Abstract
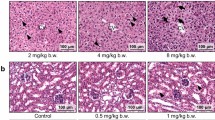
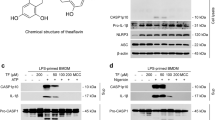
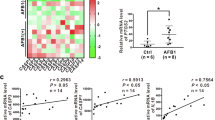
Ochratoxin A (OTA), a prevalent nephrotoxic mycotoxin contaminant in food and feedstuff, has been reported to induce renal injury. To disclose the nephrotoxicity of continuous administration of OTA and to investigate potential mechanisms related to pyroptosis, male C57BL/6 mice were intraperitoneally injected with 1.0 and 2.0 mg/kg B.W. OTA every other day for 14 days. At 2.0 mg/kg B.W. OTA administration significantly increased histological injury and renal fibrosis molecules (α-SMA, Vimentin, TGF-β) and activated the NOD-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and induced pyroptosis compared with control. In the in vitro tests, Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) epithelial cells were exposed to 0–4.0 μg/ml OTA for 24 h in serum-free medium. Data showed that OTA dose-dependently affected cell viability and significantly up-regulated renal fibrosis genes (α-SMA, Vimentin, TGF-β). 2.0 μg/ml OTA significantly induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation and caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis, increasing the expression and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) and pyroptosis-related genes (GSDMD, IL-1β, IL-18) in MDCK cells. These outcomes were significantly abrogated after inhibiting NLRP3 activation with inhibitor MCC950 and silencing NLRP3 with small interfering RNA (siRNA). Furthermore, knockdown of caspase-1 also ameliorated OTA-induced renal fibrosis via the inhibition of pyroptosis. Collectively, the chosen doses of OTA-triggered nephrotoxicity through NLRP3 inflammasome activation and caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis both in vitro and in vivo.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- OTA:
-
Ochratoxin A
- MDCK:
-
Madin–Darby canine kidney
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- GSDMD:
-
Gasdermin D
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- NLRP3:
-
NOD-like receptor protein 3
- PYD:
-
Pyrin domain
- ASC:
-
Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a C-terminal CARD
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffer saline
- TBS:
-
Tris-buffered saline
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium salt–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- BCA:
-
Bicinchoninic acid
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- SEM:
-
Standard error mean
References
Al-Jaal BA, Jaganjac M, Barcaru A, Horvatovich P, Latiff A (2019) Aflatoxin, fumonisin, ochratoxin, zearalenone and deoxynivalenol biomarkers in human biological fluids: a systematic literature review, 2001–2018. Food Chem Toxicol 129:211–228
Aukema HM, House JD, Bankovic-Calic N, Ogborn MR (2004) Increased renal fibrosis and expression of renal phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase-beta and phospholipase C (gamma1) proteins in piglets exposed to ochratoxin-A. Nephron Physiol 96(1):19–25
Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Loboda A, Jozkowicz A, Huebbe P, Blank R, Wolffram S et al (2008) Effect of ochratoxin A on redox-regulated transcription factors, antioxidant enzymes and glutathione-S-transferase in cultured kidney tubulus cells. Food Chem Toxicol 46(8):2665–2671
Broz P, von Moltke J, Jones JW, Vance RE, Monack DM (2010) Differential requirement for Caspase-1 autoproteolysis in pathogen-induced cell death and cytokine processing. Cell Host Microbe 8:471–483
Cerqueira DM, Pereira MS, Silva AL, Cunha LD, Zamboni DS (2015) Caspase-1 but not Caspase-11 is required for NLRC4-mediated pyroptosis and restriction of infection by flagellated legionella species in mouse macrophages and in vivo. J Immunol 195(5):2303–2311
Chen H, Lu Y, Cao Z, Ma Q, Pi H, Fang Y et al (2016) Cadmium induces NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis in vascular endothelial cells. Toxicol Lett 246:7–16
Chou X, Ding F, Zhang X, Ding X, Gao H, Wu Q (2019) Sirtuin-1 ameliorates cadmium-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis through XBP-1s deacetylation in human renal tubular epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol 93:965–986
Damiano S, Iovane V, Squillacioti C, Mirabella N, Prisco F, Ariano A et al (2020) Red orange and lemon extract prevents the renal toxicity induced by ochratoxin A in rats. J Cell Physiol 235:5386–5393
Ding J, Wang K, Liu W, She Y, Sun Q, Shi J et al (2016) Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature 535:111
Dirheimer G, Creppy EE (1991) Mechanism of action of ochratoxin A. IARC Sci Publ 115:171–186
Duarte SC, Pena A, Lino CM (2011) Human ochratoxin a biomarkers—from exposure to effect. Crit rev Toxicol 41(3):187–212
Fuchs R, Peraica M (2005) Ochratoxin A in human kidney diseases. Food Addit Contam 22(Suppl 1):53–57
