Abstract
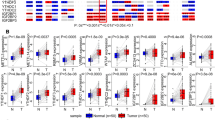
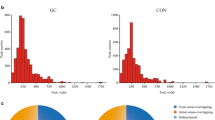
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays a vital regulatory role in tumorigenesis and development. In this study, we determined that the mRNA expression of IGF2BP1, IGF2BP2 and IGF2BP3, as the m6A modification genes, was significantly increased in gastric cancer (GC) tissues. Using a logistic regression model, we found that novel single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) rs9906944 C > T in IGF2BP1 was remarkably associated with a decreased risk of GC in discovery stage (odds ratio (OR) = 0.75, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 0.60–0.93, P = 8.51 × 10−3). This finding was repeated in an independent Nanjing population (OR = 0.76, 95% CI: 0.59–0.98, P = 3.45 × 10−2). The combined analysis including 2900 GC cases and 3,536 controls confirmed the association between rs9906944 C > T and GC risk (OR = 0.75, 95% CI: 0.64–0.88, P = 5.76 × 10−4). Furthermore, we found that GC patients with higher IGF2BP1 mRNA expression level had prominent poorer overall survival (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.49, 95% CI: 1.16–1.91, logrank P = 1.50 × 10−3). For the first time, our findings suggested the importance of genetic variants in m6A regulators in GC and indicated that IGF2BP1 plays a crucial role in GC. Genetic variants in m6A modification genes may be used for GC risk prediction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abnet CC, Freedman ND, Hu N et al (2010) A shared susceptibility locus in PLCE1 at 10q23 for gastric adenocarcinoma and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Genet 42(9):764–767. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.649
Arguello AE, DeLiberto AN, Kleiner RE (2017) RNA chemical proteomics reveals the N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A)-regulated protein-RNA interactome. J Am Chem Soc 139(48):17249–17252. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b09213
Bell JL, Wächter K, Mühleck B et al (2013) Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression? Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 70(15):2657–2675. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1186-z
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD et al (2016) Cancer statistics in China 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 66(2):115–132. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21338
Delaunay S, Frye M (2019) RNA modifications regulating cell fate in cancer. Nat Cell Biol 21(5):552–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0319-0
Farina KL, Huttelmaier S, Musunuru K, Darnell R, Singer RH (2003) Two ZBP1 KH domains facilitate beta-actin mRNA localization, granule formation, and cytoskeletal attachment. J Cell Biol 160(1):77–87. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200206003
Hansford S, Kaurah P, Li-Chang H et al (2015) Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome: CDH1 mutations and beyond. JAMA Oncol 1(1):23–32. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2014.168
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W et al (2018) Recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol 20(3):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z
Jin D, Guo J, Wu Y et al (2020) m(6)A demethylase ALKBH5 inhibits tumor growth and metastasis by reducing YTHDFs-mediated YAP expression and inhibiting miR-107/LATS2-mediated YAP activity in NSCLC. Mol Cancer 19(1):40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01161-1
Li Y, Xiao J, Bai J et al (2019) Molecular characterization and clinical relevance of m(6)A regulators across 33 cancer types. Mol Cancer 18(1):137. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1066-3
Mendel M, Chen KM, Homolka D et al (2018) Methylation of structured RNA by the m(6)A Writer METTL16 Is essential for mouse embryonic development. Mol Cell 71(6):986-1000.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.004
Meng Y, Li S, Gu D et al (2020) Genetic variants in m6A modification genes are associated with colorectal cancer risk. Carcinogenesis 41(1):8–17. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgz165
Meyer KD, Patil DP, Zhou J et al (2015) 5’ UTR m(6)A promotes cap-independent translation. Cell 163(4):999–1010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.012
Müller S, Glaß M, Singh AK et al (2019) IGF2BP1 promotes SRF-dependent transcription in cancer in a m6A- and miRNA-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res 47(1):375–390. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1012
Pinello N, Sun S, Wong JJ (2018) Aberrant expression of enzymes regulating m(6)A mRNA methylation: implication in cancer. Cancer Biol Med 15(4):323–334. https://doi.org/10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2018.0365
Saeki N, Saito A, Choi IJ et al (2011) A functional single nucleotide polymorphism in mucin 1, at chromosome 1q22, determines susceptibility to diffuse-type gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 140(3):892–902. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.10.058
Sahasrabudhe R, Lott P, Bohorquez M et al (2017) Germline mutations in PALB2, BRCA1, and RAD51C, which regulate DNA recombination repair. Patients Gastr Cancer Gastroenterol 152(5):983-986.e6. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.010
Shi Y, Hu Z, Wu C et al (2011) A genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for non-cardia gastric cancer at 3q13.31 and 5p13.1. Nat Genet 43(12):1215–1218. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.978
Tanikawa C, Kamatani Y, Toyoshima O et al (2018) Genome-wide association study identifies gastric cancer susceptibility loci at 12q24.11–12 and 20q11.21. Cancer Sci 109(12):4015–4024. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13815
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65(2):87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Wächter K, Köhn M, Stöhr N, Hüttelmaier S (2013) Subcellular localization and RNP formation of IGF2BPs (IGF2 mRNA-binding proteins) is modulated by distinct RNA-binding domains. Biol Chem 394(8):1077–1090. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2013-0111
Wang S, Chai P, Jia R, Jia R (2018) Novel insights on m(6)A RNA methylation in tumorigenesis: a double-edged sword. Mol Cancer 17(1):101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0847-4
Xiao J, Lin L, Luo D et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA TRPM2-AS acts as a microRNA sponge of miR-612 to promote gastric cancer progression and radioresistance. Oncogenesis 9(3):29. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-020-0215-2
Yan C, Zhu M, Ding Y et al (2020) Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies and functional assays decipher susceptibility genes for gastric cancer in Chinese populations. Gut 69(4):641–651. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318760
Yang F, Xue X, Zheng L et al (2014) Long non-coding RNA GHET1 promotes gastric carcinoma cell proliferation by increasing c-Myc mRNA stability. FEBS J 281(3):802–813. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.12625
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS, Yang YG (2018) Dynamic transcriptomic m(6)A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res 28(6):616–624. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0040-8
Yuan H, Li N, Fu D et al (2017) Histone methyltransferase SETD2 modulates alternative splicing to inhibit intestinal tumorigenesis. J Clin Investig 127(9):3375–3391. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci94292
Zhao Y, Shi Y, Shen H, Xie W (2020) m(6)A-binding proteins: the emerging crucial performers in epigenetics. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00872-8
Zhu M, Yan C, Ren C et al (2017) Exome array analysis identifies variants in SPOCD1 and BTN3A2 that affect risk for gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 152(8):2011–2021. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.02.017
Zhu S, Wang JZ, Chen D et al (2020) An oncopeptide regulates m(6)A recognition by the m(6)A reader IGF2BP1 and tumorigenesis. Nat Commun 11(1):1685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15403-9
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Meilin Wang for his kind help in this study. This study was partly supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grants 2018YFC1313100, 2018YFC1313102) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (81773539). Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Personalized Medicine, and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Public Health and Preventive Medicine).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD Z, HY C and J Q designed and supervised this study; XW W, D G and DF W carried out the experimental work, conducted the data analysis and wrote this manuscript; HT L and WD G helped collect samples; YL W and ML D revised this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Guan, D., Wang, D. et al. Genetic variants in m6A regulators are associated with gastric cancer risk. Arch Toxicol 95, 1081–1088 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02958-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-020-02958-1