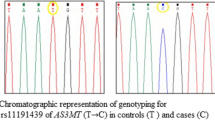
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is one of the major public health problems worldwide; both genetic and environmental factors are its risk factors. Arsenic, an environmental pollutant, might be a risk factor for T2DM, but the association of low-to-moderate level arsenic exposure with the risk of T2DM is still inconsistent. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) can affect the development of T2DM, but the study on KEAP1 rs11545829 (G>A) SNP is few. In this paper, we explored the effect of KEAP1 rs11545829 (G>A) SNP and low-to-moderate level arsenic exposure on risk of T2DM in a cross-sectional case–control study conducted in Shanxi, China. Total of 938 participants, including 318 T2DM cases and 618 controls, were enrolled. Blood glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) was detected by Automatic Biochemical Analyzer, and participants with HbA1c≧6.5% were diagnosed as T2DM. Urinary total arsenic (tAs, mg/L), as the indicator of arsenic exposure, was detected by liquid chromatography–atomic fluorescence spectrometry (LC–AFS). Genomic DNA was extracted and the genotypes of KEAP1 rs11545829 SNP were examined by multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The urinary tAs concentration in recruited participants was 0.075 (0.03–0.15) mg/L, and was associated with an increased risk of T2DM (OR = 8.45, 95% CI 2.63–27.17); rs11545829 mutation homozygote AA genotype had a protective effect on risk of T2DM (OR = 0.42, 95 % CI 0.25–0.73). Although this protective effect of AA genotype was found in participants with higher urinary tAs level (>0.032 mg/L) (OR = 0.48, 95% CI 0.26–0.86), there was no interaction effect for arsenic exposure and rs11545829 SNP on risk of T2DM. In addition, BMI modified the association between rs11545829 SNP and the risk of T2DM (RERI = −1.11, 95% CI −2.18–0.04). The present study suggest that low-to-moderate level arsenic exposure may be a risk factor, while KEAP1 rs11545829 SNP mutation homozygote AA genotype may be a protective factor for risk of T2DM, especially for T2DM patients with urinary tAs level>0.032 mg/L.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agardh E, Allebeck P, Hallqvist J et al (2011) Type 2 diabetes incidence and socio-economic position: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol 40:804–818. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyr029
Alexaki A, Hettiarachchi GK, Athey JC et al (2019) Effects of codon optimization on coagulation factor IX translation and structure: Implications for protein and gene therapies. Sci Rep 9:15449. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51984-2
Ampofo AG, Boateng EB (2020) Beyond 2020: Modelling obesity and diabetes prevalence. Diabetes Res Clin Prac 167:108362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108362
Baek K, Lee N, Chung I (2017) Association of arsenobetaine with beta-cell function assessed by homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) in nondiabetic Koreans: data from the fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2008–2009. Ann Occup Environ Med 29:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40557-017-0181-0
Barba C, Manila M, Cavalli-Sforza T et al (2004) Appropriate body-mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. The Lancet 363:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(03)15268-3
Bergstrom P, Otter MV, Nilsson S et al (2014) Association of NFE2L2 and KEAP1 haplotypes with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 15:130–137. https://doi.org/10.3109/21678421.2013.839708
Bonaventura MM, Bourguignon NS, Bizzozzero M et al (2017) Arsenite in drinking water produces glucose intolerance in pregnant rats and their female offspring. Food Chem Toxicol 100:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2016.12.025
Brookes AJ (1999) The essence of SNPs. Gene 234:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00219-X
Bruno G, Runzo C, Cavallo-Perin P et al (2005) Incidence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults aged 30–49 years: the population-based registry in the province of Turin, Italy. Diabetes Care 28:2613–2619. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.28.11.2613
Cannon A, Handelsman Y, Heile M et al (2018) Burden of Illness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Manag Care Spec Pharm 24(9-a Suppl):s5–s13. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.9-a.s5
Chen Y, Ahsan H, Slavkovich V et al (2010) No association between arsenic exposure from drinking water and diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study in Bangladesh. Environ Health Perspect 118:1299–1305. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901559
Dempsey PC, Owen N, Yates TE et al (2016) Sitting Less and Moving More: Improved Glycaemic Control for Type 2 Diabetes Prevention and Management. Curr Diab Rep 16:114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-016-0797-4
Farzan SF, Gossai A, Chen Y et al (2016) Maternal arsenic exposure and gestational diabetes and glucose intolerance in the New Hampshire birth cohort study. Environ Health 15:106. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-016-0194-0
Feseke SK, St-Laurent J, Anassour-Sidi E et al (2015) Arsenic exposure and type 2 diabetes results from the 2007–2009 Canadian Health Measures Survey. Health Promot Chronic Dis Prev Can 35:63–72. https://doi.org/10.24095/hpcdp.35.4.01
