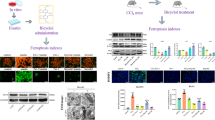
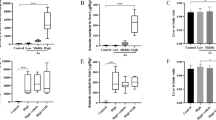
Abstract
Deoxynivalenol (DON) cannot be totally removed due to its stable chemical characteristics and chronic exposure to low doses of DON causes significant toxic effects in humans and animals. However, the potential hazard of such low-dose exposure in target organs still remains not completely understood, especially in liver, which is mainly responsible for detoxification of DON. In the present study, we demonstrated for the first time that estimated human daily DON exposure (25 μg/kg bw) for 30 and 90 days caused low-grade inflammatory infiltration around hepatic centrilobular veins, elevated systemic IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α and impaired liver function evidenced by increased serum ALT activity. At the molecular level, expressions of autophagy-related proteins as well as Cleaved Caspase-3 and Cleaved Caspase-7 were upregulated during DON exposure, which indicated the activation of autophagy and apoptosis. Importantly, AAV-mediated liver-specific overexpression of HO-1 reversed DON-induced liver damages, upregulated autophagy and attenuated apoptosis in liver, while AAV-mediated HO-1 silence aggravated DON-induced liver damages, inhibited autophagy and increased apoptosis. Furthermore, in vitro experiments demonstrated that lentivirus-mediated HO-1 overexpression in Hepa 1–6 cells prolonged the duration of autophagy and delayed the onset of apoptosis. HO-1 silence in Hepa 1–6 cells inhibited activation of autophagy and accelerated occurrence of apoptosis, and these could be recovered by CO pre-treatment. Therefore, we suppose that HO-1 might be a potential research target to protect human and animal from liver injuries induced by low dose of DON exposure.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Amuzie CJ, Harkema JR, Pestka JJ (2008) Tissue distribution and proinflammatory cytokine induction by the trichothecene deoxynivalenol in the mouse: comparison of nasal vs. oral exposure. Toxicology 248(1):39–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2008.03.005
Bensassi F, Gallerne C, Sharaf El Dein O, Lemaire C, Hajlaoui MR, Bacha H (2012) Involvement of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in deoxynivalenol cytotoxicity. Food Chem Toxicol 50(5):1680–1689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.01.015
Carchman EH, Rao J, Loughran PA, Rosengart MR, Zuckerbraun BS (2011) Heme oxygenase-1-mediated autophagy protects against hepatocyte cell death and hepatic injury from infection/sepsis in mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 53(6):2053–2062. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24324
Chen Y, Klionsky DJ (2011) The regulation of autophagy—unanswered questions. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 2):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.064576
Dennery PA (2014) Signaling function of heme oxygenase proteins. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(11):1743–1753. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5674
Girardet C, Bonnet MS, Jdir R et al (2011) Central inflammation and sickness-like behavior induced by the food contaminant deoxynivalenol: a PGE2-independent mechanism. Toxicol Sci 124(1):179–191. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfr219
Han J, Wang QC, Zhu CC et al (2016) Deoxynivalenol exposure induces autophagy/apoptosis and epigenetic modification changes during porcine oocyte maturation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 300:70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.03.006
He C, Klionsky DJ (2009) Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 43(1):67–93
Huang C, Feng L, Jiang WD et al (2019) Deoxynivalenol decreased intestinal immune function related to NF-kappaB and TOR signalling in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:470–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.039
JECFA (2011) Safety evaluation of certain contaminants in food. WHO Food Additives Series and FAO Food and Nutrition Paper: IPCS WHO-Geneve. In: 72nd meeting of the JECFA (p. 799). https://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241660631_eng.pdf
Jiao M, Ren F, Zhou L et al (2014) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha activation attenuates the inflammatory response to protect the liver from acute failure by promoting the autophagy pathway. Cell Death Dis 5:e1397. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.361
Kim HJ, Joe Y, Kim SK et al (2017) Carbon monoxide protects against hepatic steatosis in mice by inducing sestrin-2 via the PERK-eIF2alpha-ATF4 pathway. Free Radical Biol Med 110:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.05.026
Kim HJ, Joe Y, Rah SY et al (2018) Carbon monoxide-induced TFEB nuclear translocation enhances mitophagy/mitochondrial biogenesis in hepatocytes and ameliorates inflammatory liver injury. Cell Death Dis 9(11):1060. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1112-x
Lee S, Lee SJ, Coronata AA et al (2014) Carbon monoxide confers protection in sepsis by enhancing Beclin 1-dependent autophagy and phagocytosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 20(3):432–442. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5368
