Abstract
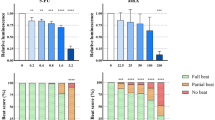
Mycophenolate mofetil is a widely used immunosuppressive drug that recently has been categorized as a human teratogen. Animal experiments indicate a teratogenic potential of the drug, but so far, it has not been studied in embryotoxicity in vitro assays. The aim of this study was to evaluate the in vitro embryotoxic potential of mycophenolic acid and investigate the ability of such tests to detect its embryotoxic potential. We used two validated assays: the rat whole embryo culture and the murine embryonic stem cell test. Rat embryos cultured from gestational day 9.5 for 48 h with the drug showed dysmorphogenic development already at a concentration of 250 μg mycophenolic acid/l medium. At concentrations of 750 μg/l and more, all rat embryos exhibited malformations. The main effects were defective yolk sac blood circulation, neural tube defects (open cranial neural pore), malformations of the head with missing eye anlagen and heart anomalies. Moreover, the exposed embryos showed a concentration-dependent decrease in protein content, crown-rump length, number of somites and morphological score. The murine embryonic stem cell test was slightly more sensitive. Proliferation and differentiation of the ES-D3-cells were significantly impaired at concentrations of 31 and 125 μg mycophenolic acid/l medium, respectively. In the differentiation assay, at a concentration of 125 μg mycophenolic acid/l medium and more, the number of wells with differentiated cardiomyocytes significantly decreased. Additionally, a cytotoxicity assay with balb/c 3T3 mouse fibroblasts was used to compare the proliferation and vitality of embryonic cells with adult cells. In the balb/c 3T3 cytotoxicity assay, the number of vital mouse fibroblasts significantly decreased at a mycophenolic acid concentration of 62 μg/l and more. In conclusion, by using the two validated in vitro tests, we showed that mycophenolic acid exhibits a pronounced embryotoxic potential at cytotoxic concentrations. This result from validated in vitro tests is of special interest, because it supports the use of the tests to detect human teratogens.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison AC, Eugui EM (2000) Mycophenolate mofetil and its mechanisms of action. Immunopharmacology 47:85–118
Betonico GN, Abudd-Filho M, Goloni-Bertollo EM, Pavarino-Bertelli E (2008) Pharmacogenetics of mycophenolate mofetil: a promising different approach to tailoring immunosuppression? J Nephrol 21:503–509
Bullingham RE, Nicholls AJ, Kamm BR (1998) Clinical pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Pharmacokinet 34:429–455
Flick B, Klug S (2006) Whole embryo culture: an important tool in developmental toxicology today. Curr Pharm Des 12:1467–1488
Fulton B, Markham A (1996) Mycophenolate mofetil. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and clinical efficacy in renal transplantation. Drugs 51:278–298
Genschow E, Spielmann H, Scholz G, Seiler A, Brown N, Piersma A, Brady M, Clemann N, Huuskonen H, Paillard F, Bremer S, Becker K (2002) The ECVAM international validation study on in vitro embryotoxicity tests: results of the definitive phase and evaluation of prediction models. European Centre for the validation of alternative methods. Altern Lab Anim 30:151–176
Kaplan B (2006) Enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium (myfortic): an overview of current and future use in transplantation. Drugs 66:1–8
Klug S, Lewandowski C, Neubert D (1985) Modification and standardization of the culture of early postimplantation embryos for toxicological studies. Arch Toxicol 58:84–88
Le Ray C, Coulomb A, Elefant E, Frydman R, Audibert F (2004) Mycophenolate mofetil in pregnancy after renal transplantation: a case of major fetal malformations. Obstet Gynecol 103:1091–1094
Mc Kay DB, Josephson MA (2006) Pregnancy in recipients of solid organs—effects on mother and child. N Engl J Med 354:1281–1293
Novartis (2008) Myfortic® (mycophenolic acid). Full prescribing information. http://www.myfortic.com
Paquette JA, Kumpf SW, Streck RD, Thomson JJ, Chapin RE, Stedman DB (2008) Assessment of the embryonic stem cell test and application and use in the pharmaceutical industry. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol 83:104–111
Perez-Aytes A, Ledo A, Boso V, Sáenz P, Roma E, Poveda JL, Vento M (2008) In utero exposure to mycophenolate mofetil: a characteristic phenotype? Am J Med Genet A 146A:1–7
Pisoni CN, D’Cruz DP (2008) The safety of mycophenolate mofetil in pregnancy. Expert Opin Drug Saf 7:219–222
Roche Pharmaceuticals (2008) CellCept® (mycophenolate mofetil). Full prescribing information. Roche Laboratories Inc., New Jersey. http://www.rocheusa.com/products/cellcept/pi.pdf
Schütz E, Shipkova M, Armstrong VW, Wieland E, Oellerich M (1999) Identification of a pharmacologically active metabolite of mycophenolic acid in plasma of transplant recipients treated with mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Chem 45:419–422
Seiler A, Buesen R, Visan A, Spielmann H (2006) Use of murine embryonic stem cells in embryotoxicity assays: the embryonic stem cell test. Methods Mol Biol 329:371–395
Shipkova M, Wieland E, Schütz E, Wiese C, Niedmann PD, Oellerich M, Armstrong VW (2001) The acyl glucuronide metabolite of mycophenolic acid inhibits the proliferation of human mononuclear leukocytes. Transplant Proc 33:1080–1081
Shipkova M, Armstrong VW, Oellerich M, Wieland E (2003) Acyl glucuronide drug metabolites: toxicological and analytical implications. Ther Drug Monit 25:1–16
Sifontis NM, Coscia LA, Constantinescu S, Lavelanet AF, Moritz MJ, Armenti VT (2006) Pregnancy outcomes in solid organ transplant recipients with exposure to mycophenolate mofetil or sirolimus. Transplantation 82:1698–1702
Staatz CE, Tett SE (2007) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of mycophenolate in solid organtransplant recipients. Clin Pharmacokinet 46:13–58
Stahlmann R, Klug S, Foerster M, Neubert D (1993) Significance of embryo culture methods for studying the prenatal toxicity of virustatic agents. Reprod Toxicol 7:129–143
van Gelder T, Le Meur Y, Shaw LM, Oellerich M, DeNofrio D, Holt C, Holt DW, Kaplan B, Kuypers D, Meiser B, Toenshoff B, Mamelok RD (2006) Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolate mofetil in transplantation. Ther Drug Monit 28:145–154
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Nicole Müller and Annegret Felies for their excellent technical assistance in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0492-1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eckardt, K., Stahlmann, R. Use of two validated in vitro tests to assess the embryotoxic potential of mycophenolic acid. Arch Toxicol 84, 37–43 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0476-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-009-0476-1