Abstract
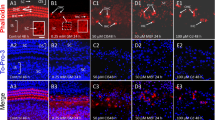
The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of apoptosis in the development of the newborn cochlear structures and hearing loss caused by prenatal cis-diaminedichloroplatinum (cisplatin) exposure. Pregnant albino guinea pigs were intraperitoneally injected with 1.5 mg/kg body weight cisplatin once a day for seven consecutive days at gestational day (GD) 51 to GD 57. At postnatal day (PND) 14, pups were examined in the distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) task. The temporal bones were then removed and immunohistochemically stained for caspase 3, using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) method. Cisplatin used during pregnancy could induce hearing loss in newborn and cochlear hair cell apoptosis. In conclusion, apoptosis may play an important role in the development of hearing impairment, caused by perinatal cisplatin exposure.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardinaal RM, de Groot JC, Huizing EH, Veldman JE, Smoorenburg GF (2000) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: morphological evidence of spontaneous outer hair cell recovery in albino guinea pigs? Hear Res 144:147–156
Cardonick E, Iacobucci A (2004) Use of chemotherapy during human pregnancy. Lancet Oncol 5:283–291
Cohen SM, Lippard SJ (2001) Cisplatin: from DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 67:93–130
Cotanche DA (2008) Genetic and pharmacological intervention for treatment/prevention of hearing loss. J Commun Disord 41:421–443
Daugaard G, Abildgaard U (1989) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 25:1–9
Devarajan P, Savoca M, Castaneda MP, Park MS, Esteban-Cruciani N, Kalinec G, Kalinec F (2007) Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in auditory cells: role of death receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Hear Res 174:45–54
Ebert U, Löffler H, Kirch W (1997) Cytotoxic therapy and pregnancy. Pharmacol Ther 74:207–220
Giurgiovich AJ, Diwan BA, Olivero OA, Anderson LM, Rice JM, Poirier MC (1997) Elevated mitochondrial cisplatin-DNA adduct levels in rat tissues after transplacental cisplatin exposure. Carcinogenesis 18:93–96
Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan GI, Green DR (2000) The coordinate release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nat Cell Biol 2:156–162
Gwyn K (2005) Children exposed to chemotherapy in utero. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 34:69–71
Heijmen PS, Klis SFL, De Groot JCMJ, Smoorenburg GF (1999) Cisplatin ototoxicity and the possibly protective effect of α-melanocyte stimulating hormone. Hear Res 128:27–39
Henley CM, Rybak LP (1995) Ototoxicity in developing mammals. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 20:68–90
Hori R, Nakagawa T, Sugimoto Y, Sakamoto T, Yamamoto N, Hamaguchi K, Ito J (2009) Prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP4 agonist protects cochleae against noise-induced trauma. Neuroscience 160:813–819
Huang X, Whitworth CA, Rybak LP (2007) Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in rats. Otol Neurotol 28:828–833
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ (2007) Cancer statistics 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 57:43–66
Jordan P, Carmo-Fonseca M (2000) Molecular mechanisms involved in cisplatin cytotoxicity. Cell Mol Life Sci 57:1229–1235
Kelley MW, Xu XM, Wagner MA, Warchol ME, Corwin JT (1993) The developing organ of Corti contains retinoic acid and forms supernumerary hair cells in response to exogenous retinoic acid in culture. Development 119:1041–1053
Knight KRG, Kraemer DF, Neuwelt EA (2005) Ototoxicity in children receiving platinum chemotherapy: underestimating a commonly occurring toxicity that may in.uence academic and social development. J Clin Oncol 23:8588–8896
Kumar S (2007) Caspase function in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 14:32–43
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA Jr, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I, Flavell RA (2006) Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311:847–851
Li Y, Womer RB, Silber JH (2004) Predicting cisplatin ototoxicity in children: the influence of age and the cumulative dose. Eur J Cancer 40:2445–2451
McKeage MJ (1995) Comparative adverse effect profiles of platinum drugs. Drug Saf 13:228–244
Mir O, Berveiller P, Ropert S, Goffinet F, Goldwasser F (2008) Use of platinum derivatives during pregnancy. Cancer 113:3069–3074
Moon HJ, Seok JH, Kim SS, Rhee GS, Lee RD, Yang JY, Chae SY, Kim SH, Kim JY, Chung JY, Kim JM, Chung SY (2009) Lactational coumestrol exposure increases ovarian apoptosis in adult rats. Arch Toxicol 83:601–608
Ognio E, Lapide M, Ottone M, Mandys V, Peterka M, Parodi B, Viale M (2003) Embryo-lethal and teratogenic effect of the new platinum compound DPR in pregnant mice. Arch Toxicol 77:584–590
Ognio E, Chiavarina B, Peterka M, Mariggiò MA, Viale M (2006) Study of feasibility of the treatment with procainamide hydrochloride and cisplatin in pregnant mice. Chem Biol Interact 164:232–240
Ohmura M, Yamamoto E (1990) Differences in endocochlear potentials in response to anoxia in naturing and mature guinea pigs. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 248:8–10
Ostrom K, Ben-Arie A, Edwards C, Gregg A, Chiu JK, Kaplan AL (2003) Uterine evacuation with misoprostol during radiotherapy for cervical cancer in pregnancy. Int J Gynecol Cancer 13:340–343
Pavlidis N (2008) Lung cancer during pregnancy: an emerging issue. Lung Cancer 59:279–281
Santos NA, Catão CS, Martins NM, Curti C, Bianchi ML, Santos AC (2007) Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is associated with oxidative stress, redox state unbalance, impairment of energetic metabolism and apoptosis in rat kidney mitochondria. Arch Toxicol 81:495–504
Schmutzhard J, Glueckert R, Sergi C, Schwentner I, Abraham I, Schrott-Fischer A (2009) Does perinatal asphyxia induce apoptosis in the inner ear? Hear Res 250:1–9
Schweitzer VG (1993) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: the effect of pigmentation and inhibitory agents. Laryngoscope 103:1–52
Stengs CHM, Klis SFL, Huizing EH, Smoorenburg GF (1997) Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity; electrophysiological evidence of spontaneous recovery in the albino guinea pig. Hear Res 111:103–113
Van Ruijven MWM, de Groot JCMJ, Klis SFL, Smoorenburg G (2005) Cochlear targets of cisplatin: an electrophysiological and morphological time-sequence study. Hear Res 205:241–248
Wang Y, Han TZ (2009) Prenatal exposure to heroin in mice elicits memory deficits that can be attributed to neuronal apoptosis. Neuroscience 160:330–338
Watanabe K, Inai S, Jinnouchi K, Baba S, Yagi T (2003) Expression of caspase-activated deoxyribonuclease (CAD) and caspase 3 (CPP32) in the cochlea of cisplatin (CDDP)-treated guinea pigs. Auris Nasus Larynx 30:219–225
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334:115–124
Yu YN, Chen H, Li Y (2009) Protect effect of bicyclol on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Arch Toxicol 83:381–387
Zhang M, Liu W, Ding D, Salvi R (2003) Pifithrin-alpha suppresses p53 and protects cochlear and vestibular hair cells from cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Neuroscience 120:191–205
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, S., Jiang, X., Yan, A. et al. Perinatal cisplatin exposure induces cochlear apoptosis in newborn guinea pigs. Arch Toxicol 85, 19–25 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0543-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0543-7