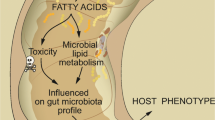
Abstract
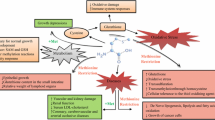
Susceptibility to toxic effects of inorganic arsenic (iAs) depends, in part, on efficiency of iAs methylation by arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase (AS3MT). As3mt-knockout (KO) mice that cannot efficiently methylate iAs represent an ideal model to study the association between iAs metabolism and adverse effects of iAs exposure, including effects on metabolic phenotype. The present study compared measures of glucose metabolism, insulin resistance and obesity in male and female wild-type (WT) and As3mt-KO mice during a 24-week exposure to iAs in drinking water (0.1 or 1 mg As/L) and in control WT and As3mt-KO mice drinking deionized water. Results show that effects of iAs exposure on fasting blood glucose (FBG) and glucose tolerance in either WT or KO mice were relatively minor and varied during the exposure. The major effects were associated with As3mt KO. Both male and female control KO mice had higher body mass with higher percentage of fat than their respective WT controls. However, only male KO mice were insulin resistant as indicated by high FBG, and high plasma insulin at fasting state and 15 min after glucose challenge. Exposure to iAs increased fat mass and insulin resistance in both male and female KO mice, but had no significant effects on body composition or insulin resistance in WT mice. These data suggest that As3mt KO is associated with an adverse metabolic phenotype that is characterized by obesity and insulin resistance, and that the extent of the impairment depends on sex and exposure to iAs, including exposure to iAs from mouse diet.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhyankar LN, Jones MR, Guallar E, Navas-Acien A (2012) Arsenic exposure and hypertension: a systematic review. Environ Health Perspect 120:494–500
Ahsan H, Chen Y, Kibriya MG, Slavkovich V, Parvez F, Jasmine F, Gamble MV, Graziano JH (2007) Arsenic metabolism, genetic susceptibility, and risk of premalignant skin lesions in Bangladesh. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:1270–1278
Antonelli R, Shao K, Thomas DJ, Sams R II, Cowden J (2014) AS3MT, GSTO, and PNP polymorphisms: impact on arsenic methylation and implications for disease susceptibility. Environ Res 132:156–167
Arnold LL, Suzuki S, Yokohira M, Kakiuchi-Kiyota S, Pennington KL, Cohen SM (2014) Time course of urothelial changes in rats and mice orally administered arsenite. Toxicol Pathol 42:855–862
Chan DC, Barrett PH, Watts GF (2004) Lipoprotein transport in the metabolic syndrome: pathophysiological and interventional studies employing stable isotopy and modelling methods. Clin Sci (Lond) 107:233–249
Chen YC, Guo YL, Su HJ, Hsueh YM, Smith TJ, Ryan LM, Lee MS, Chao SC, Lee JY, Christiani DC (2003) Arsenic methylation and skin cancer risk in southwestern Taiwan. J Occup Environ Med 45:241–248
Chen Y, Parvez F, Gamble M, Islam T, Ahmed A, Argos M, Graziano JH, Ahsan H (2009) Arsenic exposure at low-to-moderate levels and skin lesions, arsenic metabolism, neurological functions, and biomarkers for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases: review of recent findings from the Health Effects of Arsenic Longitudinal Study (HEALS) in Bangladesh. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 239:184–192
Chen B, Arnold LL, Cohen SM, Thomas DJ, Le XC (2011) Mouse arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase genotype affects metabolism and tissue dosimetry of arsenicals after arsenite administration in drinking water. Toxicol Sci 124:320–326
Chen JW, Wang SL, Wang YH, Sun CW, Huang YL, Chen CJ et al (2012) Arsenic methylation, GSTO1 polymorphisms, and metabolic syndrome in an arseniasis endemic area of southwestern Taiwan. Chemosphere 88:432–438
Cole LK, Vance JE, Vance DE (2012) Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and lipoprotein metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1821:754–761
Currier JM, Svoboda M, Matoušek T, Dĕdina J, Stýblo M (2011) Direct analysis and stability of methylated trivalent arsenic metabolites in cells and tissues. Metallomics 3:1347–1354
Del Razo LM, García-Vargas GG, Valenzuela OL, Hernandez-Castellanos E, Sánchez-Peña LC, Drobná Z, Loomis D, Stýblo M (2011) Exposure to arsenic in drinking water is associated with increased prevalence of diabetes: a cross-sectional study in the Zimapán and Lagunera Regions in Mexico. Environ Health 10:73
Díaz-Villaseñor A, Sánchez-Soto MC, Cebrián ME, Os-trosky-Wegman P, Hiriart M (2006) Sodium arsenite impairs insulin secretion and transcription in pancreatic β-cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 214:30–34
Dodmane PR, Arnold LL, Pennington KL, Thomas DJ, Cohen SM (2013) Effect of dietary treatment with dimethylarsinous acid (DMA(III)) on the urinary bladder epithelium of arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase (As3mt) knockout and C57BL/6 wild type female mice. Toxicology 305:130–135
