Abstract
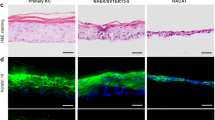
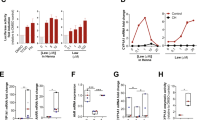
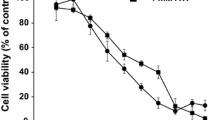
Chronic exposure to arsenic is associated with various diseases in humans. Skin hyperpigmentation is the most sensitive objective symptom for patients with arsenicosis. However, there is very limited information about the mechanism of arsenic-mediated skin hyperpigmentation in vivo. In this study, hairless homozygous mice (Hr/Hr-mice) that drank water containing 3 and 30 µM arsenic for 2 months developed skin hyperpigmentation with increased levels of arsenic and number of melanocytes in the skin. Since it is possible for humans to be exposed to 3 µM of arsenic in well drinking water, our results suggest that the Hr/Hr-mice could be a novel model sensitively reflecting arsenic-mediated skin hyperpigmentation. We then analyzed the mechanism of arsenic-mediated skin hyperpigmentation. The epidermis of Hr/Hr-mice and human HaCaT skin keratinocytes exposed to arsenic for 2 and 4 months, respectively, showed 5.4–21.5-fold increased levels of endothelin-1 (ET-1) expression via NF-kappa B activation. Coexposure of primary normal human epithelial melanocytes to arsenic and ET-1 activated their proliferation and melanin synthesis with increased levels of MITF-M and ET-1 receptor expression. Our results suggest that interaction between keratinocytes and melanocytes in the skin through ET-1 and its receptor contributes to arsenic-mediated skin pigmentation, a hallmark of arsenicosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE (1988) Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol 106(3):761–771
Brummelkamp TR, Nijman SM, Dirac AM, Bernards R (2003) Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature 424(6950):797–801. doi:10.1038/nature01811
Callender VD, St Surin-Lord S, Davis EC, Maclin M (2011) Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Am J Clin Dermatol 12(2):87–99. doi:10.2165/11536930-000000000-00000
Costin GE, Hearing VJ (2007) Human skin pigmentation: melanocytes modulate skin color in response to stress. FASEB J 21(4):976–994. doi:10.1096/fj.06-6649rev
Council NR (1999) Arsenic in drinking water. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Guha Mazumder DN, Haque R, Ghosh N et al (1998) Arsenic levels in drinking water and the prevalence of skin lesions in West Bengal, India. Int J Epidemiol 27(5):871–877
Hong GM, Bain LJ (2012) Arsenic exposure inhibits myogenesis and neurogenesis in P19 stem cells through repression of the beta-catenin signaling pathway. Toxicol Sci 129(1):146–156. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfs186
Hoque M, Amin A, Alam M, Taher A (1996) Chronic arsenic poisoning in a village of Chapai Nawabganj District—a cross sectional study. Teach Assoc J 9:9–41
IARC (2004) Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 84:1–477
Kato M, Iwashita T, Takeda K et al (2000) Ultraviolet light induces redox reaction-mediated dimerization and superactivation of oncogenic Ret tyrosine kinases. Mol Biol Cell 11(1):93–101
Kato M, Ohgami N, Kawamoto Y et al (2007) Protective effect of hyperpigmented skin on UV-mediated cutaneous cancer development. J Invest Dermatol 127(5):1244–1249. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5700659
Kumasaka MY, Yamanoshita O, Shimizu S et al (2013) Enhanced carcinogenicity by coexposure to arsenic and iron and a novel remediation system for the elements in well drinking water. Arch Toxicol 87(3):439–447. doi:10.1007/s00204-012-0964-6
Li C, Xu J, Li F et al (2011) Unfolded protein response signaling and MAP kinase pathways underlie pathogenesis of arsenic-induced cutaneous inflammation. Cancer Prev Res 4(12):2101–2109. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0343
Matteucci E, Maroni P, Bendinelli P, Locatelli A, Desiderio MA (2013) Epigenetic control of endothelin-1 axis affects invasiveness of breast carcinoma cells with bone tropism. Exp Cell Res 319(12):1865–1874. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.04.022
Mazumder DN, Das Gupta J, Santra A, Pal A, Ghose A, Sarkar S (1998) Chronic arsenic toxicity in west Bengal–the worst calamity in the world. J Indian Med Assoc 96(1):4–7, 18
Mazumder DN, Ghosh A, Majumdar KK, Ghosh N, Saha C, Mazumder RN (2010) Arsenic contamination of ground water and its health impact on population of district of Nadia, West Bengal, India. Indian J Community Med 35(2):331–338. doi:10.4103/0970-0218.66897
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2011) Crosstalk in NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol 12(8):695–708. doi:10.1038/ni.2065
