Abstract
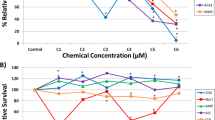
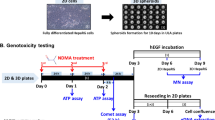
The increasing number of man-made chemicals in the environment that may pose a carcinogenic risk emphasizes the need to develop reliable time- and cost-effective approaches for carcinogen detection. To address this issue, we have investigated the utility of human hepatocytes for the in vitro identification of genotoxic and non-genotoxic carcinogens. Induced pluripotent stem-cell (iPSC)-derived human hepatocytes were treated with the genotoxic carcinogens aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P), the non-genotoxic liver carcinogen methapyrilene, and the non-carcinogens aflatoxin B2 (AFB2) and benzo[e]pyrene (B[e]P) at non-cytotoxic concentrations for 7 days, and transcriptomic and DNA methylation profiles were examined. 1569, 1693, and 2061 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected in cells treated with AFB1, B[a]P, and methapyrilene, respectively, whereas no DEGs were found in cells treated with AFB2 or B[e]P. In contrast to the profound cellular transcriptomic responses, exposure of iPSC-derived hepatocytes to the test chemicals resulted in minor random alterations in global DNA methylome, most of which were not associated with changes in gene expression. Overall, our results demonstrate that the major non-genotoxic effect of exposure to carcinogens, regardless of their mode of action, is a profound global transcriptomic response rather than global DNA methylome alterations, indicating the significance of transcriptomic alterations as an informative endpoint in short-term in vitro carcinogen testing.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ates G, Mertens B, Heymans A, Verschaeve L, Milushev D, Vanparys P, Roosens NHC, De Keersmaecker SCJ, Rogiers V, Doktorova TY (2018) A novel genotoxin-specific qPCR array based on the metabolically competent human HepaRG™ cell line as a rapid and reliable tool for improved in vitro hazard assessment. Arch Toxicol 92:1593–1608
Baylin S, Bestor TH (2002) Altered methylation patterns in cancer cell genomes: cause or consequence? Cancer Cell 1:299–305
Bell CC, Lauschke VM, Vorrink SU, Palmgren H, Duffin R, Andersson TB, Ingelman-Sundberg M (2017) Transcriptional, functional, and mechanistic comparisons of stem cell-derived hepatocytes, HepaRG cells, and three-dimensional human hepatocyte spheroids as predictive in vitro systems for drug-induced liver injury. Drug Metab Dispos 45:419–429
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol 57:289–300
Borowa-Mazgaj B, de Conti A, Tryndyak V, Steward CR, Jimenez L, Melnyk S, Seneshaw M, Mirshahi F, Rusyn I, Beland FA, Sanyal AJ, Pogribny IP (2019) Gene expression and DNA methylation alterations in the glycine N-methyltransferase gene in diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated carcinogenesis. Toxicol Sci 170:273–282
Braakhuis HM, Slob W, Olthof ED, Wolterink G, Zwart EP, Gremmer ER, Rorije E, van Benthem J, Woutersen R, van der Laan JW, Luijten M (2018) Is current risk assessment of non-genotoxic carcinogens protective? Crit Rev Toxicol 48:500–511
Cancerprogressreport.org (2018) [internet] American Association for Cancer Research, Philadelphia
Chappell G, Pogribny IP, Guyton KZ, Rusyn I (2016) Epigenetic alterations induced by genotoxic occupational and environmental carcinogens: a systematic literature review. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res 768:27–45
Corvi R, Madia F, Guyton KZ, Kasper P, Rudel R, Colacci A, Kleinjans J, Jennings P (2017) Moving forward in carcinogenicity assessment: report of an EURL ECVAM/ESTIV workshop. Toxicol In Vitro 45:278–286
Cote IL, McCullough SD, Hines RN, Vandenberg JJ (2017) Application of epigenetic data in human health risk assessment. Curr Opin Toxicol 6:71–78
