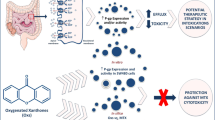
Abstract
The Caco-2 cell line is a reliable in vitro model for predicting drug intestinal absorption and P-glycoprotein (P-gp)-mediated excretion in humans. Recent in vivo studies suggested the induction of P-gp as a cellular protection tool against paraquat poisoning, through the increase in its pulmonary and intestinal excretion. Thus, the aim of the present work was to evaluate P-gp expression and activity in Caco-2 cells exposed to doxorubicin (a known P-gp inducer) and to correlate these changes with paraquat toxic effects. Cytotoxicity of doxorubicin (0–100 μM) and paraquat (0–1,000 μM) was evaluated for a maximum period of 96 h. In doxorubicin-exposed cells, P-gp expression and transport activity were evaluated by flow cytometry, using a fluorescein isothiocyanate–conjugated antibody and the P-gp fluorescent subtract rhodamine 123, respectively. A significant increase in P-gp expression was observed as soon as 6 h after exposure to 5 μM doxorubicin. P-gp activity also increased after 6 h, but only at higher doxorubicin concentrations (over 50 μM). Paraquat (0–5,000 μM) cytotoxicity was then evaluated with or without previous exposure of the cells to doxorubicin (5–100 μM, a concentration range causing both an increase in P-gp expression and activity). Under P-gp induction, a significant reduction in paraquat cytotoxicity was observed. Furthermore, when these cells were incubated with a specific P-gp inhibitor (UIC2 antibody) the doxorubicin protective effects were blocked, confirming the involvement of P-gp in the reduction in paraquat cytotoxicity. In conclusion, the human Caco-2 cell line model can be used for the study of P-gp induction as an antidotal pathway against substrates of this transporter system.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCRP:
-
Breast cancer–resistant protein
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- DOX:
-
Doxorubicin
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
- MTT:
-
(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide
- NEAA:
-
Nonessential aminoacids
- NSAIDs:
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline solution
- P-gp:
-
P-glycoprotein
- PQ:
-
Paraquat
- RHO 123:
-
Rhodamine 123
References
Ambudkar SV, Dey S, Hrycyna CA, Ramachandra M, Pastan I, Gottesman MM (1999) Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:361–398
Barta CA, Sachs-Barrable K, Feng F, Wasan KM (2008) Effects of monoglycerides on p-glycoprotein: modulation of the activity and expression in caco-2 cell monolayers. Mol Pharm 5:863–875
Chang G (2003) Multidrug resistance ABC transporters. FEBS Lett 555:102–105
Chaudhary PM, Mechetner EB, Roninson IB (1992) Expression and activity of the multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Blood 80:2735–2739
Cordon-Cardo C, O’Brien JP, Boccia J, Casals D, Bertino JR, Melamed MR (1990) Expression of the multidrug resistance gene product (P-glycoprotein) in human normal and tumor tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 38:1277–1287
Crowe AP, Lockman PR, Abbruscato TJ, Allen DD (2002) Novel choline transport characteristics in Caco-2 cells. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 28:773–781
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA, Remiao F, Sanchez-Navarro A, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2006a) Single high dose dexamethasone treatment decreases the pathological score and increases the survival rate of paraquat-intoxicated rats. Toxicology 227:73–85
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Remiao F, Duarte JA, Ferreira R, Sanchez Navarro A, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2006b) P-glycoprotein induction: an antidotal pathway for paraquat-induced lung toxicity. Free Radic Biol Med 41:1213–1224
Dinis-Oliveira RJ, Duarte JA, Sanchez-Navarro A, Remiao F, Bastos ML, Carvalho F (2008) Paraquat poisonings: mechanisms of lung toxicity, clinical features, and treatment. Crit Rev Toxicol 38:13–71
Ehret MJ, Levin GM, Narasimhan M, Rathinavelu A (2007) Venlafaxine induces P-glycoprotein in human Caco-2 cells. Hum Psychopharmacol 22:49–53
Gottesman MM, Fojo T, Bates SE (2002) Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat Rev Cancer 2:48–58
Hidalgo IJ, Jibin L (1996) Carrier-mediated transport and efflux mechanisms in Caco-2 cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 22:53–66
Hirohashi T, Suzuki H, Chu X-Y, Tamai I, Tsuji A, Sugiyama Y (2000) Function and expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein family in human colon Adenocarcinoma Cells (Caco-2). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292:265–270
Hosoya KI, Kim KJ, Lee VH (1996) Age-dependent expression of P-glycoprotein gp170 in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Pharm Res 13:885–890
