, Williams DT, Carrier R, Thomas B (1996) Pilot study on the contamination of drinking water by organotin compounds from PVC materials. Chemosphere 32(12):2389–2398
Showalter S (2005) Restrictions on the use of marine antifouling paints containing tributyltin and copper a white paper prepared by. Quality
Sushak L, Gabure S, Maise J, Arnett J, Whalen MM (2020) Dibutyltin alters immune cell production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin (IL) 1β and IL-6: Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases and changes in mRNA. J Appl Toxicol 40(8):1047–1059
Uhl S, Schmid P, Schlatter C (1986) Pharmacokinetics of pentachlorophenol in man. Arch Toxicol 58(3):182–186
Waskiewicz AJ, Flynn A, Proud CG, Cooper JA (1997) Mitogen-activated protein kinases activate the serine/threonine kinases Mnk1 and Mnk2. EMBO J 16(8):1909–1920. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/16.8.1909
Whalen MM, Loganathan BG, Kannan K (1999) Immunotoxicity of environmentally relevant concentrations of butyltins on human natural killer cells in vitro. Environ Res 81(2):108–116
Yamada S, Fujii Y, Mikami E, Kawamura N, Hayakawa J, Aoki K, Fukaya M, Terao C (1993) Small-scale survey of organotin compounds in household commodities. J AOAC Int 76(2):436–441
Acknowledgements
Supported by Grant U54CA163066 from the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ruff, A., Lewis, M. & Whalen, M. Organotin and organochlorine toxicants activate key translational regulatory proteins in human immune cells. Arch Toxicol 97, 469–493 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03413-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03413-z