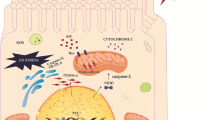
Abstract
Cisplatin and its derivatives are widely used chemotherapeutic drugs for cancer treatment. However, they have debilitating side effects in normal tissues and induce ototoxicity, neurotoxicity, and nephrotoxicity. In kidneys, cisplatin preferentially accumulates in renal tubular cells causing tubular cell injury and death, resulting in acute kidney injury (AKI). Recent studies have suggested that DNA damage and the associated DNA damage response (DDR) are an important pathogenic mechanism of AKI following cisplatin treatment. Activation of DDR may lead to cell cycle arrest and DNA repair for cell survival or, in the presence of severe injury, kidney cell death. Modulation of DDR may provide novel renoprotective strategies for cancer patients undergoing cisplatin chemotherapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu A, Krishnamurthy S (2010) Cellular responses to cisplatin-induced DNA damage. J Nucleic Acids. doi:10.4061/2010/201367
Bowden NA (2014) Nucleotide excision repair: why is it not used to predict response to platinum-based chemotherapy? Cancer Lett 346:163–171. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.01.005
Cepeda V, Fuertes MA, Castilla J, Alonso C, Quevedo C, Perez JM (2007) Biochemical mechanisms of cisplatin cytotoxicity. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 7:3–18
Choi HJ et al (2013) NEK8 links the ATR-regulated replication stress response and S phase CDK activity to renal ciliopathies. Mol Cell 51:423–439. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.006
Ciccia A, Elledge SJ (2010) The DNA damage response: making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell 40:179–204. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.019
Cuadrado M, Martinez-Pastor B, Murga M, Toledo LI, Gutierrez-Martinez P, Lopez E, Fernandez-Capetillo O (2006) ATM regulates ATR chromatin loading in response to DNA double-strand breaks. J Exp Med 203:297–303. doi:10.1084/jem.20051923
Cummings BS, Schnellmann RG (2002) Cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis: caspase 3-dependent and -independent pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:8–17
Dasari S, Tchounwou PB (2014) Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740:364–378. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.07.025
Di C et al (2013) Mechanisms, function and clinical applications of DNp73. Cell Cycle 12:1861–1867. doi:10.4161/cc.24967
Francescato HD, Costa RS, Junior FB, Coimbra TM (2007) Effect of JNK inhibition on cisplatin-induced renal damage. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:2138–2148. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm144
Fujikawa Y, Kawanishi M, Kuraoka I, Yagi T (2014) Frequencies of mutagenic translesion DNA synthesis over cisplatin-guanine intra-strand crosslinks in lacZ plasmids propagated in human cells. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 770:23–28. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2014.05.006
Gonfloni S et al (2009) Inhibition of the c-Abl-TAp63 pathway protects mouse oocytes from chemotherapy-induced death. Nat Med 15:1179–1185. doi:10.1038/nm.2033
Guggenheim ER, Xu D, Zhang CX, Chang PV, Lippard SJ (2009) Photoaffinity isolation and identification of proteins in cancer cell extracts that bind to platinum-modified DNA. Chembiochem Eur J Chem Biol 10:141–157. doi:10.1002/cbic.200800471
Guo JY et al (2008) Aven-dependent activation of ATM following DNA damage. Curr Biol CB 18:933–942. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.05.045
Hlavin EM, Smeaton MB, Miller PS (2010) Initiation of DNA interstrand cross-link repair in mammalian cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:604–624. doi:10.1002/em.20559
Hodeify R, Tarcsafalvi A, Megyesi J, Safirstein RL, Price PM (2011) Cdk2-dependent phosphorylation of p21 regulates the role of Cdk2 in cisplatin cytotoxicity. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 300:F1171–F1179. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00507.2010
Hurley PJ, Bunz F (2007) ATM and ATR: components of an integrated circuit. Cell Cycle 6:414–417
Jaamaa S et al (2010) DNA damage recognition via activated ATM and p53 pathway in nonproliferating human prostate tissue. Cancer Res 70:8630–8641. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0937
Jackson PK (2013) Nek8 couples renal ciliopathies to DNA damage and checkpoint control. Mol Cell 51:407–408. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.013
Jiang M, Dong Z (2008) Regulation and pathological role of p53 in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:300–307. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.139162
