Abstract
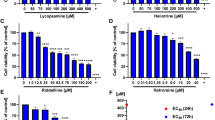
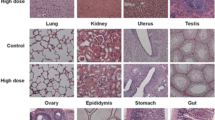
Many nitrosamines are recognized as mutagens and potent rodent carcinogens. Over the past few years, nitrosamine impurities have been detected in various drugs leading to drug recalls. Although nitrosamines are included in a ‘cohort of concern’ because of their potential human health risks, most of this concern is based on rodent cancer and bacterial mutagenicity data, and there are little data on their genotoxicity in human-based systems. In this study, we employed human lymphoblastoid TK6 cells transduced with human cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2A6 to evaluate the genotoxicity of six nitrosamines that have been identified as impurities in drug products: N-nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA), N-nitrosoethylisopropylamine (NEIPA), N-nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutanoic acid (NMBA), N-nitrosomethylphenylamine (NMPA), N-nitrosodiisopropylamine (NDIPA), and N-nitrosodibutylamine (NDBA). Using flow cytometry-based assays, we found that 24-h treatment with NDEA, NEIPA, NMBA, and NMPA caused concentration-dependent increases in the phosphorylation of histone H2A.X (γH2A.X) in CYP2A6-expressing TK6 cells. Metabolism of these four nitrosamines by CYP2A6 also caused significant increases in micronucleus frequency as well as G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest. In addition, nuclear P53 activation was found in CYP2A6-expressing TK6 cells exposed to NDEA, NEIPA, and NMPA. Overall, the genotoxic potency of the six nitrosamine impurities in our test system was NMPA > NDEA ≈ NEIPA > NMBA > NDBA ≈ NDIPA. This study provides new information on the genotoxic potential of nitrosamines in human cells, complementing test results generated from traditional assays and partially addressing the issue of the relevance of nitrosamine genotoxicity for humans. The metabolically competent human cell system reported here may be a useful model for risk assessment of nitrosamine impurities found in drugs.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiub CA, Pinto LF, Felzenszwalb I (2003) N-Nitrosodiethylamine mutagenicity at low concentrations. Toxicol Lett 145(1):36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4274(03)00263-7
Arimoto-Kobayashi S, Kaji K, Sweetman GM, Hayatsu H (1997) Mutation and formation of methyl- and hydroxylguanine adducts in DNA caused by N-nitrosodimethylamine and N-nitrosodiethylamine with UVA irradiation. Carcinogenesis 18(12):2429–2433. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/18.12.2429
Bellec G, Dréano Y, Lozach P, Ménez JF, Berthou F (1996) Cytochrome P450 metabolic dealkylation of nine N-nitrosodialkylamines by human liver microsomes. Carcinogenesis 17(9):2029–2034. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/17.9.2029
Bonassi S, El-Zein R, Bolognesi C, Fenech M (2011) Micronuclei frequency in peripheral blood lymphocytes and cancer risk: evidence from human studies. Mutagenesis 26(1):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/geq075
Bonfanti M, Magagnotti C, Galli A et al (1990) Determination of O6-butylguanine in DNA by immunoaffinity extraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Cancer Res 50(21):6870–6875
Brambilla G, Cavanna M, Pino A, Robbiano L (1981) Quantitative correlation among DNA damaging potency of six N-nitroso compounds and their potency in inducing tumor growth and bacterial mutations. Carcinogenesis 2(5):425–429. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/2.5.425
Brendler SY, Tompa A, Hutter KF, Preussmann R, Pool-Zobel BL (1992) In vivo and in vitro genotoxicity of several N-nitrosamines in extrahepatic tissues of the rat. Carcinogenesis 13(12):2435–2441. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/13.12.2435
Bryce SM, Bernacki DT, Bemis JC, Dertinger SD (2016) Genotoxic mode of action predictions from a multiplexed flow cytometric assay and a machine learning approach. Environ Mol Mutagen 57(3):171–189. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.21996
Bryce SM, Bernacki DT, Smith-Roe SL, Witt KL, Bemis JC, Dertinger SD (2018) Investigating the generalizability of the MultiFlow DNA damage assay and several companion machine learning models with a set of 103 diverse test chemicals. Toxicol Sci 162(1):146–166. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfx235
Chen S, Wu Q, Li X et al (2021) Characterization of cytochrome P450s (CYP)-overexpressing HepG2 cells for assessing drug and chemical-induced liver toxicity. J Environ Sci Health C Toxicol Carcinog 39(1):68–86. https://doi.org/10.1080/26896583.2021.1880242
Cross KP, Ponting DJ (2021) Developing structure-activity relationships for N-nitrosamine activity. Comput Toxicol 20:100186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comtox.2021.100186