Lee SJ, Ryter SW, Xu JF et al (2011) Carbon monoxide activates autophagy via mitochondrial reactive oxygen species formation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 45(4):867–873. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2010-0352OC
Li X, Mu P, Qiao H, Wen J, Deng Y (2018) JNK-AKT-NF-kappaB controls P-glycoprotein expression to attenuate the cytotoxicity of deoxynivalenol in mammalian cells. Biochem Pharmacol 156:120–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.08.020
Maines MD (1988) Heme oxygenase: function, multiplicity, regulatory mechanisms, and clinical applications. FASEB J 2(10):2557–2568
Maresca M (2013) From the gut to the brain: journey and pathophysiological effects of the food-associated trichothecene mycotoxin deoxynivalenol. Toxins 5(4):784–820. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5040784
Marra E, Passarella S, Casamassima E, Perlino E, Doonan S, Quagliariello E (1985) Kinetic studies of the uptake of aspartate aminotransferase and malate dehydrogenase into mitochondria in vitro. Biochem J 228(2):493–503
Mishra S, Dixit S, Dwivedi PD, Pandey HP, Das M (2014) Influence of temperature and pH on the degradation of deoxynivalenol (DON) in aqueous medium: comparative cytotoxicity of DON and degraded product. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 31(1):121–131. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2013.861613
Mizunoe Y, Kobayashi M, Sudo Y et al (2018) Trehalose protects against oxidative stress by regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 and autophagy pathways. Redox Biol 15:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.007
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM, Klionsky DJ (2008) Autophagy fights disease through cellular self-digestion. Nature 451(7182):1069–1075. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06639
Motterlini R, Sawle P, Hammad J et al (2005) CORM-A1: a new pharmacologically active carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. FASEB J 19(2):284–286. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.04-2169fje
Nakatogawa H, Suzuki K, Kamada Y, Ohsumi Y (2009) Dynamics and diversity in autophagy mechanisms: lessons from yeast. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10(7):458–467. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2708
Netto GJ, Altrabulsi B, Katabi N et al (2006) Radio-frequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma before liver transplantation: a histologic and 'TUNEL' study. Liver Int 26(6):746–751. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1478-3231.2006.01278.x
Peng Z, Liao Y, Chen L et al (2019) Heme oxygenase-1 attenuates low-dose of deoxynivalenol-induced liver inflammation potentially associating with microbiota. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 374:20–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2019.04.020
Pestka JJ (2010) Deoxynivalenol: mechanisms of action, human exposure, and toxicological relevance. Arch Toxicol 84(9):663–679. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0579-8
Pestka JJ, Zhou HR, Moon Y, Chung YJ (2004) Cellular and molecular mechanisms for immune modulation by deoxynivalenol and other trichothecenes: unraveling a paradox. Toxicol Lett 153(1):61–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2004.04.023
Renner L, Kahlert S, Tesch T et al (2017) Chronic DON exposure and acute LPS challenge: effects on porcine liver morphology and function. Mycotoxin Res 33(3):207–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12550-017-0279-9
Sass G, Soares MC, Yamashita K et al (2003) Heme oxygenase-1 and its reaction product, carbon monoxide, prevent inflammation-related apoptotic liver damage in mice. Hepatology (Baltimore, MD) 38(4):909–918. https://doi.org/10.1053/jhep.2003.50386
Schmidt R, Tritschler E, Hoetzel A et al (2007) Heme oxygenase-1 induction by the clinically used anesthetic isoflurane protects rat livers from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Ann Surg 245(6):931–942. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.sla.0000256891.45790.4d
Takahashi T, Morita K, Akagi R, Sassa S (2004) Heme oxygenase-1: a novel therapeutic target in oxidative tissue injuries. Curr Med Chem 11(12):1545–1561
Tang Y, Li J, Li F et al (2015) Autophagy protects intestinal epithelial cells against deoxynivalenol toxicity by alleviating oxidative stress via IKK signaling pathway. Free Radical Biol Med 89:944–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.09.012
Tardivel C, Airault C, Djelloul M et al (2015) The food born mycotoxin deoxynivalenol induces low-grade inflammation in mice in the absence of observed-adverse effects. Toxicol Lett 232(3):601–611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2014.12.017
Tenhunen R, Marver HS, Schmid R (1968) The enzymatic conversion of heme to bilirubin by microsomal heme oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 61(2):748–755