Fukushima-Uesaka H, Saito Y, Maekawa K et al (2007) Genetic variations and haplotype structures of transcriptional factor Nrf2 and its cytosolic reservoir protein Keap1 in Japanese. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 22:212–219. https://doi.org/10.2133/dmpk.22.212
Gao LB, Yuan F, Che GL et al (2019) Epigenetic modifications but not genetic polymorphisms regulate KEAP1 expression in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem 120:12311–12320. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28495
Gao YH, Sun DJ, Zhao LJ et al (2020) Safety guidance value of urinary arsenic for population. National Health Commission PRC
Gauderman J, Morrison J (2007) Quanto
Grau-Perez M, Navas-Acien A, Galan-Chilet I et al (2018) Arsenic exposure, diabetes-related genes and diabetes prevalence in a general population from Spain. Environ Pollut 235:948–955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.008
Hall MN, Niedzwiecki M, Liu XH et al (2013) Chronic arsenic exposure and blood glutathione and glutathione disulfide concentrations in Bangladeshi adults. Environ Health Perspect 121:1068–1074. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1205727
Hartikainen JM, Tengstrom M, Winqvist R et al (2015) KEAP1 genetic polymorphisms associate with breast cancer risk and survival outcomes. Clin Cancer Res 21:1591–1601. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1887
Holcomb N, Goswami M, Han SG et al (2017) Inorganic arsenic inhibits the nucleotide excision repair pathway and reduces the expression of XPC. DNA Repair (amst) 52:70–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.02.009
Hu YX, Li J, Lou B et al (2020) The role of reactive oxygen species in arsenic toxicity. Biomolecules 10:240. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020240
Huang HW, Lee CH, Yu HS (2019) Arsenic-induced carcinogenesis and immune dysregulation. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:2746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16152746
Huang JW, Cheng YY, Sung TC et al (2014) Association between arsenic exposure and diabetes mellitus in Cambodia. Biomed Res Int 2014:683124. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/683124
Hunt R, Hettiarachchi G, Katneni U et al (2019) A single synonymous variant (c.354G>A [p. P118P]) in ADAMTS13 confers enhanced specific activity. Int J Mol Sci 20:5734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225734
2018 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension, Writing Group of 2018 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension 2019.
IDF(2019). IDF DIABETES ATLAS:Ninth edition 2019.
James KA, Marshall JA, Hokanson JE et al (2013) A case-cohort study examining lifetime exposure to inorganic arsenic in drinking water and diabetes mellitus. Environ Res 123:33–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2013.02.005
Janssen LMM, Hiligsmann M, Elissen AMJ et al (2020) Burden of disease of type 2 diabetes mellitus: cost of illness and quality of life estimated using the Maastricht Study. Diabet Med 37:1759–1765. https://doi.org/10.1111/dme.14285
Kamura Y, Iwata M, Maeda S et al (2016) FTO gene polymorphism is associated with type 2 diabetes through its effect on increasing the maximum BMI in Japanese men. PLoS ONE 11:e0165523. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165523
Kopacz A, Kloska D, Forman HJ et al (2020) Beyond repression of Nrf2: An update on Keap1. Free Radic Biol Med 157:63–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.03.023
Korytina GF, Akhmadishina LZ, Aznabaeva YG et al (2019) Associations of the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway and antioxidant defense gene polymorphisms with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Gene 692:102–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.12.061
Kramer EB, Vallabhaneni H, Mayer LM et al (2010) A comprehensive analysis of translational missense errors in the yeast saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA 16:1797–1808. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2201210
Kuo CC, Howard BV, Umans JG et al (2015) Arsenic exposure, arsenic metabolism, and incident diabetes in the strong heart study. Diabetes Care 38:620–627. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc14-1641
Li J, Wang SS, Jia QZ et al (2016) Investigation of arsenic level in drinking water from rural areas of Shanxi. Chinese Preventive Medicine 17:180–182. https://doi.org/10.16506/j.1009-6639.2016.03.006
Liu C, Li YF, Guan TW et al (2018) ACE2 polymorphisms associated with cardiovascular risk in Uygurs with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17:127. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0771-3
Maull EA, Ahsan H, Edwards J et al (2012) Evaluation of the association between arsenic and diabetes: a National Toxicology Program workshop review. Environ Health Perspect 120:1658–1670. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1104579
Mendez WM, Eftim S, Cohen J et al (2017) Relationships between arsenic concentrations in drinking water and lung and bladder cancer incidence in U.S. counties. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 27:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2016.58
Mericq V, Martinez-Aguayo A, Uauy R et al (2017) Long-term metabolic risk among children born premature or small for gestational age. Nat Rev Endocrinol 13:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.127
