Abstract
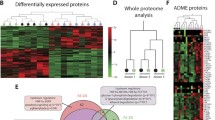
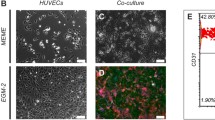
Liver injury as a result of a sterile inflammation is closely linked to the activation of immune cells, including macrophages, by damaged hepatocytes. This interaction between immune cells and hepatocytes is as yet not considered in any of the in vitro test systems applied during the generation of new drugs. Here, we established and characterized a novel in vitro co-culture model with two human cell lines, HepG2 and differentiated THP-1. Ketoconazole, an antifungal drug known for its hepatotoxicity, was used as a model compound in the testing of the co-culture. Single cultures of HepG2 and THP-1 cells were studied as controls. Different metabolism patterns of ketoconazole were observed for the single and co-culture incubations as well as for the different cell types. The main metabolite N-deacetyl ketoconazole was found in cell pellets, but not in supernatants of cell cultures. Global proteome analysis showed that the NRF2-mediated stress response and the CXCL8 (IL-8) pathway were induced by ketoconazole treatment under co-culture conditions. The upregulation and ketoconazole-induced secretion of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, including CXCL8, TNF-α and CCL3, was observed in the co-culture system only, but not in single cell cultures. Taking together, we provide evidence that the co-culture model applied might be suitable to serve as tool for the prediction of chemical-induced sterile inflammation in liver tissue in vivo.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CCL3:
-
Chemokine (C–C-motif) ligand 3
- CD54:
-
Cluster of differentiation 54
- CXCL8:
-
C–X–C-motif ligand 8, interleukin 8
- DAK:
-
N-deacetyl ketoconazole
- GM-CSF:
-
Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- HMGB1:
-
High-mobility group box 1
- IL-1rα:
-
Interleukin 1 receptor-α
- KTZ:
-
Ketoconazole
- LC50 :
-
Half maximal toxic concentration
- MIF:
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- Serpin E1:
-
Serpin peptide inhibitor clade E (nexin, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1)
References
Adams DH, Ju C, Ramaiah SK et al (2010) Mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury. Toxicol Sci 115:307–321
Au JS, Navarro VJ, Rossi S (2011) Review article : drug-induced liver injury—its pathophysiology and evolving diagnostic tools. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34:11–20
Bass DA, Parce JW, Dechatelet LR et al (1983) Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: a graded response to membrane stimulation. J Immunol 130:1910–1917
Baxter JG, Brass C, Schentag JJ, Slaughter RL (1986) Pharmacokinetics of ketoconazole administered intravenously to dogs and orally as tablet and solution to humans and dogs. J Pharm Sci 75:443–447
Blazka ME, Wilmer JL, Holladay SD et al (1995) Role of proinflammatory cytokines in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 133:43–52
Bourdi M, Masubuchi Y, Reilly TP et al (2002a) Protection against acetaminophen-induced liver injury and lethality by interleukin 10: role of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Hepatology 35:289–298
Bourdi M, Reilly TP, Elkahloun AG et al (2002b) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor in drug-induced liver injury: a role in susceptibility and stress responsiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 294:225–230
Brenner C, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Kroemer G (2013) Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J Hepatol 59:583–594
Chen M, Vijay V, Shi Q et al (2011) FDA-approved drug labeling for the study of drug-induced liver injury. Drug Discov Today 16:697–703
Dong Z, Wei H, Sun R, Tian Z (2007) The roles of innate immune cells in liver injury and regeneration. Cell Mol Immunol 4:241–252
Donnelly SC, Haslett C, Reid PT et al (1997) Regulatory role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat Med 3:320–323
Dragomir A-C, Laskin JD, Laskin DL (2011) Macrophage activation by factors released from acetaminophen-injured hepatocytes: potential role of HMGB1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 253:170–177
Dykens J, Will Y (2007) The significance of mitochondrial toxicity testing in drug development. Drug Discov Today 12:777–785
Edling Y, Sivertsson LK, Butura A et al (2009) Increased sensitivity for troglitazone-induced cytotoxicity using a human in vitro co-culture model. Toxicol Vitr 23:1387–1395