Dreval K, Tryndyak K, de Conti A, Beland FA, Pogribny IP (2019) Gene expression and DNA methylation alterations during non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated liver carcinogenesis. Front Genet 10:486
Fang H, Harris SC, Su Z, Chen M. Qian F, Shi L, Perkins R, Tong W (2017) ArrayTrack: an FDA and public genomic tool. In: Tatarinova TV and Nikolsky Y (eds) Biological networks and pathway analysis. Methods Mol Biol vol 1613. pp. 333–353
Farmen E, Hultman MT, Anglès d’Auriac M, Tollefsen KE (2014) Development of a screening system for the detection of chemically induced DNA methylation alterations in a zebrafish liver cell line. J Toxicol Environ Health A 77:587–599
Gaylor DW (2005) Are tumor incidence rates from chronic bioassays telling us what we need to know about carcinogens? Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 41:128–133
Gómez-Lechón MJ, Tolosa L (2016) Human hepatocytes derived from pluripotent stem cells: a promising cell model for drug hepatotoxicity screening. Arch Toxicol 90:2049–2061
Grimm FA, Iwata Y, Sirenko O, Bittner M, Rusyn I (2015) High-content assay multiplexing for toxicity screening in induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Assay Drug Dev Technol 13:529–546
Herceg Z, Ghantous A, Wild CP, Sklias A, Casati L, Duthie SJ, Fry R, Issa J-P, Kellermayer R, Koturbash I, Kondo Y, Lepeule J, Lima SCS, Marsit CJ, Rakyan V, Saffery R, Taylor JA, Teschendorff AE, Ushijima T, Vineis P, Walker CL, Waterland RA, Wiemels J, Ambatipudi S, Degli Esposti D, Hernandez-Vargas H (2018) Roadmap for investigating epigenome deregulation and environmental origins of cancer. Int J Cancer 142:874–882
Hu G, Li P, Li Y, Wang T, Gao X, Zhang W, Jia G (2016) Methylation levels of P16 and TP53 that are involved in DNA strand breakage of 16HBE cells treated by hexavalent chromium. Toxicol Lett 249:15–21
Jacobs AC, Hattfield KP (2013) History of chronic toxicity and animal carcinogenicity studies for pharmaceuticals. Vet Pathol 50:324–333
Jennings P, Weiland C, Limonciel A, Bloch KM, Radford R, Aschauer L, McMorrow T, Wilmes A, Pfaller W, Ahr HJ, Slattery C, Lock EA, Ryan MP, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H (2012) Transcriptomic alterations induced by Ochtatoxin A in rat and human proximal tubular in vitro models and comparison to a rat in vivo model. Arch Toxicol 86:571–589
Kuppusamy SP, Kaiser JP, Wesselkamper SC (2015) Epigenetic regulation in environmental chemical carcinogenesis and its applicability in human risk assessment. Int J Toxicol 34:384–392
Li H-H, Chen R, Hyduke DR, Williams A, Frötschl R, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H, O’Lone R, Yauk CL, Aubrecht J, Fornace AJ Jr (2017) Development and validation of a high-throughput transcriptomic biomarker to address 21st century genetic toxicology needs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:E10881–E10889
Li A, Lu X, Natoli T, Bittker J, Sipes NS, Subramanian A, Auerbach S, Sherr DH, Monti S (2019) The carcinogenome project: in vitro gene expression profiling of chemical perturbations to predict long-term carcinogenicity. Environ Health Perspect 127:047002
Long MD, Smiraglia DJ, Campbell MJ (2017) The genomic impact of DNA CpG methylation on gene expression; relationships in prostate cancer. Biomolecules 7:15
Marone PA, Hall WC, Hayes AW (2014) Reassessing the 2-year rodent carcinogenicity bioassay: a review of the applicability to human risk and current perspectives. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 68:108–118
Mascolo MG, Perdichizzi S, Vaccari M, Rotondo F, Zanzi C, Grilli S, Paparella M, Jacobs MN, Colacci A (2018) The transformics assay: first steps for the development of an integrated approach to investigate the malignant cell transformation in vitro. Carcinogenesis 39:955–967
