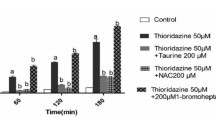
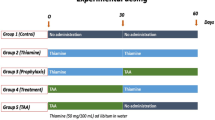
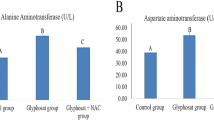
Abstract
We investigated hepatotoxicity induced by ticlopidine (TIC) in glutathione (GSH)-depleted rats by pre-treatment of a well-known GSH synthesis inhibitor, l-buthionine-S,R-sulfoxinine (BSO). Although sole administration of either TIC or BSO showed no signs of hepatotoxicity, combined administration of TIC with BSO induced hepatotoxicity, which was characterized by centrilobular necrosis of the hepatocytes and an elevation of plasma alanine aminotransferase activity. Administration of radio-labeled TIC in combination with BSO resulted in significantly higher covalent binding to rat liver proteins than that observed after sole dosing of radio-labeled TIC. Pre-treatment of 1-Aminobenzotriazole, a non-specific inhibitor of P450s, completely suppressed both hepatotoxicity and the increased hepatic covalent binding caused by TIC co-treatment with BSO. The results obtained in this animal model suggest that GSH depletion and covalent binding may be involved in hepatotoxicity induced by TIC. These observations may help to understand the risk factors and the mechanism of hepatotoxicity of TIC in humans.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis SR, Quinlivan EP, Stacpoole PW, Gregory JF III (2006) Plasma glutathione and cystathionine concentrations are elevated but cysteine flux is unchanged by dietary vitamin B-6 restriction in young men and women. J Nutr 136:373–378
Drew R, Miners JO (1984) The effects of buthionine sulfoximine (BSO) on glutathione depletion and xenobiotic biotransformation. Biochem Pharmacolo 33:2989–2994
Griffith OW, Meister A (1979) Potent and specific inhibition of glutathione synthesis by buthionine sulfoximine (S-n-butyl homocysteine sulfoximine). J Biol Chem 254:7558–7560
Ha-Duong NT, Dijols S, Macherey AC, Goldstein JA, Dansette PM, Mansuy D (2001) Ticlopidine as a selective mechanism-based inhibitor of human cytochrome P450 2C19. Biochemistry 40:12112–12122
Hernanz A, Fernández-Vivancos E, Montiel C, Vazquez JJ, Arnalich F (2000) Changes in the intracellular homocysteine and glutathione content associated with aging. Life Sci 67:1317–1324
Hirata K, Takagi H, Yamamoto M, Matsumoto T, Nishiya T, Mori K, Shimizu S, Masumoto H, Okutani Y (2008) Ticlopidine-induced hepatotoxicity is associated with specific human leukocyte antigen genomic subtypes in Japanese patients: a preliminary case-control study. Pharmacogenomics J 8:29–33
Ip C (1984) Comparative effects of antioxidants on enzymes involved in glutathione metabolism. Life Sci 34:2501–2506
Jacobson AK (2004) Platelet ADP receptor antagonists: ticlopidine and clopidogrel. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 17:55–64
Lauterburg BH, Velez ME (1988) Glutathione deficiency in alcoholics: risk factor for paracetamol hepatotoxicity. Gut 2:1153–1157
Li AP (2002) A review of the common properties of drugs with idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity and the “multiple determinant hypothesis” for the manifestation of idiosyncratic drug toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 142:7–23
Mataix R, Ojeda E, Perez MC, Jimenez S (1992) Ticlopidine and severe aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol 80:125–126
Micke P, Beeh KM, Buhl R (2002) Effects of long-term supplementation with whey proteins on plasma glutathione levels of HIV-infected patients. Eur J Nutr 4:12–18
Mitchell JR, Jollow DJ, Potter WZ, Gillette JR, Brodie BB (1973) Acetaminophene-induced hepatic necrosis. IV. Protective role of glutathione. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 187:211–217
Mizushima M, Iwata N, Fujimoto TT, Ishikawa K, Fujimura K (2005) Patient characteristics in ticlopidine hydrochloride-induced liver injury: Case-control study. Hepatol Res 33:234–240
Mizutani T, Nomura H, Nakanishi K, Fujita S (1987) Hepatotoxicity of butylated hydroxytoluene and its analogs in mice depleted of hepatic glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 87:166–176
Mizutani T, Satoh K, Nomura H, Nakanishi K (1991) Hepatotoxicity of eugenol in mice depleted of glutathione by treatment with DL-buthionine sulfoximine. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 71:219–230
Mizutani T, Irie Y, Nakanishi K (1994a) Styrene-induced hepatotoxicity in mice depleted of glutahione. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 86:361–374
Mizutani T, Nakahori Y, Yamamoto K (1994b) p-Dichlorobenzene-induced hepatotoxicity in mice depleted of glutathione treated with buthionine sulfoximine. Toxicology 94:57–67
Mizutani T, Murakami M, Shirai M, Tanaka M, Nakanishi K (1999) Metabolism-dependent hepatotoxicity of Methimazole in mice depleted of glutathione. J Appl Toxicol 19:193–198
Mugford CA, Mortillo M, Mico BA, Tarloff JB (1992) 1-Aminobenzotriazole-induced destruction of hepatic and renal cytochromes P450 in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol 19:43–49