Gagliano N, Torri C, Donetti E, Grizzi F, Costa F, Bertelli AA et al (2005) Ochratoxin A-induced renal cortex fibrosis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: molecular mechanisms of ochratoxin A-injury and potential effects of red wine. Mol Med 11:30–38
Gan F, Zhou X, Zhou Y, Hou L, Chen X, Pan C et al (2019) Nephrotoxicity instead of immunotoxicity of OTA is induced through DNMT1-dependent activation of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting SOCS3. Arch Toxicol 93(4):1067–1082
Ge L, Lin Z, Le G, Hou L, Mao X, Liu S et al (2020) Nontoxic-dose deoxynivalenol aggravates lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammation and tight junction disorder in IPEC-J2 cells through activation of NF-kappaB and LC3B. Food Chem Toxicol 145:111712
Gekle M, Schwerdt G, Freudinger R, Mildenberger S, Wilflingseder D, Pollack V et al (2000) Ochratoxin A induces JNK activation and apoptosis in MDCK-C7 cells at nanomolar concentrations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293(3):837–844
Gekle M, Sauvant C, Schwerdt G (2005) Ochratoxin A at nanomolar concentrations: a signal modulator in renal cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 49(2):118–130
Gross O, Poeck H, Bscheider M, Dostert C, Hannesschläger N, Endres S et al (2009) Syk kinase signalling couples to the Nlrp3 inflammasome for anti-fungal host defence. Nature 459:433–436
Hennemeier I, Humpf HU, Gekle M, Schwerdt G (2012) The food contaminant and nephrotoxin ochratoxin A enhances Wnt1 inducible signaling protein 1 and tumor necrosis factor-α expression in human primary proximal tubule cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 56(9):1375–1384
Huang X, Feng Y, Xiong G, Whyte S, Duan J, Yang Y et al (2019) Caspase-11, a specific sensor for intracellular lipopolysaccharide recognition, mediates the non-canonical inflammatory pathway of pyroptosis. Cell Biosci 9:31
Jiao J, Zhao G, Wang Y, Ren P, Wu M (2020) MCC950, a selective inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome, reduces the inflammatory response and improves neurological outcomes in mice model of spinal cord injury. Front Mol Biosci 7:37
Kasper L, König A, Koenig PA, Gresnigt MS, Westman J, Drummond RA et al (2018) The fungal peptide toxin Candidalysin activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and causes cytolysis in mononuclear phagocytes. Nat Commun 9(1):4260
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, O’Rourke K, Anderson K, Warming S et al (2015) Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 526:666–671
Kuiper-Goodman T, Scott PM (1989) Risk assessment of the mycotoxin ochratoxin A. Biomed Environ Sci 2(3):179–248
Lamkanfi M, Dixit VM (2012) Inflammasomes and their roles in health and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28:137–161
Latz E, Xiao TS, Stutz A (2013) Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat Rev Immunol 13:397–411
Lebrun S, Föllmann W (2002) Detection of ochratoxin A-induced DNA damage in MDCK cells by alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis (comet assay). Arch Toxicol 75(11–12):734–741
Liang R, Shen XL, Zhang B, Li Y, Xu W, Zhao C et al (2015) Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 promotes Ochratoxin A-induced renal cytotoxicity. Sci Rep 5:8078
Loboda A, Stachurska A, Sobczak M, Podkalicka P, Mucha O, Jozkowicz A et al (2017) Nrf2 deficiency exacerbates ochratoxin A-induced toxicity in vitro and in vivo. Toxicology 389:42–52
Malekinejad H, Farshid AA, Mirzakhani N (2011) Liquorice plant extract reduces ochratoxin A-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 63:125–130
Malir F, Ostry V, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Malir J, Toman J (2016) Ochratoxin A: 50 years of research. Toxins (Basel). 8(7):191
Mally A, Decker M, Bekteshi M, Dekant W (2006) Ochratoxin A alters cell adhesion and gap junction intercellular communication in MDCK cells. Toxicology 223(1–2):15–25
Mantle P, Kilic MA, Mor F, Ozmen O (2015) Contribution of organ vasculature in rat renal analysis for ochratoxin a: relevance to toxicology of nephrotoxins. Toxins (Basel) 7(4):1005–1017
Meucci V, Luci G, Vanni M, Guidi G, Perondi F, Intorre L (2017) Serum levels of ochratoxin A in dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD): a retrospective study. J Vet Med Sci 79:440–447
O’Brien E, Dietrich DR (2005) Ochratoxin A: the continuing enigma. Crit rev Toxicol 35:33–60
Özcan Z, Gül G, Yaman I (2015) Ochratoxin A activates opposing c-MET/PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK 1–2 pathways in human proximal tubule HK-2 cells. Arch Toxicol 89(8):1313–1327
Petrik J, Mali A, Barii K, Rumora L, Epelak I (2005) Ochratoxin A induces apoptotic and necrotic renal cell death. Croat Chem Acta 78(3):447–453
Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Manderville RA (2007) Ochratoxin A: An overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol Nutr Food Res 51(1):61–99
Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Manderville RA (2012) An update on direct genotoxicity as a molecular mechanism of ochratoxin a carcinogenicity. Chem Res Toxicol 25(2):252–262
