Abstract
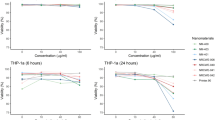
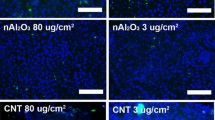
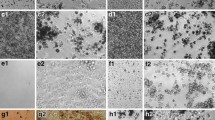
Manufactured nanomaterials (MNMs) have the potential to improve everyday life as they can be utilised in numerous medical applications and day-to-day consumer products. However, this increased use has led to concerns about the potential environmental and human health impacts. The protein p53 is a key transcription factor implicated in cellular defence and reparative responses to various stress factors. Additionally, p53 has been implicated in cellular responses following exposure to some MNMs. Here, the role of the MNM mediated p53 induction and activation and its downstream effects following exposure to five well-characterised materials [namely two types of TiO2, two carbon black (CB), and one single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT)] were investigated. MNM internalisation, cellular viability, p53 protein induction and activation, oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis were measured in murine cell line and primary pulmonary macrophage models. It was observed that p53 was implicated in the biological responses to MNMs, with oxidative stress associated with p53 activation (only following exposure to the SWCNT). We demonstrate that p53 acted as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory in macrophage responses to SWCNT and CB NMs. However, p53 was neither involved in MNM-induced cellular toxicity, nor in the apoptosis induced by these MNMs. Moreover, the physicochemical characteristics of MNMs seemed to influence their biological effects-SWCNT the materials with the largest surface area and a fibrous shape were the most cytotoxic in this study and were capable of the induction and activation of p53.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bann RK, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Cogliano V (2006) Carcinogenicity of carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. Lancet Oncol 7:295–296
Basich BL, Corson NM, Wade-Mercer P, Gelein R, Kennell AJ, Ocerdorster G, Elder A (2014) Equivalebt titanium dioxide nanoparticle deposition by intratracheal instillation and whole body inhalation: the effect of dose rate on acute repiratoty tract inflammation. Part Fibre Toxicol 11:5
Beg S, Rizwan M, Sheikh AM, Hasnain MS, Anwer K, Kohli K (2011) Advancement in carbon nanotubes: basics, biomedical applications and toxicity. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:141–163
Bensaad K, Vousden KH (2005) Savior and slayer: the two faces of p53. Nat Med 11:1278–1279
Bhattacharya K, Davoren M, Boertz J, Schins RP, Hoffmann E, Dopp E (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA-adduct formation but not DNA-breakage in human lung cells. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:17
Burnett ME, Wang SQ (2011) Current sunscreen controversies: a critical review. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 27:58–67
Bussy C, Paineau E, Cambedouzou J, Brun N, Mory C, Fayard B, Salome M, Pinault M, Huard M, Belade E, Armad L, Boczkowski J, Launois P, Lanone S (2013) Intracellular fate of carbon nanotubes inside murine macrophages: pH-dependent detachment of iron catalystnanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:24
Cho WS, Duffin R, Bradley M, Megson IL, MacNee W, Lee JK, Jeong J, Donaldson D (2013) Predictive value of in vitro assays depends on the mechanism of toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol 10:55
Cuartero M, del Rio JS, Blondeau P, Ortuno JA, Rius FX, Andrade FJ (2014) Rubber based substrates modified with carbon nanotubes inks to build flexible electrochemical sensors. Analytica Chemica Acta 827:95–102