Jiang M, Wei Q, Wang J, Du Q, Yu J, Zhang L, Dong Z (2006) Regulation of PUMA-alpha by p53 in cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis. Oncogene 25:4056–4066. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209440
Jiang M et al (2007) Nutlin-3 protects kidney cells during cisplatin therapy by suppressing Bax/Bak activation. J Biol Chem 282:2636–2645. doi:10.1074/jbc.M606928200
Jiang Z, Kamath R, Jin S, Balasubramani M, Pandita TK, Rajasekaran B (2011) Tip60-mediated acetylation activates transcription independent apoptotic activity of Abl. Mol Cancer 10:88. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-10-88
Kang KP et al (2011) Luteolin ameliorates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice by regulation of p53-dependent renal tubular apoptosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:814–822. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfq528
Kemp MG, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Sancar A (2011) The DNA damage response kinases DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK) and ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) Are stimulated by bulky adduct-containing DNA. J Biol Chem 286:19237–19246. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.235036
Kharbanda S et al (2000) Activation of MEK kinase 1 by the c-Abl protein tyrosine kinase in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 20:4979–4989
Kim WJ, Rajasekaran B, Brown KD (2007) MLH1- and ATM-dependent MAPK signaling is activated through c-Abl in response to the alkylator N-methyl-N’-nitro-N’-nitrosoguanidine. J Biol Chem 282:32021–32031. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701451200
Koike M, Mashino M, Sugasawa J, Koike A (2008) Histone H2AX phosphorylation independent of ATM after X-irradiation in mouse liver and kidney in situ. J Radiat Res 49:445–449
Kruger K, Thomale J, Stojanovic N, Osmak M, Henninger C, Bormann S, Fritz G (2015) Platinum-induced kidney damage: unraveling the DNA damage response (DDR) of renal tubular epithelial and glomerular endothelial cells following platinum injury. Biochim Biophys Acta 1854:685–698. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.12.033
Kutuk O, Temel SG, Tolunay S, Basaga H (2010) Aven blocks DNA damage-induced apoptosis by stabilising Bcl-xL. Eur J Cancer 46:2494–2505. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2010.06.011
Lando DY, Chang CL, Fridman AS, Grigoryan IE, Galyuk EN, Hsueh YW, Hu CK (2014) Comparative thermal and thermodynamic study of DNA chemically modified with antitumor drug cisplatin and its inactive analog transplatin. J Inorg Biochem 137:85–93. doi:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2014.04.010
Levy D, Adamovich Y, Reuven N, Shaul Y (2007) The Yes-associated protein 1 stabilizes p73 by preventing Itch-mediated ubiquitination of p73. Cell Death Differ 14:743–751. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402063
Levy D, Adamovich Y, Reuven N, Shaul Y (2008) Yap1 phosphorylation by c-Abl is a critical step in selective activation of proapoptotic genes in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell 29:350–361. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.12.022
Li GM (2008) Mechanisms and functions of DNA mismatch repair. Cell Res 18:85–98. doi:10.1038/cr.2007.115
Livingston MJ, Dong Z (2014) Autophagy in acute kidney injury. Semin Nephrol 34:17–26. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2013.11.004
Lovejoy CA, Cortez D (2009) Common mechanisms of PIKK regulation. DNA Repair 8:1004–1008. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.04.006
Ma Z, Wei Q, Dong G, Huo Y, Dong Z (2014) DNA damage response in renal ischemia-reperfusion and ATP-depletion injury of renal tubular cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1842:1088–1096. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.04.002
Megyesi J, Safirstein RL, Price PM (1998) Induction of p21WAF1/CIP1/SDI1 in kidney tubule cells affects the course of cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. J Clin Investig 101:777–782. doi:10.1172/JCI1497
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2:2490–2518. doi:10.3390/toxins2112490
Miyaji T, Kato A, Yasuda H, Fujigaki Y, Hishida A (2001) Role of the increase in p21 in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 12:900–908
Myers K, Gagou ME, Zuazua-Villar P, Rodriguez R, Meuth M (2009) ATR and Chk1 suppress a caspase-3-dependent apoptotic response following DNA replication stress. PLoS Genet 5:e1000324. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000324
Nakano K, Vousden KH (2001) PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol Cell 7:683–694
Nehme A, Baskaran R, Nebel S, Fink D, Howell SB, Wang JY, Christen RD (1999) Induction of JNK and c-Abl signalling by cisplatin and oxaliplatin in mismatch repair-proficient and -deficient cells. Br J Cancer 79:1104–1110. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690176