Dodmane PR, Arnold LL, Muirhead DE, Suzuki S, Yokohira M, Pennington KL, Dave BJ, Lu X, Le XC, Cohen SM (2014) Characterization of intracellular inclusions in the urothelium of mice exposed to inorganic arsenic. Toxicol Sci 137:36–46
Douillet C, Currier JM, Saunders J, Bodnar W, Matoušek T, Stýblo M (2013) Methylated trivalent arsenicals are potent inhibitors of glucose stimulated insulin secretion by murine pancreatic islets. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 267:11–15
Drobná Z, Naranmandura H, Kubachka KM, Edwards BC, Herbin-Davis K, Styblo M, Le XC, Creed JT, Maeda N, Hughes MF et al (2009) Disruption of the arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase gene in the mouse alters the phenotype for methylation of arsenic and affects distribution and retention of orally administered arsenate. Chem Res Toxicol 22:1713–1720
Ferrannini E (1998) Insulin resistance versus insulin deficiency in non-insulindependent diabetes mellitus: problems and prospects. Endocr Rev 19:477–490
Fu J, Woods CG, Yehuda-Shnaidman E, Zhang Q, Wong V, Collins S, Sun G, Andersen ME, Pi J (2010) Low-level arsenic impairs glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells: involvement of cellular adaptive response to oxidative stress. Environ Health Perspect 118:864–870
Hernández-Zavala A, Matoušek T, Drobná Z, Adair BM, Dĕdina J, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M (2008) Speciation of arsenic in biological matrices by automated hydride generation-cryotrapping-atomic absorption spectrometry with multiple microflame quartz tube atomizer (multiatomizer). J Anal At Spectrom 23:342–351
Huang YK, Pu YS, Chung CJ, Shiue HS, Yang MH, Chen CJ, Hsueh YM (2008) Plasma folate level, urinary arsenic methylation profiles, and urothelial carcinoma susceptibility. Food Chem Toxicol 46:929–938
Huang MC, Douillet C, Su M, Zhou K, Wu T, Chen W, Galanko JA, Drobná Z, Saunders RJ, Martin E, Fry RC, Jia W, Stýblo M (2016a) Metabolomic profiles of arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase knockout mice: effect of sex and arsenic exposure. Arch Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00204-016-1676-0
Huang MC, Douillet CC, Stýblo M (2016b) Knockout of arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase results in sex-dependent changes in phosphatidylcholine metabolism in mice. Arch Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00204-016-1844-2
Hughes MF, Edwards BC, Herbin-Davis KM, Saunders J, Styblo M, Thomas DJ (2010) Arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase genotype affects steady-state distribution and clearance of arsenic in arsenate-treated mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 249:217–223
IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2004) Volume 84, some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. WHO-International Agency for Research on Cancer, Lyon
Kim NH, Mason CC, Nelson RG, Afton SE, Essader AS, Medlin JE, Levine KE, Hoppin JA, Lin C, Knowler WC, Sandler DP (2013) Arsenic exposure and incidence of type 2 diabetes in Southwestern American Indians. Am J Epidemiol 177:962–969
Kligerman AD, Malik SI, Campbell JA (2010) Cytogenetic insights into DNA damage and repair of lesions induced by a monomethylated trivalent arsenical. Mutat Res 695:2–8
Li X, Li B, Xi S, Zheng Q, Wang D, Sun G (2013) Association of urinary monomethylated arsenic concentration and risk of hypertension: a cross-sectional study from arsenic contaminated areas in northwestern China. Environ Health 12:37
Lin S, Shi Q, Nix FB, Styblo M, Beck MA, Herbin-Davis KM, Hall LL, Simeonsson JB, Thomas DJ (2001) A novel S-adenosyl-l-methionine:arsenic(III) methyltransferase from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem 277:10795–10803
Matoušek T, Hernández-Zavala A, Svoboda M, Langerová L, Adair BM, Drobná Z, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M, Dĕdina J (2008) Oxidation state specific generation of arsines from methylated arsenicals based on l-cysteine treatment in buffered media for speciation analysis by hydride generation—automated cryotrapping—gas chromatography-atomic absorption spectrometry with the multiatomizer. Spetrochim Acta Part B 63:396–406
Maull EA, Ahsan H, Cooper G, Edwards J, Longnecker M, Navas-Acien A, Pi J, Silbergeld E, Styblo M, Tseng C-H, Thayer K, Loomis D (2012) Evaluation of the association be-tween arsenic and diabetes: a National Toxicology Program workshop review. Environ Health Perspect 120:1658–1670
Mendez MA, González-Horta C, Sánchez-Ramírez B, Ballinas-Casarrubias L, Hernández Cerón R, Viniegra Morales D, Baeza Terrazas FA, Ishida MC, Gutiérrez-Torres DS, Saunders RJ, Drobná Z, Fry RC, Buse JB, Loomis D, García-Vargas GG, Del Razo LM, Stýblo M (2016) Chronic exposure to arsenic and markers of cardiometabolic risk: a cross-sectional study in Chihuahua, Mexico. Environ Health Perspect 124:104–111
Moon K, Guallar E, Navas-Acien A (2012) Arsenic exposure and cardiovascular disease: an updated systematic review. Curr Atheroscler Rep 14:542–555