De Souza VHR, Oliveira MM, Zarbin AJG (2014) Thin and flexible all-solid supercapacitor from novel single wall carbon nanotubes/polyaniline thin films obtained in liquid–liquid interfaces. J Power Sources 260:34–42
Demokritou P, Gass S, Pyrgiotakis G, Cohen JM, Goldsmith W, McKinney W, Frazer D, Ma J, Schwegler-Berry D, Brain J, Castranova V (2013) An in vivo and in vitro toxicological characterisation of realistic nanoscale CeO2 inhalation exposures. Nanotoxicology 7:1338–1350
Donaldson K, Tran L, Jimenez LA, Duffin R, Newby DE, Mills N, Macnee W, Stone V (2005) Combustion-derived nanoparticles: a review of their toxicology following inhalation exposure. Part Fibre Toxicol 2:10
Dowding JM, Das S, Kumar A, Dosani T, McCormack R, Gupta A, Sayle TXT, Sayle DC, von Kalm L, Seal S, Self WT (2013) Cellular interaction and toxicity depend on physicochemical properties and surface modification of redox-active nanomaterials. ACS Nano 7:4855–4868
Ema M, Kobayashi N, Naya M, Hansai S, Nakanishi J (2010) Reproductive and developmental toxicity studies of manufactured nanomaterials. Reprod Toxicol 30:343–352
Gaiser BK, Hirn S, Kermanizadeh A, Kanase N, Fytianos K, Wenk A, Haberl N, Brunelli A, Kreyling WG, Stone V (2012) Effects of silver nanoparticles on the liver and hepatocytes in vitro. Toxicol Sci 131:537–547
Gangwal S, Brown JS, Wang A, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Hubal EAC (2011) Informing selection of nanomaterial concentrations for ToxCast in vitro testing based on occupational exposure potential. Environ Health Perspect 119:1539–1546
Giono LE, Manfredi JJ (2006) The p53 tumor suppressor participates in multiple cell cycle checkpoints. J Cell Physiol 209:13–20
Goven D, Boutten A, Lecon-Malas V, Marchal-Somme J, Soler P, Boczkowski J, Bonay M (2010) Induction of heme oxygenase-1, biliverdin reductase and H-ferritin in lung macrophage in smokers with primary spontaneous pneumothorax: role of HIF-1alpha. PLoS ONE 5:e10886
Hussain S, Bolan S, Baewa-Squibqn A, Hamel R, Thomassen LC, Martens JA, Billon-Galland MA, Fleury-Feith J, Moisan F, Pairon JC, Marano F (2009) Oxidative stress and proinflammatory effects of carbon black and titanium dioxide nanoparticles: role of particle surface area and internalized amount. Toxicology 260:142–149
Kagan VE, Tyurina YY, Tyurin VA, Konduru NV, Potapovich AI, Osipov AN, Kisin ER, Schwegler-Berry D, Mercer R, Castranova V, Shvedova AA (2006) Direct and indirect effects of single walled carbon nanotubes on RAW 264.7 macrophages: role of iron. Toxicol Lett 165:88–100
Kang SJ, Kim BM, Lee YJ, Chung HW (2008) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles trigger p53-mediated damage response in peripheral blood lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 49:399–405
Kermanizadeh A, Gaiser BK, Hutchison GR, Stone V (2012) An in vitro liver model–assessing oxidative stress and genotoxicity following exposure of hepatocytes to a panel of engineered nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol 9:28
Kermanizadeh A, Chauché C, Balharry D, Brown DM, Kanase N, Boczkowski J, Lanone S, Stone V (2013) The role of kupffer cells in the hepatic response to silver nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology. doi:10.3109/17435390.2013.866284
Konczol M, Weiss A, Gminski R, Merfort I, Mersch-Sundermann V (2013) Oxidative stress and inflammatory response to printer toner particles in human epithelial A549 lung cells. Toxicol Lett 216:171–180
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87:99–163
Landsiedel R, Ma-Hock L, Kroll A, Hahn D, Schnekenburger J, Wiench K, Wohlleben W (2010) Testing metal oxide nanomaterials for human safety. Adv Mater 22:2601–2627
Lanone S, Boczkowski J (2006) Biomedical applications and potential health risks of nanomaterials: molecular mechanisms. Curr Mol Med 6:651–663
