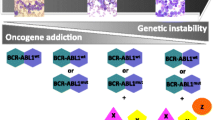
Abstract
Despite the clinical efficacy achieved with frontline therapies for BCR-ABL-positive disease, such as imatinib and second-generation ABL inhibitors like nilotinib or dasatinib that were originally designed to override insensitivity to imatinib, drug resistance still remains a challenge, especially for patients with advanced-stage chronic myeloid leukemia or Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The discovery of BCR-ABL point mutations has been a great asset to furthering our understanding of a major cause of drug resistance, as has discovery of multidrug resistance proteins, dysregulation of signaling molecules downstream of BCR-ABL, and insights into the underlying causes of stromal-mediated chemoresistance. Such elucidation of mechanisms of resistance associated with leukemic cell survival is essential for the optimization of current therapies and enhancement of patient survival via delaying or preventing disease recurrence. Here, we present an overview of the use of nilotinib in combination with other agents against BCR-ABL-positive leukemia, as well as solid tumors, for the purpose of increasing clinical efficacy and overriding drug resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram CL, Courtneidge SA (2000) SRC family tyrosine kinases and growth factor signaling. Exp Cell Res 254:1–13
Adrian FJ, Ding Q, Sim T et al (2006) Allosteric inhibitors of BCR-ABL-dependent cell proliferation. Nat Chem Biol 2:95–102
Bonifacio M, Rigo A, Guardalben E, Bergamini C, Cavalieri E, Fato R (2012) α-Bisabolol is an effective proapoptotic agent against BCR-ABL(+) cells in synergism with imatinib and nilotinib. PLoS One 7:e46674
Bradeen HA, Eide CA, O’Hare T et al (2006) Comparison of imatinib mesylate, dasatinib (BMS-354825), and nilotinib (AMN107) in an N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU)-based mutagenesis screen: high efficacy of drug combinations. Blood 108:2332–2338
Brendel C, Scharenberg C, Dohse M et al (2007) Imatinib mesylate and nilotinib (AMN107) exhibit high-affinity interaction with ABCG2 on primitive hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia 21:1267–1275
Buchdunger E, Matter A, Druker BJ (2001) BCR-ABL inhibition as a modality of CML therapeutics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1551:M11–M18
Burgess MR, Skaggs BJ, Shah NP, Lee FY, Sawyers CL (2005) Comparative analysis of two clinically active BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors reveals the role of conformation-specific binding in resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:3395–3400
Carter TA, Wodicka LM, Shah NP et al (2005) Inhibition of drug-resistant mutants of ABL, KIT, and EGF receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(31):11011–11016
Cavalieri E, Rigo A, Bonifacio M et al (2011) Pro-apoptotic activity of α-bisabolol in preclinical models of primary human acute leukemia cells. J Transl Med 9:45
Chahardouli B, Zaker F, Mousavi SA et al (2013) Evaluation of T315I mutation frequency in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after imatinib resistance. Hematology 18:158–162
Chan WW, Wise SC, Kaufman MD et al (2011) Conformational control inhibition of the BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase, including the gatekeeper T315I mutant, by the switch-control inhibitor DCC-2036. Cancer Cell 19:556–568
Cho JH, Kim KM, Kwon M, Kim JH, Lee J (2012) Nilotinib in patients with metastatic melanoma harboring KIT gene aberration. Invest New Drugs 30:2008–2014
Choi HG, Ren P, Adrian F et al (2010) A type-II kinase inhibitor capable of inhibiting the T315I “gatekeeper” mutant of BCR-ABL. J Med Chem 53:5439–5448
Copland M, Hamilton A, Elrick LJ et al (2006) Dasatinib (BMS-354825) targets an earlier progenitor population than imatinib in primary CML but does not eliminate the quiescent fraction. Blood 107:4532–4539
Cortes J, Rousselot P, Kim DW et al (2007) Dasatinib induces complete hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis. Blood 109:3207–3213
Cortes JE, Kim DW, Pinilla-lbarz J et al (2013) A phase 2 trial of ponatinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med 369:1
Coude MM, Luycx O, Cariou ME et al (2012) Undetectable molecular residual disease after omacetaxine and nilotinib combination therapy in an imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia patient harbouring the BCR-ABL1 T315I gatekeeper mutation. Br J Haematol 157:407–410
Cowan-Jacob SW, Guez V, Fendrich G et al (2004) Imatinib (STI571) resistance in chronic myelogenous leukemia: molecular basis of the underlying mechanisms and potential strategies for treatment. Mini Rev Med Chem 4:285–299