Tomas-Hernandez S, Blanco J, Rojas C et al (2018) Resveratrol potently counteracts quercetin starvation-induced autophagy and sensitizes HepG2 cancer cells to apoptosis. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201700610
Travassos LH, Vasconcellos LR, Bozza MT, Carneiro LA (2017) Heme and iron induce protein aggregation. Autophagy 13(3):625–626. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1271515
Vasconcellos LR, Dutra FF, Siqueira MS et al (2016) Protein aggregation as a cellular response to oxidative stress induced by heme and iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113(47):E7474
Wang H, Zhu YY, Wang L et al (2017a) Mangiferin ameliorates fatty liver via modulation of autophagy and inflammation in high-fat-diet induced mice. Biomed Pharmacother 96:328–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.022
Wang L, Wang Y, Shao H et al (2017b) In vivo toxicity assessment of deoxynivalenol-contaminated wheat after ozone degradation. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 34(1):103–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2016.1253112
Wu F, Groopman JD, Pestka JJ (2014) Public health impacts of foodborne mycotoxins. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 5:351–372. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-food-030713-092431
Wu Q, Lohrey L, Cramer B, Yuan Z, Humpf HU (2011) Impact of physicochemical parameters on the decomposition of deoxynivalenol during extrusion cooking of wheat grits. J Agric Food Chem 59(23):12480–12485. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2038604
Xu D, Chen L, Chen X et al (2017) The triterpenoid CDDO-imidazolide ameliorates mouse liver ischemia-reperfusion injury through activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway enhanced autophagy. Cell Death Dis 8(8):e2983. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.386
Yang W, Yu M, Fu J et al (2014) Deoxynivalenol induced oxidative stress and genotoxicity in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Food Chem Toxicol 64:383–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.12.012
Yao P, Nussler A, Liu L et al (2007) Quercetin protects human hepatocytes from ethanol-derived oxidative stress by inducing heme oxygenase-1 via the MAPK/Nrf2 pathways. J Hepatol 47(2):253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2007.02.008
Yun N, Cho HI, Lee SM (2014) Impaired autophagy contributes to hepatocellular damage during ischemia/reperfusion: heme oxygenase-1 as a possible regulator. Free Radical Biol Med 68:168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.12.014
Zhou HR, Islam Z, Pestka JJ (2005) Induction of competing apoptotic and survival signaling pathways in the macrophage by the ribotoxic trichothecene deoxynivalenol. Toxicol Sci 87(1):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfi234
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1603100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC81502811), Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (ZRMS2017000504) and Hubei Province Health and Family Planning Scientific Research Project (WJ2019M114). All authors read and approved the final manuscript. We would like to thank all the participants for their contribution to this study. We also like to thank Ms. Svetlana Gasimova (Department of Traumatology, BG Trauma center, Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen) for editing the manuscript. Meantime, we would also thank Ms. Lu Gao, Lecturer, (School of Art, Wuhan Bussiness University) for editing figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

204_2019_2649_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Fig. S1 Cell viabilities of Hepa 1-6 cells exposed to 5, 10, 20, 30, 50, 100 nM DON for 0, 1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 24, 48 hours were measured by LDH detection. The cell viability at 0 h was regarded as 100% in each group. Three parallel samples for each time point. Data were presented as mean ± SD (JPG 335 kb)

204_2019_2649_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Fig. S2 Constructions of HO-1OE and HO-1shRNA AAV8 vectors. (a) HMOX1 sequence was inserted into pHBAAV-CMV-MCS-ZsGreen vector digested by KpnI and BamHI enzymes. (b) shRNA3 sequence was inserted into pHBAAV-U6-ZsGreen vector digested by BamHI and EcoRI enzymes. All vectors were labeled with green fluorescent protein genes and puromycin resistance genes. (JPG 2261 kb)

204_2019_2649_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Fig. S3 Constructions of HO-1OE and HO-1shRNA lentiviral vectors. (a) HMOX1 sequence was packaged into pHBLV-CMVIE-ZsGreen-Puro vector digested by BamHI and EcoRI enzymes. (b) Three different shRNAs were packaged into pHBLV-U6-Scramble-ZsGreen-Puro vector digested by BamHI and EcoRI enzymes to examine the most efficient shRNA. All vectors were labeled with green fluorescent protein genes and puromycin resistance genes. (JPG 2547 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, Z., Liao, Y., Wang, X. et al. Heme oxygenase-1 regulates autophagy through carbon–oxygen to alleviate deoxynivalenol-induced hepatic damage. Arch Toxicol 94, 573–588 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02649-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02649-6