Lanone S, Rogerieux F, Geys J, Dupont A, Maillot-Marechal E, Boczkowski J, Lacroix G, Hoet P (2009) Comparative toxicity of 24 manufactured nanoparticles in human alveolar epithelial and macrophage cell lines. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:14
Lanone S, Andujar P, Kermanizadeh A, Boczkowski J (2013) Determinants of carbon nanotube toxicity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:2063–2069
Maynard AD, Warheit DB (2011) Philbert MA (2011) The new toxicology of sophisticated materials: nanotoxicology and beyond. Toxicol Sci 120:109–129
Mroz RM, Schins RP, Li H, Drost EM, Macnee W, Donaldson K (2007) Nanoparticle carbon black driven DNA damage induces growth arrest and AP-1 and NFkappaB DNA binding in lung epithelial A549 cell line. J Physiol Pharmacol 58:461–470
Mroz RM, Schins RP, Li H, Jimenez LA, Drost EM, Holownia A, Macnee W, Donaldson K (2008) Nanoparticle-driven DNA damage mimics irradiation-related carcinogenesis pathways. Eur Respir J 31:241–251
Muller J, Huaux F, Moreau N, Misson P, Heilier JF, Delos M, Fonseca A, Nagy JB, Lison D (2005) Respiratory toxicity of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Toxicol Appl Toxicol 207:221–231
Murphy FA, Poland CA, Duffin R, Donaldson K (2013) Length dependant pleural inflammation and parietal pleural responses after deposition of carbon nanotubes in the pulmonary airspaces of mice. Nanotoxicology 7:1157–1167
Oberdorster G (2010) Safety assessment for nanotechnology and nanomedicine: concepts of nanotoxicology. J Int Med 267:89–105
Oberdorster G (2012) Nanotoxicology: in vitro–in vivo dosimetry. Environmental Health Perspectives 120
Park EJ, Roh J, Kim SN, Kang MS, Han YA, Kim Y, Hong JT, Choi K (2011) A single intratracheal instillation of single-walled carbon nanotubes induced early lung fibrosis and sub-chronic tissue damage in mice. Arch Toxicol 85:1121–1131
Petkovic J, Zegura B, Stevanovic M, Drnovsek N, Uskokovic D, Novak S, Filipic M (2011) DNA damage and alterations in expression of DNA damage responsive genes induced by TiO2 nanoparticles in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Nanotoxicology 5:341–353
Poland CA, Duffin R, Kinloch I, Maynard A, Wallace WA, Seaton A, Stone V, Brown S, MacNee W, Donaldson K (2008) Carbon nanotubes introduced into the abdominal cavity of mice show asbestos-like pathogenicity in a pilot study. Nat Nanotechnol 3:423–428
Ravichandran P, Baluchamy S, Gopikrishnan R, Biradar S, Ramesh V, Goornavar V, Thomas R, Wilson BL, Jeffers R, Hall JC, Ramash GT (2011) Pulmonary biocompatibility assessment of inhaled single-wall and multiwall carbon nanotubes in BALB/c mice. J Biol Chem 286:29725–29733
Riedl SJ, Salvesen GS (2007) The apoptosome: signaling platform of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:405–413
Sabina AA, Budanov AV, Ilvinskava GV, Agapova LS, Kravchenko JE, Chumakov PM (2005) The antioxidant function of the p53 tumor suppressor. Nat Med 11:1306–1313
Shi Y, Wang F, He J, Yaday S, Wang H (2010) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles cause apoptosis in BEAS-2B cells through the caspase 8/t-Bid-independent mitochondrial pathway. Toxicol Lett 196:21–27
Shvedova AA, Kisin ER, Mercer AR, Murray AR, Johnson VJ, Potapovich AI, Tyurina YY, Gorelik O, Arepalli S, Schwegler-Berry D, Hubbs AF, Antonini J, Evans DE, Ku BK, Ramsey D, Maynard A, Kagen VE, Castranova V, Baron P (2005) Unusual inflammatory and fibrogenic pulmonary responses to single-walled carbon nanotubes in mice. Am J Cell Mol Physiol 289:698–708
Simon-Deckers A, Gouget B, Mayne-L’hermite M, Herlin-Boime N, Reynaud C, Carriere M (2008) In vitro investigation of oxide nanoparticle and carbon nanotube toxicity and intracellular accumulation in A549 human pneumocytes. Toxicology 253:137–146