Hunter J, Jepson MA, Tsuruo T, Simmons NL, Hirst BH (1993) Functional expression of P-glycoprotein in apical membranes of human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Kinetics of vinblastine secretion and interaction with modulators. J Biol Chem 268:14991–14997
Huynh-Delerme C, Huet H, Noel L, Frigieri A, Kolf-Clauw M (2005) Increased functional expression of P-glycoprotein in Caco-2 TC7 cells exposed long-term to cadmium. Toxicol In Vitro 19:439–447
Kamath AV, Darling IM, Morris ME (2003) Choline uptake in human intestinal Caco-2 cells is carrier-mediated. J Nutr 133:2607–2611
Lohner K, Schnabele K, Daniel H, Oesterle D, Rechkemmer G, Gottlicher M, Wenzel U (2007) Flavonoids alter P-gp expression in intestinal epithelial cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:293–300
Mechetner E (2007) Detection of the MDR1 P-glycoprotein expression and function. Methods Mol Biol 378:175–193
Mechetner EB, Roninson IB (1992) Efficient inhibition of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance with a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:5824–5828
Nagao M, Saitoh H, Zhang WD, Iseki K, Yamada Y, Takatori T, Miyazaki K (1993) Transport characteristics of paraquat across rat intestinal brush-border membrane. Arch Toxicol 67:262–267
Shen S, He Y, Zeng S (2007) Stereoselective regulation of MDR1 expression in Caco-2 cells by cetirizine enantiomers. Chirality 19:485–490
Shirasaka Y, Kawasaki M, Sakane T, Omatsu H, Moriya Y, Nakamura T, Sakaeda T, Okumura K, Langguth P, Yamashita S (2006) Induction of human P-glycoprotein in Caco-2 cells: development of a highly sensitive assay system for P-glycoprotein-mediated drug transport. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 21:414–423
Shirasaka Y, Sakane T, Yamashita S (2008) Effect of P-glycoprotein expression levels on the concentration-dependent permeability of drugs to the cell membrane. J Pharm Sci 97:553–565
Silverman JA (1999) Multidrug-resistance transporters. Pharm Biotechnol 12:353–386
Sugihara N, Toyama K, Okamoto T, Kadowaki M, Terao K, Furuno K (2007) Effects of benzo(e)pyrene and benzo(a)pyrene on P-glycoprotein-mediated transport in Caco-2 cell monolayer: a comparative approach. Toxicol In Vitro 21:827–834
Taipalensuu J, Tornblom H, Lindberg G, Einarsson C, Sjoqvist F, Melhus H, Garberg P, Sjostrom B, Lundgren B, Artursson P (2001) Correlation of gene expression of ten drug efflux proteins of the ATP-binding cassette transporter family in normal human jejunum and in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 299:164–170
Takara K, Hayashi R, Kokufu M, Yamamoto K, Kitada N, Ohnishi N, Yokoyama T (2009) Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the expression and function of P-glycoprotein/MDR1 in Caco-2 cells. Drug Chem Toxicol 32:332–337
Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC (1987) Cellular localization of the multidrug-resistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:7735–7738
Watanabe T, Onuki R, Yamashita S, Taira K, Sugiyama Y (2005) Construction of a functional transporter analysis system using MDR1 knockdown Caco-2 cells. Pharm Res 22:1287–1293
Yamashita S, Furubayashi T, Kataoka M, Sakane T, Sezaki H, Tokuda H (2000) Optimized conditions for prediction of intestinal drug permeability using Caco-2 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci 10:195–204
Yamashita S, Hattori E, Shimada A, Endoh Y, Yamazaki Y, Kataoka M, Sakane T, Sezaki H (2002a) New methods to evaluate intestinal drug absorption mediated by oligopeptide transporter from in vitro study using Caco-2 cells. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 17:408–415
Yamashita S, Konishi K, Yamazaki Y, Taki Y, Sakane T, Sezaki H, Furuyama Y (2002b) New and better protocols for a short-term Caco-2 cell culture system. J Pharm Sci 91:669–679
Zhou SF (2008) Structure, function and regulation of P-glycoprotein and its clinical relevance in drug disposition. Xenobiotica 38:802–832
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) - project [PTDC/SAU-OSM/101437/2008] - QREN initiative with EU/FEDER financing through COMPETE - Operational Programme for Competitiveness Factors. Renata Silva acknowledges FCT for her PhD grant [SFRH/BD/29,559/2006]. Ricardo Dinis-Oliveira acknowledges FCT for his pos-Doc grant [SFRH/BPD/36,865/2007].
Caco-2 cells were kindly provided by Rosário Monteiro from the Biochemistry Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Porto, Portugal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, R., Carmo, H., Dinis-Oliveira, R. et al. In vitro study of P-glycoprotein induction as an antidotal pathway to prevent cytotoxicity in Caco-2 cells. Arch Toxicol 85, 315–326 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0587-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0587-8