Morris AP, Voight BF, Teslovich TM et al (2012) Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 44:981–990. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2383
Naujokas MF, Anderson B, Ahsan H et al (2013) The broad scope of health effects from chronic arsenic exposure: update on a worldwide public health problem. Environ Health Perspect 121:295–302. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1205875
Navas-Acien A, Silbergeld EK, Streeter RA et al (2006) Arsenic exposure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of the experimental and epidemiological evidence. Environ Health Perspect 114:641–648. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8551
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 284:13291–13295. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R900010200
Osman W, Tay GK, Alsafar H (2018) Multiple genetic variations confer risks for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Arab descendants from UAE. Int J Obes (lond) 42:1345–1353. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-018-0057-6
Pan WC, Seow WJ, Kile ML et al (2013) Association of low to moderate levels of arsenic exposure with risk of type 2 diabetes in Bangladesh. Am J Epidemiol 178:1563–1570. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwt195
Rao XQ, Patel P, Puett R et al (2015) Air pollution as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Toxicol Sci 143:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfu250
Rhee SY, Hwang YC, Woo JT et al (2013) Arsenic exposure and prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Korean adults. J Korean Med Sci 28:861–868. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.6.861
Sole X, Guino E, Valls J et al (2006) SNPStats: a web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics 22:1928–1929. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl268
Sripaoraya K, Siriwong W, Pavittranon S et al (2017) Environmental arsenic exposure and risk of diabetes type 2 in Ron Phibun subdistrict, Nakhon Si Thammarat Province, Thailand: unmatched and matched case–control studies. Risk Manag Healthc Policy 10:41–48. https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S128277
Takayama Y, Masuzaki Y, Mizutani F et al (2021) Associations between blood arsenic and urinary arsenic species concentrations as an exposure characterization tool. Sci Total Environ 750:141517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141517
Tu WJ, Wang H, Li S et al (2019) The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in chronic diseases. Aging Dis 10:637–651. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2018.0513
Umapathy D, Ponjayanth B, Vanniya P et al (2019) Association of SNP rs7181866 in the nuclear respiratory factor-2 beta subunit encoding GABPB1 gene with obesity and type-2 diabetes mellitus in South Indian population. Int J Biol Macromol 132:606–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.125
Uruno A, Yagishita Y, Yamamoto M (2015) The Keap1-Nrf2 system and diabetes mellitus. Arch Biochem Biophys 566:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2014.12.012
Wang XY, Gao D, Zhang GF et al (2020) Exposure to multiple metals in early pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study. Environ Int 135:105370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105370
Wong TF, Yoshinaga K, Monma Y et al (2011) Association of Keap1 and Nrf2 genetic mutations and polymorphisms with endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma survival. Int J Gynecol Cancer 21:1428–1435. https://doi.org/10.1097/IGC.0b013e31822d0eb2
Yamamoto M, Kensler TW, Motohashi H (2018) The KEAP1-NRF2 system: a thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol Rev 98:1169–1203. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00023.2017
Zhang Q, Hou YX, Wang D et al (2020) Interactions of arsenic metabolism with arsenic exposure and individual factors on diabetes occurrence: baseline findings from arsenic and non-communicable disease cohort (AsNCD) in China. Environ Pollut 265:114968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114968
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank all study participants, research staffs who participated in this work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key projects of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81830099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CF: conceptualization, methodology, visualization, and writing-original draft. ZZ: formal analysis and resources. XZ: formal analysis and resources. QL: investigation. N Gi: investigation. MS: resources. YG: resources. LW: formal analysis, resources, and investigation. WH: resources and investigation. MZ: resources and investigation. FY: investigation. YW: validation. JP: project administration and funding acquisition. YX: validation. YY: conceptualization, methodology, writing-review and editing, and supervision. YG: conceptualization, methodology, writing-review and editing, supervision, and project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, C., Zhan, Z., Zhang, X. et al. Research for type 2 diabetes mellitus in endemic arsenism areas in central China: role of low level of arsenic exposure and KEAP1 rs11545829 polymorphism. Arch Toxicol 96, 1673–1683 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03279-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03279-1