Crawford LJ, Chan ET, Aujay M et al (2014) Synergistic effects of proteasome inhibitor carfilzomib in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in imatinib-sensitive and -resistant chronic myeloid leukemia models. Oncogenesis 3:e90
Danisz K, Blasiak J (2013) Role of anti-apoptotic pathways activated by BCR/ABL in the resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia cells to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Biochim Pol 60:503–514
Das J, Chen P, Norris D et al (2006) 2-Aminothiazole as a novel kinase inhibitor template. Structure-activity relationship studies towards the discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazinyl)]-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinyl]amino)]-1,3-thiazole-5-carboxamide (Dasatinib; BMS-354825) as a potent pan-Src kinase inhibitor. J Med Chem 49:6819–6832
de Weger VA, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH (2014) Cellular and clinical pharmacology of the taxanes docetaxel and paclitaxel—a review. Anticancer Drugs 25:488–494
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV (2000) The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 96:3343–3356
Deng X, Okram B, Ding Q et al (2010) Expanding the diversity of allosteric BCR-ABL inhibitors. J Med Chem 53:6934–6946
Ding J, Romani J, Zaborski M et al (2013) Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR overcomes nilotinib resistance in BCR-ABL1 positive leukemia cells through translational down-regulation of MDM2. PLoS One 8:e83510
Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E et al (1996) Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of BCR-ABL positive cells. Nat Med 2:561–566
Eide CA, Adrian LT, Tyner JW et al (2011) The ABL switch control inhibitor CDD-2036 is active against the chronic myeloid leukemia mutant BCR-ABLT315I and exhibits a narrow resistance profile. Cancer Res 71:3189–3195
Engler JR, Frede A, Saunders VA et al (2010) Chronic myeloid leukemia CD34+ cells have reduced uptake of imatinib due to low OCT-1 activity. Leukemia 24:765–770
Fancelli D, Moll J, Varasi M et al (2006) 1, 4, 5, 6-Tetrahydropyrrolo[3, 4-c]pyrazoles: identification of a potent aurora kinase inhibitor with a favorable antitumor kinase inhibition profile. J Med Chem 49:7247–7251
Fielding AK, Rowe JM, Buck G et al (2014) UKALLX11/ECOG2993: addition of imatinib to a standard treatment regimen enhances long-term outcomes in Philadelphia positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 123:843–850
Gallipoli P, Cook A, Rhodes S, et al (2014) JAK2/STAT5 inhibition by nilotinib with ruxolitinib contributes to the elimination of chronic phase CML CD34+ cells in vitro and in vivo. Blood 124:1492–1501
Gambacorti-Passerini C, Barni R, le Coutre P et al (2000) Role of alpha1 acid glycoprotein in the in vivo resistance of human BCR-ABL (+) leukemic cells to the abl inhibitor STI571. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:1641–1650
Geisler K, Reischer A, Kroeger I et al (2014) Nilotinib combined with interleukin-2 mediates antitumor and immunological effects in a B16 melanoma model. Oncol Rep 31:2015–2020
Giles FJ, Cortes J, Jones D et al (2007) MK-0457, a novel kinase inhibitor, is active in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia or acute lymphocytic leukemia with the T315I BCR-ABL mutation. Blood 109:500–502
Golas JM, Arndt K, Etienne C et al (2003) SKI-606, a 4-anilino-3-quinolinecarbonitrile dual inhibitor of SRC and ABL kinases, is a potent antiproliferative agent against chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in culture and causes regression of K562 xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Res 63:375–381
Gorre ME, Mohammed M, Ellwood K et al (2001) Clinical resistance to STI-571 cancer therapy caused by BCR-ABL gene mutation or amplification. Science 293:876–880
Gumireddy K, Baker SJ, Cosenza SC et al (2005) A non-ATP-competitive inhibitor of BCR-ABL overrides imatinib resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1992–1997
Gurion R, Gaffer-Gvili A, Vidal L et al (2013) Has the time for first-line treatment with second generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia already come? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Haematologica 98:95–102
Hegedus C, Ozvegy-Laczka C, Apati A et al (2009) Interaction of nilotinib, dasatinib and bosutinib with ABCB1 and ABCG2: implications for altered anti-cancer effects and pharmacological properties. Br J Pharmacol 158:1153–1164
Hochhaus A, Kreil S, Corbin AS (2002) Molecular and chromosomal mechanisms of resistance to imatinib (STI571) therapy. Leukemia 16:2190–2196