Fajen JM, Carson GA, Rounbehler DP et al (1979) N-nitrosamines in the rubber and tire industry. Science 205(4412):1262–1264. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.472741
FDA (2020) Control of nitrosamine impurities in human drugs. US Food and Drug Administration https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/control-nitrosamine-impurities-human-drugs (accessed 15 Apr. 2022)
Fowler P, Smith K, Young J et al (2012) Reduction of misleading (“false”) positive results in mammalian cell genotoxicity assays. I. Choice of cell type. Mutat Res 742(1–2):11–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2011.10.014
Fowler P, Smith R, Smith K et al (2014) Reduction of misleading (“false”) positive results in mammalian cell genotoxicity assays. III: sensitivity of human cell types to known genotoxic agents. Mutat Res 767:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrgentox.2014.03.001
Fujita K, Kamataki T (2001) Role of human cytochrome P450 (CYP) in the metabolic activation of N-alkylnitrosamines: application of genetically engineered Salmonella typhimurium YG7108 expressing each form of CYP together with human NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Mutat Res 483(1–2):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00223-8
George J, Tsuchishima M, Tsutsumi M (2020) Metabolism of N-nitrosodimethylamine, methylation of macromolecules, and development of hepatic fibrosis in rodent models. J Mol Med (berl) 98(9):1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-020-01950-7
Hidajat M, McElvenny DM, Ritchie P et al (2019) Lifetime exposure to rubber dusts, fumes and N-nitrosamines and cancer mortality in a cohort of British rubber workers with 49 years follow-up. Occup Environ Med 76(4):250–258. https://doi.org/10.1136/oemed-2018-105181
Honma M, Kitazawa A, Cayley A et al (2019) Improvement of quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) tools for predicting Ames mutagenicity: outcomes of the Ames/QSAR International Challenge Project. Mutagenesis 34(1):3–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gey031
ICH (2017) M7(R1) Assessment and control of DNA reactive (mutagenic) impurities in pharmaceuticals to limit potential carcinogenic risk. https://www.ich.org/page/multidisciplinary-guidelines#7-2 (Accessed 12 Mar. 2022)
Inami K, Ishikawa S, Mochizuki M (2009) Activation mechanism of N-nitrosodialkylamines as environmental mutagens and its application to antitumor research. Genes Environ 31(4):97–104. https://doi.org/10.3123/jemsge.31.97
Jakszyn P, Gonzalez CA (2006) Nitrosamine and related food intake and gastric and oesophageal cancer risk: a systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. World J Gastroenterol 12(27):4296–4303. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i27.4296
Koepke SR, Kroeger-Koepke MB, Michejda CJ (1990) Evidence for an unstable DNA adduct from N-nitroso-N-methylaniline. Chem Res Toxicol 3(1):17–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx00013a003
Kroeger-Koepke MB, Reuber MD, Iype PT, Lijinsky W, Michejda CJ (1983) The effect of substituents in the aromatic ring on carcinogenicity of N-nitrosomethylaniline in F344 rats. Carcinogenesis 4(2):157–160. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/4.2.157
Kuroki T, Drevon C, Montesano R (1977) Microsome-mediated mutagenesis in V79 Chinese hamster cells by various nitrosamines. Cancer Res 37(4):1044–1050
Kushida H, Fujita K, Suzuki A et al (2000) Metabolic activation of N-alkylnitrosamines in genetically engineered Salmonella typhimurium expressing CYP2E1 or CYP2A6 together with human NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Carcinogenesis 21(6):1227–1232. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/21.5.227
Larsson SC, Bergkvist L, Wolk A (2006) Processed meat consumption, dietary nitrosamines and stomach cancer risk in a cohort of Swedish women. Int J Cancer 119(4):915–919. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21925
Li Y, Hecht SS (2022) Metabolic activation and DNA Interactions of carcinogenic N-nitrosamines to which humans are commonly exposed. Int J Mol Sci 23(9):4559. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23094559
Li X, Chen S, Guo X et al (2020a) Development and application of TK6-derived cells expressing human cytochrome P450s for genotoxicity testing. Toxicol Sci 175(2):251–265. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfaa035
Li X, He X, Chen S et al (2020b) Evaluation of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced genotoxicity using metabolically competent TK6 cell lines. Food Chem Toxicol 145:111662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111662
Li X, Li Y, Ning KG et al (2022) The expression of Phase II drug-metabolizing enzymes in human B-lymphoblastoid TK6 cells. J Environ Sci Health C Toxicol Carcinog 40(1):106–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/26896583.2022.2044242