Singh S, Shi T, Duffin R, Albrecht C, van Berlo D, Hohr D, Fubini B, Martra G, Fenoglio I, Borm PJ, Schins RP (2007) Endocytosis, oxidative stress and IL-8 expression in human lung epithelial cells upon treatment with fine and ultrafine TiO2: role of the specific surface area and of surface methylation of the particles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:141–151
Tabet L, Bussy C, Amara N, Setyan A, Grodet A, Rossi MJ, Pairon JC, Boczkowski J, Lanone S (2009) Adverse effects of industrial multi-walled carbon nanotubes on human pulmonary cells. J Toxicol Environ Health 72:60–73
Takagi A, Hirose A, Nishimura T, Fukumori N, Ogata A, Ohashi N, Kitajima S, Kanno J (2008) Induction of mesothelioma in p53 ± mouse by intraperitoneal application of multi-wall carbon nanotube. J Toxicol Sci 33:105–116
Tanaka K, Kitamura N, Morita M, Inubushi T, Chuio Y (2008) Assembly system of direct modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for target-specific MRI contrast agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:5463–5465
Tian L, Lin ZQ, Lin BC, Liu HL, Yan J, Xi ZG (2013) Single wall carbon nanotube induced inflammation in Cruor-Fibrinolysis system. Biomed Environ Sci 26:338–345
Trouiller B, Reliene R, Westbrook A, Solaimani P, Schiestl RH (2009) Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce DNA damage and genetic instability in vivo in mice. Cancer Res 69:8784–8789
Watanabe M, Okada M, Kudo Y, Tonori Y, Niitsuya M, Sato T, Aizawa Y, Kotani M (2002) Differences in the effects of fibrous and particulate titanium dioxide on alveolar macrophages of Fischer 344 rats. J Toxicol Environ Health 65:1047–1060
Wawrzyniak A, Gornicka M, Hamulka J, Gajewska M, Drywien M, Pierzynowska J, Gronowska A (2013) α-Tocopherol, ascorbic acid, and β-carotene protect against oxidative stress but reveal no direct influence on p53 expression in rats subjected to stress. Nutr Res 33:868–875
Wilhelmi V, Fischer U, van Berlo D, Schulze-Osthoff K, Schins RPF, Albrexht A (2012) Evaluation of apoptosis in RAW 264.7 macrophages: facts and artefacts. Toxicol vitro 26:323–334
Wu J, Sun J, Xue Y (2010) Involvement of JNK and p53 activation in G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in neuron cells. Toxicol Lett 199:269–276
Ye SF, Wu YH, Hou ZQ, Zhqng QQ (2009) ROS and NF-kappaB are involved in upregulation of IL-8 in A549 cells exposed to multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 379:643–648
Yun YP, Lee JY, Ahn EK, Lee KH, Yoon HK, Lim Y (2009) Diesel exhaust particles induce apoptosis via p53 and Mdm2 in J774A.1 macrophage cell line. Toxicolo Vitro 23:21–28
Zilfou JT, Lowe SW (2009) Tumor suppressive functions of p53. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1:a001883
Zuckerman V, Wolyniec K, Sionov RV, Haupt S, Haupt Y (2009) Tumour suppression by p53: the importance of apoptosis and cellular senescence. J Pathol 219:3–15
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the “Labex Serenade (11-LABX-0064)”, the “Agence nationale de sécurité sanitaire de l’Alimentation, de l’Environnement et du Travail”–PhD grants of Lucie Armand and Jean-Marie Gagliolo. Angélique Simon-Deckers was funded from ANR, while Sandra Chrusciel was supported by AREMCAR. Jorge Boczwoski and Sophie Lanone were both recipients of a Contrat de Recherche Translationnelle, between Inserm and CHU Mondor (JB) and Inserm and CHI Créteil (SL). Finally, a special thank you to the Hospital University Department (DHU) Aging-Thorax, Vessels, Blood (A-TVB) for their support of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belade, E., Chrusciel, S., Armand, L. et al. The role of p53 in lung macrophages following exposure to a panel of manufactured nanomaterials. Arch Toxicol 89, 1543–1556 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1324-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1324-5