Oh GS, Kim HJ, Shen A, Lee SB, Khadka D, Pandit A, So HS (2014) Cisplatin-induced kidney dysfunction and perspectives on improving treatment strategies. Electrolyte Blood Press 12:55–65. doi:10.5049/EBP.2014.12.2.55
Pabla N, Dong Z (2008) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int 73:994–1007. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5002786
Pabla N, Dong Z (2012) Sibling rivalry in checkpoint control of cell cycle and DNA damage response. Cell Cycle 11:1866–1867. doi:10.4161/cc.20416
Pabla N, Huang S, Mi QS, Daniel R, Dong Z (2008) ATR-Chk2 signaling in p53 activation and DNA damage response during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 283:6572–6583. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707568200
Pabla N, Dong G, Jiang M, Huang S, Kumar MV, Messing RO, Dong Z (2011a) Inhibition of PKCdelta reduces cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity without blocking chemotherapeutic efficacy in mouse models of cancer. J Clin Investig 121:2709–2722. doi:10.1172/JCI45586
Pabla N, Ma Z, McIlhatton MA, Fishel R, Dong Z (2011b) hMSH2 recruits ATR to DNA damage sites for activation during DNA damage-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 286:10411–10418. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.210989
Pabla N, Bhatt K, Dong Z (2012) Checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1)-short is a splice variant and endogenous inhibitor of Chk1 that regulates cell cycle and DNA damage checkpoints. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:197–202. doi:10.1073/pnas.1104767109
Patil M, Pabla N, Ding HF, Dong Z (2013a) Nek1 interacts with Ku80 to assist chromatin loading of replication factors and S-phase progression. Cell Cycle 12:2608–2616. doi:10.4161/cc.25624
Patil M, Pabla N, Dong Z (2013b) Checkpoint kinase 1 in DNA damage response and cell cycle regulation. Cell Mol Life Sci CMLS 70:4009–4021. doi:10.1007/s00018-013-1307-3
Paull TT, Lee JH (2005) The Mre11/Rad50/Nbs1 complex and its role as a DNA double-strand break sensor for ATM. Cell Cycle 4:737–740
Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Jiang M, Wei Q, Smith R, Yin XM, Dong Z (2008) Autophagy is cytoprotective during cisplatin injury of renal proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int 74:631–640. doi:10.1038/ki.2008.214
Preyer M, Shu CW, Wang JY (2007) Delayed activation of Bax by DNA damage in embryonic stem cells with knock-in mutations of the Abl nuclear localization signals. Cell Death Differ 14:1139–1148. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402119
Price PM, Megyesi J, Saf Irstein RL (2004a) Cell cycle regulation: repair and regeneration in acute renal failure. Kidney Int 66:509–514. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.761_8.x
Price PM, Safirstein RL, Megyesi J (2004b) Protection of renal cells from cisplatin toxicity by cell cycle inhibitors. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 286:F378–F384. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00192.2003
Price PM, Yu F, Kaldis P, Aleem E, Nowak G, Safirstein RL, Megyesi J (2006) Dependence of cisplatin-induced cell death in vitro and in vivo on cyclin-dependent kinase 2. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 17:2434–2442. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006020162
Price PM, Safirstein RL, Megyesi J (2009) The cell cycle and acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 76:604–613. doi:10.1038/ki.2009.224
Roos WP, Kaina B (2013) DNA damage-induced cell death: from specific DNA lesions to the DNA damage response and apoptosis. Cancer Lett 332:237–248. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2012.01.007
Sahu BD, Kuncha M, Sindhura GJ, Sistla R (2013) Hesperidin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute renal injury by decreasing oxidative stress, inflammation and DNA damage. Phytomed Int J Phytother Phytopharmacol 20:453–460. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2012.12.001
Sanchez-Prieto R, Sanchez-Arevalo VJ, Servitja JM, Gutkind JS (2002) Regulation of p73 by c-Abl through the p38 MAP kinase pathway. Oncogene 21:974–979. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205134
Seth R, Yang C, Kaushal V, Shah SV, Kaushal GP (2005) p53-dependent caspase-2 activation in mitochondrial release of apoptosis-inducing factor and its role in renal tubular epithelial cell injury. J Biol Chem 280:31230–31239. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503305200
Shimodaira H, Yoshioka-Yamashita A, Kolodner RD, Wang JY (2003) Interaction of mismatch repair protein PMS2 and the p53-related transcription factor p73 in apoptosis response to cisplatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2420–2425. doi:10.1073/pnas.0438031100