Muszkat M, Shapira MY, Sviri S, Linton DM, Caraco Y (1998) Ticlopidine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Pharmacotherapy 18:1352–1355
Nakamura S, Kugiyama K, Sugiyama S, Miyamoto S, Koide S, Fukushima H, Honda O, Yoshimura M, Ogawa H (2002) Polymorphism in the 5′-flanking region of human glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit gene is associated with myocardial infarction. Circulation 105:2968–2973
Nishiya T, Mori K, Hattori C, Kai K, Kataoka H, Masubuchi N, Jindo T, Manabe S (2008) The crucial protective role of glutathione against tienilic acid hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 232:280–291
Nishiya Y, Hagihara K, Ito T, Tajima M, Miura S, Kurihara A, Farid NA, Ikeda T (2009) Mechanism-based inhibition of human cytochrome P450 2B6 by ticlopidine, clopidogrel, and the thiolactone metabolite of prasugrel. Drug Metab Dispos 37:589–593
Ono K, Kurohara K, Yoshihara M, Shimamoto Y, Yamaguchi M (1991) Agranulocytosis caused by ticlopidine and its mechanism. Am J Hematol 37:239–242
Panak E, Maffrand JP, Picard-Fraire C, Vallée E, Blanchard J, Roncucci R (1983) Ticlopidine: a promise for the prevention and treatment of thrombosis and its complications. Haemostasis 13(Suppl 1):1–54
Pizarro AE, Andrade RJ, García-Cortés M, Lucena MI, Pérez-Moreno JM, Puertas M, Sánchez-Martínez H, Montero JL, Durán JA, Jiménez M, Ruiz-Montero A, Soto-Conesa MJ, Rodrigo L, de Francisco R, Alcántara R, Camargo R (2001) Acute hepatitis due to ticlopidine. A report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Rev Neurol 33:1014–1020
Quinn MJ, Fitzgerald DJ (1999) Ticlopidine and clopidogrel. Circulation 100:1667–1672
Richter T, Mürdter TE, Heinkele G, Pleiss J, Tatzel S, Schwab M, Eichelbaum M, Zanger UM (2004) Potent mechanism-based inhibition of human CYP2B6 by clopidogrel and ticlopidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:189–197
Ruan Q, Zhu M (2010) Investigation of Bioactivation of Ticlopidine Using Linear Ion Trap/Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry and an Improved Mass Defect Filtering Technique. Chem Res Toxicol 23:909–917
Savi P, Herbert JM (2005) Clopidogrel and ticlopidine: P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate-receptor antagonists for the prevention of atherothrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost 31:174–183
Sedlak J, Lindsay RH (1968) Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman’s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Shimizu S, Atsumi R, Itokawa K, Iwasaki M, Aoki T, Ono C, Izumi T, Sudo K, Okazaki O (2009a) Metabolism-dependent hepatotoxicity of amodiaquine in glutathione-depleted mice. Arch Toxicol 83:701–707
Shimizu S, Atsumi R, Nakazawa T, Fujimaki Y, Sudo K, Okazaki O (2009b) Metabolism of ticlopidine in rats: Identification of the main biliary metabolite as a GSH conjugate of S-oxide. Drug Metab Dispos 37:1904–1915
Staal FJ, Ela SW, Roederer M, Anderson MT, Herzenberg LA (1992) Glutathione deficiency and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Lancet 339:909–912
Steinhubl SR, Tan WA, Foody JM, Topol EJ (1999) Incidence and clinical course of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura due to ticlopidine following coronary stenting. EPISTENT Investigators. Evaluation of Platelet IIb/IIIa Inhibitor for Stenting. JAMA 281:806–810
Takikawa H (2005) Lessons from ticlopidine-induced liver injury. Hepatol Res 33:193–194
Tsai MH, Tsai SL, Chen TC, Liaw YF (2000) Ticlopidine-induced cholestatic hepatitis with anti-nuclear antibody in serum. J Formos Med Assoc 99:866–869
Usui T, Mise M, Hashizume T, Yabuki M, Komuro S (2009) Evaluation of the potential for drug-induced liver injury based on in vitro covalent binding to human liver proteins. Drug Metab Dispos 37:2383–2392
van Zanten SV, McCormic CW (1996) Antinuclear antibody-positive ticlopidine-induced hepatitis. Can J Gastroenterol 10:231–232
Watanabe T, Sagisaka H, Arakawa S, Shibaya Y, Watanabe M, Igarashi I, Tanaka K, Totsuka S, Takasaki W, Manabe S (2003) A novel model of continuous depletion of glutathione in mice treated with l-buthionine (S, R)-sulfoximine. J Toxicol Science 28:455–463
Yoneda K, Iwamura R, Kishi H, Mizukami Y, Mogami K, Kobayashi S (2004) Identification of the active metabolite of ticlopidine from rat in vitro metabolites. Br J Pharmacol 142:551–557
Zhou SF, Liu JP, Chowbay B (2009) Polymorphism of human cytochrome P450 enzymes and its clinical impact. Drug Metab Rev 41:89–295
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Minoru Inoue and Yutaka Iigo for their excellent assistance with the histopathological evaluations. We are also very grateful to Takatoshi Nishiya for his helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimizu, S., Atsumi, R., Nakazawa, T. et al. Ticlopidine-induced hepatotoxicity in a GSH-depleted rat model. Arch Toxicol 85, 347–353 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0594-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0594-9