Hofmann WK, Komor M, Wassmann B et al (2003) Presence of the BCR-ABL mutation Glu255Lys prior to STI571 (imatinib) treatment in patients with Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 102:659–661
Iacob RE, Zhang J, Gray NS, Engen JR (2011) Allosteric interactions between the myristate- and ATP-site of the Abl kinase. PLoS One 6:e15929
Itonaga H, Tsushima H, Hata T et al (2012) Successful treatment of a chronic phase T-315I-mutated chronic myelogenous leukemia patient with a combination of imatinib and interferon alfa. Int J Hematol 95:209–213
Jabbour E, Kantarjian HM, Saglio G et al (2014) Early response with dasatinib or imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia: 3-year follow-up from a randomized phase 3 trial (DASISION). Blood 123:494–500
Jayson GC, Parker GJ, Mullamitha S et al (2005) Blockade of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta by CDP860, a humanized PEGylated di-Fab, leads to a fluid accumulation and is associated with increased tumor vascularized volume. J Clin Oncol 23:973–981
Kantarjian H, Giles F, Wunderle L et al (2006) Nilotinib in imatinib-resistant CML and Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. N Engl J Med 354:2542–2551
Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A et al (2010) Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 362:2260–2270
Kelly KR, Ecsedy J, Medina E et al (2011) The novel Aurora A kinase inhibitor MLN8237 is active in resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia and significantly increases the efficacy of nilotinib. J Cell Mol Med 15:2057–2070
Kimura S, Naito H, Segawa H et al (2005) NS-187, a potent and selective dual BCR-ABL/Lyn tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is a novel agent for imatinib-resistant leukemia. Blood 106:3948–3954
Kodama M, Kitadai Y, Sumida T et al (2010) Expression of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-B and PDGF-receptor β is associated with lymphatic metastasis in human gastric carcinoma. Cancer Sci 101:1984–1989
Koldehoff M, Kordelas L, Beelen DW, Elmaagacli AH (2010) Small interfering RNA against BCR-ABL transcripts sensitize mutated T315I cells to nilotinib. Haematologica 95:388–397
Kumagai M, Manabe A, Pui CH et al (1996) Stroma-supported culture in childhood B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells predicts treatment outcome. J Clin Invest 97:755–760
le Coutre P, Tassi E, Varella-Garcia M et al (2000) Induction of resistance to the Abelson inhibitor STI571 in human leukemic cells through gene amplification. Blood 95:1758–1766
le Coutre P, Ottmann OG, Giles F et al (2008) Nilotinib (formerly AMN107), a highly selective BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is active in patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant accelerated-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 111:1834–1839
Liu Y, Gray NS (2006) Rational design of inhibitors that bind to inactive kinase conformations. Nat Chem Biol 2:358–364
Mahon FX, Deininger MW, Schultheis B (2000) Selection and characterization of BCR-ABL positive cell lines with differential sensitivity to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571: diverse mechanisms of resistance. Blood 96:1070–1079
Manley PW, Cowan-Jacob SW, Buchdunger E et al (2002) Imatinib: a selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Eur J Cancer 38:S19–S27
Melnick JS, Janes J, Kim S et al (2006) An efficient rapid system for profiling the cellular activities of molecular libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3153–3158
Mian AA, Metodieva A, Badura S et al (2012) Allosteric inhibition enhances the efficacy of ABL kinase inhibitors to target unmutated BCR-ABL and BCR-ABL-T315I. BMC Cancer 12:411
Michor F, Hughes TP, Iwasa Y et al (2005) Dynamics of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Nature 435:1267–1270
Nagar B, Bornmann WG, Pellicena P et al (2002) Crystal structures of the kinase domain of c-Abl in complex with the small molecule inhibitors PD173955 and imatinib (STI-571). Cancer Res 62:4236–4243
O’Hare T, Shakespeare WC, Zhu X et al (2009) AP24534, a pan-BCR-ABL inhibitor for chronic myeloid leukemia, potently inhibits the T315I mutant and overcomes mutation-based resistance. Cancer Cell 16:401–412
O’Hare T, Walters DK, Stoffregen EP et al (2005) Combined Abl inhibitor therapy for minimizing drug resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia: Src/Abl inhibitors are compatible with imatinib. Clin Cancer Res 11:6987–6993
Okabe S, Tauchi T, Tanaka Y et al (2014) Efficacy of the dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 in combination with nilotinib against BCR-ABL-positive leukemia cells involves the ABL kinase domain mutation. Cancer Biol Ther 15:207–215