Silva BA, Stambaugh JR, Yokomori K, Shah JV, Berns MW (2014) DNA damage to a single chromosome end delays anaphase onset. J Biol Chem 289:22771–22784. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.535955
Sridevi P, Nhiayi MK, Wang JY (2013) Genetic disruption of Abl nuclear import reduces renal apoptosis in a mouse model of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Cell Death Differ 20:953–962. doi:10.1038/cdd.2013.42
Stojic L, Brun R, Jiricny J (2004) Mismatch repair and DNA damage signalling. DNA Repair 3:1091–1101. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.06.006
Tang J, Wang JY, Parker LL (2012) Detection of early Abl kinase activation after ionizing radiation by using a peptide biosensor. Chembiochem Eur J Chem Biol 13:665–673. doi:10.1002/cbic.201100763
Thomasova D, Anders HJ (2014) Cell cycle control in the kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfu395
Toh WH, Siddique MM, Boominathan L, Lin KW, Sabapathy K (2004) c-Jun regulates the stability and activity of the p53 homologue, p73. J Biol Chem 279:44713–44722. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407672200
Topping RP, Wilkinson JC, Scarpinato KD (2009) Mismatch repair protein deficiency compromises cisplatin-induced apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem 284:14029–14039. doi:10.1074/jbc.M809303200
Tsuruya K et al (2008) Involvement of p53-transactivated Puma in cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell death. Life Sci 83:550–556. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2008.08.002
Vasquez KM (2010) Targeting and processing of site-specific DNA interstrand crosslinks. Environ Mol Mutagen 51:527–539. doi:10.1002/em.20557
Wang JY (2000) Regulation of cell death by the Abl tyrosine kinase. Oncogene 19:5643–5650. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203878
Wang D, Lippard SJ (2005) Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:307–320. doi:10.1038/nrd1691
Wang J, Pabla N, Wang CY, Wang W, Schoenlein PV, Dong Z (2006) Caspase-mediated cleavage of ATM during cisplatin-induced tubular cell apoptosis: inactivation of its kinase activity toward p53. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 291:F1300–F1307. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00509.2005
Wang J et al (2013) Repression of ATR pathway by miR-185 enhances radiation-induced apoptosis and proliferation inhibition. Cell Death Dis 4:e699. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.227
Wei Q, Dong G, Yang T, Megyesi J, Price PM, Dong Z (2007) Activation and involvement of p53 in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 293:F1282–F1291. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00230.2007
Woods D, Turchi JJ (2013) Chemotherapy induced DNA damage response: convergence of drugs and pathways. Cancer Biol Ther 14:379–389. doi:10.4161/cbt.23761
Yoshida K (2008) Nuclear trafficking of pro-apoptotic kinases in response to DNA damage. Trends Mol Med 14:305–313. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2008.05.003
Yoshida K, Miki Y (2005) Enabling death by the Abl tyrosine kinase: mechanisms for nuclear shuttling of c-Abl in response to DNA damage. Cell Cycle 4:777–779
Yuan M, Luong P, Hudson C, Gudmundsdottir K, Basu S (2010) c-Abl phosphorylation of DeltaNp63alpha is critical for cell viability. Cell Death Dis 1:e16. doi:10.1038/cddis.2009.15
Zannini L, Delia D, Buscemi G (2014) CHK2 kinase in the DNA damage response and beyond. J Mol Cell Biol 6:442–457. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mju045
Zhang YX et al (2013) Cisplatin upregulates MSH2 expression by reducing miR-21 to inhibit A549 cell growth. Biomed Pharmacother 67:97–102. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2012.11.008
Zhang D, Liu Y, Wei Q, Huo Y, Liu K, Liu F, Dong Z (2014) Tubular p53 regulates multiple genes to mediate AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol JASN 25:2278–2289. doi:10.1681/ASN.2013080902
Zhou H et al (2004) The induction of cell cycle regulatory and DNA repair proteins in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 200:111–120. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2004.04.003
Acknowledgments
The study was supported in part by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China [81430017], National Basic Research Program of China 973 Program No. 2012CB517601, and the National Institutes of Health and Department of Veterans Administration of USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Pabla, N., Tang, C. et al. DNA damage response in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 89, 2197–2205 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1633-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1633-3