McKay JA, Adriaens M, Evelo CT, Ford D, Mathers JC (2016) Gene promoter DNA methylation patterns have a limited role in orchestrating transcriptional changes in the fetal liver in response to maternal folate depletion during pregnancy. Mol Nutr Food Res 60:2031–2042
Paparella M, Colacci A, Jacobs MN (2017) Uncertainties of testing methods: what do we (want to) know about carcinogenicity? Altex 34:235–252
Parfett CL, Desaulniers D (2017) A Tox21 approach to altered epigenetic landscapes: assessing epigenetic toxicity pathways leading to altered gene expression and oncogenic transformation in vitro. Int J Mol Sci 18:1179
Ramaiahgari SC, Auerbach SS, Saddler TO, Rice JR, Dunlap PE, Sipes NS, DeVito MJ, Shah RR, Bushel PR, Merrick BA, Paules RS, Ferguson SS (2019) The power of resolution: contextualized understanding of biological responses to liver injury chemicals using high-throughput transcriptomics and benchmark concentration modeling. Toxicol Sci 169:553–566
Rieswijk L, Claessen SMH, Bekers O, van Herwijnen M, Theunissen DHJ, Jennen DGJ, de Kok TMCM, Kleinjans JCS, van Breda SGJ (2016) Aflatoxin B1 induces persistent epigenomic effects in primary human hepatocytes associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Toxicology 350–352:31–39
Schaap MM, Wackers PFK, Zwart EP, Huijskens I, Jonker MJ, Hendriks G, Breit TM, van Steed H, van de Water B, Luijten M (2015) A novel toxicogenomics-based approach to categorize (non-) genotoxic carcinogens. Arch Toxicol 89:2413–2427
Steinberg P (2017) In vivo-in vitro carcinogenicity. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 157:81–96
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM, Jemal A (2016) Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends—an update. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 25:16–27
Tryndyak V, Kindrat I, Dreval K, Churchwell MI, Beland FA, Pogribny IP (2018) Effect of aflatoxin B1, benzo[a]pyrene, and methapyrilene on transcriptomic and epigenetic alterations in human liver HepaRG cells. Food Chem Toxicol 121:214–223
Wild CP (2009) Environmental exposure measurement in cancer epidemiology. Mutagenesis 24:117–125
Wilde EC, Chapman KE, Stannard LM, Seager AL, Brüsehafer K, Shah U-K, Tonkin JA, Brown MR, Verma JR, Doherty AT, Johnson GE, Doak SH, Jenkins GJS (2018) A novel, integrated in vitro carcinogenicity test to identify genotoxic and non-genotoxic carcinogens using human lymphoblastoid cells. Arch Toxicol 92:935–951
World Cancer Report (2014) Stewart BW, Wild CP (eds) International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Wu S, Powers S, Zhu W, Hannun YA (2016) Substantial contribution of extrinsic risk factors to cancer development. Nature 529:43–47
Zhang X, Wallace AD, Du P, Kibbe WA, Jafari N, Xie H, Lin S, Baccarelli A, Soares MB, Hou L (2012) DNA methylation alterations in response to pesticide exposure in vitro. Environ Mol Mutagen 53:542–549
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by appointment (BBM) to the Postgraduate Research Program at the NCTR administered by the Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education (ORISE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The views expressed in this manuscript do not necessarily represent those of the US Food and Drug Administration.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tryndyak, V., Borowa-Mazgaj, B., Beland, F.A. et al. Gene expression and cytosine DNA methylation alterations in induced pluripotent stem-cell-derived human hepatocytes treated with low doses of chemical carcinogens. Arch Toxicol 93, 3335–3344 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02569-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02569-5