Fitch WL, Tran T, Young M et al (2009) Revisiting the metabolism of ketoconazole using accurate mass. Drug Metab Lett 3:191–198
Grattagliano I, Bonfrate L, Diogo CV et al (2009) Biochemical mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: certainties and doubts. World J Gastroenterol 15:4865–4876
Greenblatt DJ (2014) The ketoconazole legacy. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 3:1–3
Gupta AK, Daigle D, Foley KA (2015) Drug safety assessment of oral formulations of ketoconazole. Expert Opin Drug Saf 14:325–334
Heel RC, Brogden RN, Carmine A et al (1982) Ketoconazole: a review of its therapeutic efficacy in superficial and systemic fungal infections. Drugs 23:1–36
Herpers B, Wink S, Fredriksson L et al (2015) Activation of the Nrf2 response by intrinsic hepatotoxic drugs correlates with suppression of NF-κB activation and sensitizes toward TNFα-induced cytotoxicity. Arch Toxicol [Epub ahead of print]
Hitzler M, Bergert A, Luch A, Peiser M (2013) Evaluation of selected biomarkers for the detection of chemical sensitization in human skin: a comparative study applying THP-1, MUTZ-3 and primary dendritic cells in culture. Toxicol In Vitro 27:1659–1669
Hoebe KH, Witkamp RF, Fink-Gremmels J et al (2001) Direct cell-to-cell contact between Kupffer cells and hepatocytes augments endotoxin-induced hepatic injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 280:G720–G728
Hoeke H, Roeder S, Bertsche T et al (2015) Monitoring of drug intake during pregnancy by questionnaires and LC-MS/MS drug urine screening: evaluation of both monitoring methods. Drug Test Anal 7:695–702
Hoofnagle JH, Serrano J, Knoben JE, Navarro VJ (2013) LiverTox: a website on drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology 57:873–874
Huang Y-C, Colaizzi JL, Bierman RH et al (1986) Pharmacokinetics and dose proportionality of Ketoconazole in normal volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 206–210
Jaeschke H, Williams CD, Ramachandran A, Bajt ML (2012) Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and repair: the role of sterile inflammation and innate immunity. Liver Int 32:8–20
Kaplowitz N (2005) Idiosyncratic drug hepatotoxicity. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:489–499
Kiorpelidou E, Foster B, Farrell J et al (2012) IL-8 release from human neutrophils cultured with pro-haptenic chemical sensitizers. Chem Res Toxicol 25:2054–2056
Krenkel O, Mossanen JC, Tacke F (2014) Immune mechanisms in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 3:331–343
Liu SF, Ye X, Malik AB (1999) Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation by pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate prevents In vivo expression of proinflammatory genes. Circulation 100:1330–1337
Louis H, Van Laethem JL, Wu W et al (1998) Interleukin-10 controls neutrophilic infiltration, hepatocyte proliferation, and liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice. Hepatology 28:1607–1615
Lu P, Nakamoto Y, Nemoto-Sasaki Y et al (2003) Potential interaction between CCR1 and its ligand, CCL3, induced by endogenously produced interleukin-1 in human hepatomas. Am J Pathol 162:1249–1258
Marques PE, Amaral SS, Pires DA et al (2012) Chemokines and mitochondrial products activate neutrophils to amplify organ injury during mouse acute liver failure. Hepatology 56:1971–1982
Marques PE, Oliveira AG, Pereira RV et al (2015) Hepatic DNA deposition drives drug-induced liver injury and inflammation in mice. Hepatology 61:348–360
Masson MJ, Collins LA, Pohl LR (2010) The role of cytokines in the mechanism of adverse drug reactions. Handb Exp Pharmacol 195–231
Melino M, Gadd VL, Walker GV et al (2012) Macrophage secretory products induce an inflammatory phenotype in hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 18:1732–1744
Mickelson JK, Kukielka G, Bravenec JS et al (1995) Differential expression and release of CD54 induced by cytokines. Hepatology 2:866–875
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Murphy MP (2009) How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem J 417:1–13
Navarro VJ, Barnhart H, Bonkovsky HL et al (2014) Liver injury from herbals and dietary supplements in the US Drug Induced Liver Injury Network. Hepatology 60:1399–1408
Pessayre D, Fromenty B, Berson A et al (2012) Central role of mitochondria in drug-induced liver injury. Drug Metab Rev 44:34–87