Nizam S, Kato M, Yatsuya H, Khalequzzaman M, Ohnuma S, Naito H, Nakajima T (2013) Differences in urinary arsenic metabolites between diabetic and non-diabetic subjects in Bangladesh. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:1006–1019
Paul DS, Harmon AW, Devesa V, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M (2007a) Molecular mechanisms of the diabetogenic effects of arsenic: inhibition of insulin signaling by arsenite and methylarsonous acid. Environ Health Perspect 115:734–742
Paul DS, Hernández-Zavala A, Walton FS, Adair BM, Dĕdina J, Matoušek T, Styblo M (2007b) Examination of the effects of arsenic on glucose homeostasis in cell culture and animal studies: development of a mouse model for arsenic-induced diabetes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:305–314
Paul DS, Walton FS, Saunders RJ, Styblo M (2011) Characterization of the impaired glucose homeostasis produced in C57BL/6 mice by chronic exposure to arsenic and high-fat diet. Environ Health Perspect 119:1104–1109
States JC, Srivastava S, Chen Y, Barchowsky A (2009) Arsenic and cardiovascular disease. Toxicol Sci 107:312–323
Stýblo M, Del Razo LM, Vega L, Germolec DR, LeCluyse EL, Hamilton GA, Reed W, Wang C, Cullen WR, Thomas DJ (2000) Comparative toxicity of trivalent and pentavalent inorganic and methylated arsenicals in human cells. Arch Toxicol 74:289–299
Stýblo M, Drobná Z, Jaspers I, Lin S, Thomas DJ (2002) The role of biomethylation in toxicity and carcinogenicity of arsenic: a research update. Environ Health Perspect 110(Suppl 5):767–771
Thomas DJ, Li J, Waters SB, Xing W, Adair BM, Drobna Z, Devesa V, Styblo M (2007) Arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase and the methylation of arsenicals. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 232:3–13
Tseng C-H (2009) A review on environmental factors regulating arsenic methylation in humans. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 235:338–350
Vahter M (1994) Species differences in the metabolism of arsenic compounds. Appl Organomet Chem 8:175–182
Walton FS, Harmon AW, Paul DS, Drobna Z, Patel YM, Styblo M (2004) Inhibition of insulin-dependent glucose uptake by trivalent arsenicals: possible mechanism of arsenic-induced diabetes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198:424–433
Wang SL, Chang FH, Liou SH, Wang HJ, Li WF, Hsieh DP (2007) Inorganic arsenic exposure and its relation to metabolic syndrome in an industrial area of Taiwan. Environ Int 33:805–811
Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Pratley RE (2001) Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction are independent predictors of worsening of glucose tolerance during each stage of type 2 diabetes development. Diabetes Care 24:89–94
Wnek SM, Kuhlman CL, Camarillo JM, Medeiros MK, Liu KJ, Lau SS, Gandolfi AJ (2011) Interdependent genotoxic mechanisms of monomethylarsonous acid: role of ROS-induced DNA damage and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition in the malignant transformation of urothelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 257:1–13
Wu F, Jasmine F, Kibriya MG, Liu M, Wójcik O, Parvez F, Rahaman R, Roy S, Paul-Brutus R, Segers S, Slavkovich V, Islam T, Levy D, Mey JL, van Geen A, Graziano JH, Ahsan H, Chen Y (2012) Association between arsenic exposure from drinking water and plasma levels of cardiovascular markers. Am J Epidemiol 175:1252–1261
Yokohira M, Arnold LL, Pennington KL, Suzuki S, Kakiuchi-Kiyota S, Herbin-Davis K, Thomas DJ, Cohen SM (2010) Severe systemic toxicity and urinary bladder cytotoxicity and regenerative hyperplasia induced by arsenite in arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase knockout mice. A preliminary report. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 246:1–7
Yokohira M, Arnold LL, Pennington KL, Suzuki S, Kakiuchi-Kiyota S, Herbin-Davis K, Thomas DJ, Cohen SM (2011) Effect of sodium arsenite dose administered in the drinking water on the urinary bladder epithelium of female arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase knockout mice. Toxicol Sci 121:257–266
Yu RC, Hsu KH, Chen CJ, Froines JR (2000) Arsenic methylation capacity and skin cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 9:1259–1262
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. David Thomas (US EPA) for his continuous support and advice regarding the establishment and maintenance of As3mt-KO mouse colony at UNC Chapel Hill.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Institute of Health (R01ES022697 and DK 056350) and in part by National Research Service Award from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH (T32 ES007126).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douillet, C., Huang, M.C., Saunders, R.J. et al. Knockout of arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase is associated with adverse metabolic phenotype in mice: the role of sex and arsenic exposure. Arch Toxicol 91, 2617–2627 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1890-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1890-9