Onoyama M, Kitadai Y, Tanaka Y et al (2013) Combining molecular targeted drugs to inhibit both cancer cells and activated stromal cells in gastric cancer. Neoplasia 15:1391–1399
Ostman A (2004) PDGF receptors-mediators of autocrine tumor growth and regulators of tumor vasculature and stroma. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:275–286
Pantaleo MA, Nannini M, Saponara M et al (2012) Impressive long-term stabilization by nilotinib in two pretreated patients with KIT/PDGFRA wild-type metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Anticancer Drugs 23:567–572
Parameswaran R, Yu M, Lim M, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N (2011) Combination of drug therapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia with a CXCR4 antagonist. Leukemia 25:1314–1323
Puttini M, Coluccia AM, Boschelli F (2006) In vitro and in vivo activity of SKI-606, a novel Src-Abl inhibitor, against imatinib resistant BCR-ABL+ neoplastic cells. Cancer Res 66:11314–11322
Radujkovic A, Fruehauf S, Zeller WJ, Ho AD, Topaly J (2010) Synergistic activity of nilotinib and established chemotherapeutic drugs in imatinib-sensitive and -resistant BCR-ABL-positive cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 66:255–264
Ray A, Cowan-Jacob SW, Manley PW et al (2007) Identification of BCR-ABL point mutations conferring resistance to the Abl kinase inhibitor AMN107 (nilotinib) by a random mutagenesis study. Blood 109:5011–5015
Risau W, Drexler H, Mironov V et al (1992) Platelet-derived growth factor is angiogenic in vivo. Growth Factors 7:261–266
Roche-Lestienne C, Soenen-Cornu V, Grardel-Duflos N et al (2002) Several types of mutations of the ABL gene can be found in chronic myeloid leukemia patients resistant to STI571, and they can pre-exist to the onset of treatment. Blood 100:1014–1018
Roeder I, Horn M, Glauche I et al (2006) Dynamic modeling of imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia: functional insights and clinical implications. Nat Med 12:1181–1184
Rourmiantsev S, Shah NP, Gorre ME et al (2002) Clinical resistance to the kinase inhibitor STI-571 in chronic myeloid leukemia by mutation of Tyr-253 in the ABL kinase domain P-loop. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:10700–10705
Saglio G, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S et al (2010) ENESTnd Investigators. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 362:2251–2259
Schindler T, Bornmann W, Pellicena P, Miller WT, Clarkson B, Kuriyan J (2000) Structural mechanism for STI-571 inhibition of Abelson tyrosine kinase. Science 289:1938–1942
Schneider M, Korzeniewski N, Merkle K, et al (2014) The tyrosine kinase inhibitor nilotinib has antineoplastic activity in prostate cancer cells but up-regulates the ERK survival signal- Implications for targeted therapies. Urol Oncol. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2014.06.001
Shah NP, Nicoll JM, Nagar B, Gorre ME, Paquette RL, Kuriyan J, Sawyers CL (2002) Multiple BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations confer polyclonal resistance to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor imatinib (STI571) in chronic phase and blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2:117–125
Shah NP, Tran C, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Sawyers CL (2004) Overriding imatinib resistance with a novel ABL kinase inhibitor. Science 305:399–401
Shah NP, Skaggs BJ, Branford S et al (2007) Sequential ABL kinase inhibitor therapy selects for compound drug-resistant BCR-ABL mutations with altered oncogenic potency. J Clin Invest 117:2562–2569
Shen T, Kuang YH, Ashby CR et al (2009) Imatinib and nilotinib reverse multidrug resistance in cancer cells by inhibiting the efflux activity of the MRP7 (ABCC10). PLoS One 4:e7520
Skora L, Mestan J, Fabbro D, Jahnke W, Grzesiek S (2013) NMR reveals the allosteric opening and closing of Abelson tyrosine kinase by ATP-site and myristoyl pocket inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:E4437–E4445
Soverini S, Martinelli G, Rosti G et al (2005) ABL mutations in late chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with up-front cytogenetic resistance to imatinib are associated with a greater likelihood of progression to blast crisis and shorter survival: a study by the GIMEMA Working Party on Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 23:4100–4109
Talpaz M, Shah NP, Kantarjian H et al (2006) Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Eng J Med 354:2531–2541
Tauchi T, Okabe S, Ashihara E, Kimura S, Maekawa T, Ohyashiki K (2011) Combined effects of novel heat shock protein 90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922 and nilotinib in a random mutagenesis screen. Oncogene 30:2789–2797