R Core Team (2013) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Raschi E, Poluzzi E, Koci A et al (2014) Assessing liver injury associated with antimycotics: concise literature review and clues from data mining of the FAERS database. World J Hepatol 6:601–612
Reers M, Smith TW, Chen LB (1991) J-aggregate formation of a carbocyanine as a quantitative fluorescent indicator of membrane potential. Biochemistry 30:4480–4486
Ren Y, Tsui H-T, Poon RT-P et al (2003) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: roles in regulating tumor cell migration and expression of angiogenic factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 107:22–29
Ritz C, Streibig JC (2005) Bioassay Analysis Using R. J Stat Softw 12:1–22
Roberts RA, Ganey PE, Ju C et al (2007) Role of the Kupffer cell in mediating hepatic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Toxicol Sci 96:2–15
Rodriguez RJ, Acosta D (1997a) N-deacetyl ketoconazole-induced hepatotoxicity culture system of rat hepatocytes. Toxicology 117:123–131
Rodriguez RJ, Acosta D (1997b) Metabolism of ketoconazole and deacetylated ketoconazole by rat hepatic microsomes and flavin-containing monooxygenases. Drug Metab Dispos 25:772–777
Rodriguez RJ, Miranda CL (2000) Isoform specificity of N-deacetyl ketoconazole by human and rabbit flavin-containing monooxygenases. Drug Metab Dispos 28:1083–1086
Roebuck KA, Finnegan A (1999) Regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (CD54) gene expression. J Leukoc Biol 66:876–888
Salbach J, Kliemt S, Rauner M et al (2012) The effect of the degree of sulfation of glycosaminoglycans on osteoclast function and signaling pathways. Biomaterials 33:8418–8429
Smiley ST, Reers M, Mottola-Hartshorn C et al (1991) Intracellular heterogeneity in mitochondrial membrane potentials revealed by a J-aggregate-forming lipophilic cation JC-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3671–3675
Steuerwald NM, Foureau DM, Norton HJ et al (2013) Profiles of serum cytokines in acute drug-induced liver injury and their prognostic significance. PLoS ONE 8:81974
Sugar AM, Alsip SG, Galgiani JN et al (1987) Pharmacology and toxicity of high-dose ketoconazole. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31:1874–1878
Thompson K, Maltby J, Fallowfield J et al (1998) Interleukin-10 expression and function in experimental murine liver inflammation and fibrosis. Hepatology 28:1597–1606
Tsuchiya S, Kobayashi Y, Goto Y et al (1982) Induction of maturation in cultured human monocytic leukemia cells by a Phorbol Diester. Cancer Res 42:1530–1536
Tukov FF, Maddox JF, Amacher DE et al (2006) Modeling inflammation-drug interactions in vitro: a rat Kupffer cell-hepatocyte coculture system. Toxicol In Vitro 20:1488–1499
Wanninger J, Neumeier M, Weigert J et al (2009) Adiponectin-stimulated CXCL8 release in primary human hepatocytes is regulated by ERK1/ERK2, p38 MAPK, NF-kappaB, and STAT3 signaling pathways. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 297:G611–G618
Wissenbach DK, Meyer MR, Remane D et al (2011) Development of the first metabolite-based LC-MS(n) urine drug screening procedure-exemplified for antidepressants. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:79–88
Yuan Y, Liu J, Liu T et al (2010) Chemokine CCL3 facilitates the migration of hepatoma cells by changing the concentration intracellular Ca2+. Hepatol Res 40:424–431
Zimmermann HW, Seidler S, Gassler N et al (2011) Interleukin-8 is activated in patients with chronic liver diseases and associated with hepatic macrophage accumulation in human liver fibrosis. PLoS ONE 6:21381
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Barbara Gerding for excellent technical assistance and S. Weichenhain for discussions. The financial support of the BfR through intramural Grants SFP 1322-530 and 1329-529 is gratefully acknowledged. Florent Jouy and Scarlett Gebauer acknowledge network funding through Helmholtz Interdisciplinary Graduate School for Environmental Research (HIGRADE). We also acknowledge the ProVis platform in general and in particular Benjamin Scheer for excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Franziska Wewering, Florent Jouy and Dirk K. Wissenbach have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wewering, F., Jouy, F., Wissenbach, D.K. et al. Characterization of chemical-induced sterile inflammation in vitro: application of the model compound ketoconazole in a human hepatic co-culture system. Arch Toxicol 91, 799–810 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1686-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1686-y