Lijinsky W, Taylor HW (1979) Carcinogenicity of methylated derivatives of N-nitrosodiethylamine and related compounds in Sprague-Dawley rats2. J Natl Cancer Inst 62(2):407–410. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/62.2.407
Lijinsky W, Reuber MD, Saavedra JE, Singer GM (1983) Carcinogenesis in F344 rats by N-nitrosomethyl-n-propylamine derivatives. J Natl Cancer Inst 70(5):959–963. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/70.5.959
Liviac D, Creus A, Marcos R (2011) Genotoxic evaluation of the non-halogenated disinfection by-products nitrosodimethylamine and nitrosodiethylamine. J Hazard Mater 185(2–3):613–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.062
Mišík M, Nersesyan A, Kment M et al (2021) Micronucleus assays with the human derived liver cell line (Huh6): a promising approach to reduce the use of laboratory animals in genetic toxicology. Food Chem Toxicol 154:112355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2021.112355
Mukherjee B, Kessinger C, Kobayashi J et al (2006) DNA-PK phosphorylates histone H2AX during apoptotic DNA fragmentation in mammalian cells. DNA Repair (amst) 5(5):575–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.01.011
OECD (2016) In vitro mammalian cell micronucleus test, OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, No. 487. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (Paris, France) https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264264861-en (assessed 15 Apr. 2022)
O’Neill JP, Machanoff R, San Sebastian JR, Hsie AW (1982) Cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of dimethylnitrosamine in mammalian cells (CHO/HGPRT system); enhancement by calcium phosphate. Environ Mutagen 4(1):7–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/em.2860040103
Shao K, Shapiro AJ (2018) A web-based system for Bayesian benchmark dose estimation. Environ Health Perspect 126(1):017002. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP1289
Taylor WR, Stark GR (2001) Regulation of the G2/M transition by p53. Oncogene 20(15):1803–1815. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1204252
Thresher A, Foster R, Ponting DJ, Stalford SA, Tennant RE, Thomas R (2020) Are all nitrosamines concerning? A review of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity data. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 116:104749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104749
Tsuda H, Mera Y, Seki K, Aoki T, Fukushima S, Ito N (1987) Induction of tumors in the liver, urinary bladder, esophagus and forestomach by short-term treatment with different doses of N, N’-dibutylnitrosamine in rats. Jpn J Cancer Res 78(3):227–234. https://doi.org/10.20772/cancersci1985.78.3_227
WHO (2019) Update on nitrosamine impurities. World Health Organization https://www.who.int/news/item/20-11-2019-information-note-nitrosamine-impurities (accessed 15 Apr. 2022)
Yamazaki H, Inui Y, Yun CH, Guengerich FP, Shimada T (1992) Cytochrome P450 2E1 and 2A6 enzymes as major catalysts for metabolic activation of N-nitrosodialkylamines and tobacco-related nitrosamines in human liver microsomes. Carcinogenesis 13(10):1789–1794. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/13.10.1789
Zeller A, Duran-Pacheco G, Guerard M (2017) An appraisal of critical effect sizes for the benchmark dose approach to assess dose-response relationships in genetic toxicology. Arch Toxicol 91(12):3799–3807. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-2037-3
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by funding from the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Regulatory Science Research program. YL was supported by an appointment to the Postgraduate Research Program at the National Center for Toxicological Research (NCTR) administered by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science Education through an interagency agreement between the U.S. Department of Energy and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). We thank Drs. Robert Dorsam, Sruthi King, Naomi Kruhlak from CDER for their valuable comments regarding nitrosamine impurities and Dr. Tao Chen and Ms. Roberta Mittelstaedt for their critical review of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This article reflects the views of the authors and does not necessarily reflect those of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Any mention of commercial products is for clarification only and is not intended as approval, endorsement, or recommendation. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., He, X., Le, Y. et al. Genotoxicity evaluation of nitrosamine impurities using human TK6 cells transduced with cytochrome P450s. Arch Toxicol 96, 3077–3089 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03347-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03347-6