Tiwari AK, Sodani K, Wang SR et al (2009) Nilotinib (AMN107, Tasigna) reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting the activity of the ABCB1/Pgp and ABCG2/BCRP/MXR transporters. Biochem Pharmacol 78:153–161
Tokarski JS, Newitt JA, Chang CY et al (2006) The structure of Dasatinib (BMS-354825) bound to activated ABL kinase domain elucidates its inhibitory activity against imatinib-resistant ABL mutants. Cancer Res 66:5790–5797
Vardiman JW, Harris NL, Brunning RD (2002) The World Health Organization (WHO) classification of the myeloid neoplasms. Blood 100:2292
Villar VH, Vogler O, Martinez-Serra J et al (2012) Nilotinib counteracts P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance and synergizes the antitumoral effect of doxorubicin in soft-tissue sarcomas. PLoS One 7:e37735
Von Bubnoff N, Schneller F, Peschel C, Duyster J (2002) BCR-ABL gene mutations in relation to clinical resistance of Philadelphia-chromosome-positive leukaemia to STI571: a prospective study. Lancet 359:487–491
Von Bubnoff N, Manley PW, Mestan J et al (2006) BCR-ABL resistance screening predicts a limited spectrum of point mutations to be associated with clinical resistance to the Abl kinase inhibitor nilotinib (AMN107). Blood 108:1328–1333
Wang Y, Wang M, Qi H et al (2014) Pathway-dependent inhibition of paclitaxel hydroxylation by kinase inhibitors and assessment of drug–drug interaction potentials. Drug Metab Dispos 42:782–795
Weisberg E, Griffin JD (2000) Mechanism of resistance to the ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 in BCR/ABL-transformed hematopoietic cell lines. Blood 95:3498–3505
Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W et al (2005) Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant BCR-ABL. Cancer Cell 7:129–141
Weisberg E, Catley L, Wright RD et al (2007) Beneficial effects of combining nilotinib and imatinib in preclinical models of BCR-ABL+ leukemias. Blood 109:2112–2120
Weisberg E, Banerji L, Wright RD et al (2008a) Potentiation of antileukemic therapies by the dual PI3K/PDK-1 inhibitor, BAG956: effects on BCR-ABL- and mutant FLT3-expressing cells. Blood 111:3723–3734
Weisberg E, Wright RD, McMillin DW et al (2008b) Stromal-mediated protection of tyrosine kinase inhibitor-treated BCR-ABL-expressing leukemia cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1121–1129
Weisberg E, Choi HG, Ray A et al (2010) Discovery of a small-molecule type II inhibitor of wild-type and gatekeeper mutants of BCR-ABL, PDGFRalpha, Kit, and Src kinases: novel type II inhibitor of gatekeeper mutants. Blood 115:4206–4216
Weisberg E, Azab AK, Manley PW et al (2012) Inhibition of CXCR4 in CML cells disrupts their interaction with the bone marrow microenvironment and sensitizes them to nilotinib. Leukemia 26:985–990
White DL, Saunders VA, Dang P et al (2006) OCT-1-mediated influx is a key determinant of the intracellular uptake of imatinib but not nilotinib (AMN107): reduced OCT-1 activity is the cause of low in vitro sensitivity to imatinib. Blood 108:697–704
Wilda M, Fuchs U, Wossmann W, Borkhardt A (2002) Killing of leukemic cells with a BCR/ABL fusion gene by RNA interference (RNAi). Oncogene 21:5716–5724
Wohlbold L, van der Kuip H, Miething C et al (2003) Inhibition of bcr-abl gene expression by small interfering RNA sensitizes for imatinib mesylate (STI571). Blood 102:2236–2239
Wu J, Meng F, Kong LY et al (2008) Association between imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutation-negative leukemia and persistent activation of LYN kinase. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:926–939
Xia Y, Fang H, Zhang J, Du Y (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in imatinib-resistant leukemic K562-r cells triggered by AMN107 combined with arsenic trioxide. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 238:932–942
Xing H, Yang X, Liu T, Lin J, Chen X, Gong Y (2012) The study of resistant mechanisms and reversal in an imatinib resistant Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell line. Leuk Res 36:509–513
Zhang J, Adrian FJ, Jahnke W et al (2010) Targeting BCR-ABL by combining allosteric with ATP-binding site inhibitors. Nature 463:501–506
Zhu GR, Ji O, Ji JM et al (2012) Combining nilotinib and imatinib improves the outcome of imatinib-resistant blast phase CML. Acta Haematol 127:152–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weisberg, E., Nonami, A. & Griffin, J.D. Combination therapy with nilotinib for drug-sensitive and drug-resistant BCR-ABL-positive leukemia and other malignancies. Arch Toxicol 88, 2233–2242 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1385-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1385-5