Pyo M, Chae S, Yoo H, Lee K (2020) Ochratoxin A induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis through TGF-β/Smad2/3 and Wnt1/β-catenin signaling pathways in vitro and in vivo. Arch Toxicol 94:3329
Qian G, Liu D, Hou L, Hamid M, Chen X, Gan F et al (2018) Ochratoxin A induces cytoprotective autophagy via blocking AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in PK-15 cells. Food Chem Toxicol 122:120–131
Roberts AB, Tian F, Byfield SD, Stuelten C, Ooshima A, Saika S et al (2006) Smad3 is key to TGF-β-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, fibrosis, tumor suppression and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:19–27
Rogers C, Erkes DA, Nardone A, Aplin AE, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2019) Gasdermin pores permeabilize mitochondria to augment caspase-3 activation during apoptosis and inflammasome activation. Nat Commun 10:1689
Sauvant C, Holzinger H, Gekle M (2005) The nephrotoxin ochratoxin A induces key parameters of chronic interstitial nephropathy in renal proximal tubular cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 15:125–134
Schroder K, Tschopp J (2010) The inflammasomes. Cell 140:821–832
Schwerdt G, Freudinger R, Mildenberger S, Silbernagl S, Gekle M (1999) The nephrotoxin ochratoxin A induces apoptosis in cultured human proximal tubule cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 15(6):405–415
Shen T, Miao Y, Ding C, Fan W, Liu S, Lv Y et al (2019) Activation of the p38/MAPK pathway regulates autophagy in response to the CYPOR-dependent oxidative stress induced by zearalenone in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Food Chem Toxicol 131:110527
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y, Huang H et al (2015) Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 526:660–665
Songsermsakul P, Razzazi-Fazeli E, Böhm J, Zentek J (2007) Occurrence of deoxynivalenol (DON) and ochratoxin A (OTA) in dog foods. Mycotoxin Res 23:65
Szczech GM, Carlton WW, Tuite J (1973) Ochratoxicosis in Beagle dogs. I. Clinical and clinicopathological features. Vet Pathol. 10:135–154
Takahashi M (2014) NLRP3 inflammasome as a novel player in myocardial infarction. Int Heart J 55(2):101–105
Tang Z, Liu X, Su B, Chen Q, Cao H, Yun Y et al (2020) Ultrasensitive and rapid detection of ochratoxin A in agro-products by a nanobody-mediated FRET-based immunosensor. J Hazard Mater 387:121678
van der Merwe KJ, Steyn PS, Fourie L, Scott DB, Theron JJ (1965) Ochratoxin A, a toxic metabolite produced by Aspergillus ochraceus Wilh. Nature 205:1112–1113
Wang H, Chen Y, Zhai N, Chen X, Gan F, Li H et al (2017) Ochratoxin A-induced apoptosis of IPEC-J2 cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening pathway. J Agric Food Chem 65(48):10630–10637
Wang X, Jiang L, Shi L, Yao K, Sun X, Yang G et al (2019) Zearalenone induces NLRP3-dependent pyroptosis via activation of NF-kappaB modulated by autophagy in INS-1 cells. Toxicology 428:152304
Xue Z, Xi Q, Liu H, Guo X, Zhang J, Zhang Z et al (2019) miR-21 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation to mediate pyroptosis and endotoxic shock. Cell Death Dis 10:461
Yang Q, He X, Li X, Xu W, Luo Y, Yang X et al (2014) DNA damage and S phase arrest induced by Ochratoxin A in human embryonic kidney cells (HEK 293). Mutat Res 765:22–31
Yazdi AS, Guarda G, Riteau N, Drexler SK, Tardivel A, Couillin I et al (2010) Nanoparticles activate the NLR pyrin domain containing 3 (Nlrp3) inflammasome and cause pulmonary inflammation through release of IL-1α and IL-1β. Proc Natl Sci U S A 107(45):19449–19454
Zhang X, Luan J, Chen W, Fan J, Nan Y, Wang Y et al (2018) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles induced hepatotoxicity via NLRP3 inflammasome activation and caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis. Nanoscale 10:9141–9152
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972745, 31811530300), the National Key R & D Program (2017YFD0501001), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Jiangsu, China), MOE Joint International Research Laboratory of Animal Health and Food Safety, College of Veterinary Medicine, Nanjing Agricultural University and Project of National Center for International Research on Animal Gut Nutrition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL and XM designed the research and wrote the paper; JS, BL and RMM assisted in performing the in vivo and in vitro experiments; DL, CP, FG and YL guided the experiments and image acquisition; KH and XC modified the syntax of the paper; XC assisted in designing the research and approved the final version to be submitted.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Mao, X., Liu, K. et al. Ochratoxin A induces nephrotoxicity in vitro and in vivo via pyroptosis. Arch Toxicol 95, 1489–1502 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-02993-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-02993-6