Ohgami N, Mitsumatsu Y, Ahsan N et al (2015) Epidemiological analysis of the association between hearing and barium in humans. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. doi:10.1038/jes.2015.62
Pasparakis M, Haase I, Nestle FO (2014) Mechanisms regulating skin immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 14(5):289–301. doi:10.1038/nri3646
Quehenberger P, Bierhaus A, Fasching P et al (2000) Endothelin 1 transcription is controlled by nuclear factor-kappaB in AGE-stimulated cultured endothelial cells. Diabetes 49(9):1561–1570
Ren X, McHale CM, Skibola CF, Smith AH, Smith MT, Zhang L (2011) An emerging role for epigenetic dysregulation in arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Environ Health Perspect 119(1):11–19. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002114
Sato-Jin K, Nishimura EK, Akasaka E et al (2008) Epistatic connections between microphthalmia-associated transcription factor and endothelin signaling in Waardenburg syndrome and other pigmentary disorders. FASEB J 22(4):1155–1168. doi:10.1096/fj.07-9080com
Sikder M, Maidul A, Momin A (1999) Clinical manifestation of chronic Arsenic toxicity in Bangladesh—a 250 case study. Bangladesh J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 16(1):6–8
Sikder M, Maidul A, Khan M, Haq M, Choudhury S, Mishbahuddin M (2000) Effect of spirulina in the treatment of chronic arsenicosis. Bangladesh J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 17(1):9–13
Takai D, Yagi Y, Wakazono K et al (2001) Silencing of HTR1B and reduced expression of EDN1 in human lung cancers, revealed by methylation-sensitive representational difference analysis. Oncogene 20(51):7505–7513. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204940
Tseng WP (1977) Effects and dose–response relationships of skin cancer and blackfoot disease with arsenic. Environ Health Perspect 19:109–119
Wang L, Hitron JA, Wise JT et al (2015) Ethanol enhances arsenic-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression via both NFAT and NF-kappaB signalings in colorectal cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 288(2):232–239. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2015.07.019
Yajima I, Sato S, Kimura T et al (1999) An L1 element intronic insertion in the black-eyed white (Mitf[mi-bw]) gene: the loss of a single Mitf isoform responsible for the pigmentary defect and inner ear deafness. Hum Mol Genet 8(8):1431–1441
Yajima I, Kumasaka MY, Thang ND et al (2011) Molecular network associated with mitf in skin melanoma development and progression. J Skin Cancer 2011:730170. doi:10.1155/2011/730170
Yajima I, Uemura N, Nizam S et al (2012) Barium inhibits arsenic-mediated apoptotic cell death in human squamous cell carcinoma cells. Arch Toxicol 86(6):961–973. doi:10.1007/s00204-012-0848-9
Yajima I, Kumasaka MY, Ohnuma S et al (2015) Arsenite-mediated promotion of anchorage-independent growth of HaCaT cells through placental growth factor. J Invest Dermatol. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.514
Yang Q, Huang W, Jozwik C et al (2005) Cardiac glycosides inhibit TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB signaling by blocking recruitment of TNF receptor-associated death domain to the TNF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102(27):9631–9636. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504097102
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (A) (15H01743 and 15H02588), (B) (16H02962, 24390157 and 24406002) and (C) (No. 25460178, 25340052, 16K10152, 16K08343), Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Exploratory Research (26670525), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (24108001 and 16H01639), COE Project for Private Universities (Nutritional Health Science Research Center; No. S1201007) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Kurita Water and Environment Foundation, the Japan Health Foundation, the Mitsui & Co., Ltd. Environment Fund, Foundation from Center for Advanced Medical and Clinical Research Nagoya University Hospital, The Mitsubishi Foundation, The Research Foundation for Health Sciences (The KENKO-KAGAKU Zaidan), Ichihara International Scholarship Foundation, The Cosmetology Research Foundation, Kao Melanin Workshop, AEON Environmental Foundation, the Sumitomo Foundation, the Salt Acience Research Foundation and Nagono Medical Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yajima, I., Kumasaka, M.Y., Iida, M. et al. Arsenic-mediated hyperpigmentation in skin via NF-kappa B/endothelin-1 signaling in an originally developed hairless mouse model. Arch Toxicol 91, 3507–3516 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-1975-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-017-1975-0