Abstract
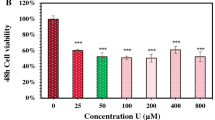
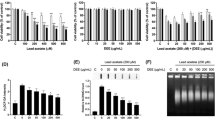
Uranium is a naturally occurring radioactive material present everywhere in the environment. It is toxic because of its chemical or radioactive properties. Uranium enters environment mainly from mines and industry and cause threat to human health by accumulating in lungs as a result of inhalation. In our previous study, we have shown the effectiveness of antioxidant system response to the oxidative stress induced by uranyl acetate (UA) in rat lung epithelial (LE) cells. As part of our continuing studies; here, we investigated the mechanism underlying when LE cells are exposed to different concentration of UA. Oxidative stress may lead to apoptotic signaling pathways. LE cells treated with 0.25, 0.5 and 1 mM of UA results in dose and time-dependent increase in activity of both caspases-3 and -8. Increase in the concentration of cytochrome-c oxidase in cytosol was seen in LE cells treated with 1 mM UA as a result of mitochondria membrane permeability. The cytochrome-c leakage may trigger the apoptotic pathway. TUNEL assay performed in LE cells treated with 1 mM of UA showed significant incorporation of dNTPs in the nucleus after 24 h. In the presence of the caspase inhibitors, we observed the significant decrease in the activity of caspases-8 and -3 in 0.5 and 1 mM UA-treated LE cells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertin G, Averbeck D (2006) Cadmium: cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences (a review). Biochimie 88:1549–1559
Bin W, James FT, Terry SW, Gary SS (2006) In vitro immune toxicity of depleted uranium: effects on murine macrophages, CD4 + T cells, and gene expression profiles. Environ Health Perspect 114(1):85–91
Bleise A, Danesi PR, Burkart W (2003) Properties, use and health effects of depleted uranium (DU): a general overview. J Environ Radioact 64:93–112
Bradley RH, Caldwell BM (1978) Screening the environment. Am J Orthopsychiatry 48(1):114–130
Celine T, Marie C, Sarah M, Angelique S, Laure A, Barbara G (2007) Uranium induces apoptosis and is genotoxic to normal rat kidney (NRK-52E) proximal cells. Toxicol Sci 98(2):479–487
Chobanova N, Genchev G, Yagova A, Georgieva L (2003) Cancer in populations living in regions with radio ecological problems in Bulgaria. J BUON (official journal of the Balkan Union of Oncology 8(2):143–146
Grosche B, Kreuzer M, Kreisheimer M, Schnelzer M, Tschense A (2006) Lung cancer risk among German male uranium miners: a cohort study, 1946–1998. Br J Cancer 95:1280–1287
Ivan S (2006) Common mechanisms in nephropathy induced by toxic metals. Nephron Physiol 104:107–114
James KA, Andrew GP (2007) Apoptosis commitment—translating survival signals into decisions on mitochondria. Cell Res 17:976–984
Joachim S, Monika P, Paria Y, Thilo D, Hans-Joachim W (2007) ATM gene mutations in former uranium miners of SDAG Wismut: a pilot study. Oncol Rep 17:477–482
John KF, Narayani R, Vilmar V, David ME (2002) Depleted uranium/uranyl chloride induces apoptosis in mouse J774 macrophages. Toxicology 179:105–114
Kanno S, Kitajima Y, Kakuta M, Osanai Y, Kurauchi K, Ujibe M, Ishikawa M (2008) Costunolide-induced apoptosis is caused by receptor-mediated pathway and inhibition of telomerase activity in NALM-6 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 5:1024–1028
Kendra CL, Geoffrey HG (2007) Regulation of the cellular DNA double-strand break response. Biochem Cell Biol 85:663–674
Klervi L, Solenne B, Dominique B, Margot T, Sylvaine C, Benoıt Q, Dominique L (2007) Lung cancer risk associated to exposure to radon and smoking in a case–control study of French uranium miners. Health Phys 92(4):371–378
Kryscio A, Ulrich Muller WU, Wojcik A, Kotschy N, Grobelny S, Streffer C (2001) A cytogenetic analysis of the long-term effect of uranium mining on peripheral lymphocytes using the micronucleus—centromere assay. Int J Radiat Biol 77(11):1087–1093
Levine S, Saltzman A (1994) The balance between lymphatic and systemic absorption determines the outcome of sensitization for anaphylaxis in rats. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 105(1):91–95
Marjorie M, Michel MD, Francxois P, Valerie C, Gerard D, Marie D (2006) Genotoxic and inflammatory effects of depleted uranium particles inhaled by rats. Toxicol Sci 89(1):287–295
Monica Y, Shania GL, Edgar CR, Diane SM (2003) Uranyl acetate causes DNA single strand breaks in-vitro in the presence of ascorbate (Vitamin C). Chem Res Toxicol 16(4):524–530
Padmavati S, Arora R (1976) Beta-adrenergic blocking agents in cardiology. J Assoc Physicians of India 24(11):725–728
Periyakaruppan A, Kumar F, Sarkar S, Sharma CS, Ramesh GT (2007) Uranium induces oxidative stress in lung epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol 81(6):389–395
Prat O, Berenguer F, Malard V, Tavan E, Sage N, Steinmetz G, Quemeneur E (2005) Transcriptomic and proteomic responses of human renal HEK293 cells to uranium toxicity. Proteomics 5:297–306
Sandra WS, Douglas TW, AbouEl–Makarim A, Michael MD, John WP Sr (2007) Particulate depleted uranium is cytotoxic and clastogenic to human lung cells. Chem Res Toxicol 20(5):815–820
Seon–Hee O, Sung–Chul L (2006) A rapid and transient ROS generation by cadmium triggers apoptosis via caspase-dependent pathway in HepG2 cells and this is inhibited through N-acetylcysteine-mediated catalase upregulation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 212:212–223
Seon–Hee O, Byung-Hoon L, Sung-Chul L (2004) Cadmium induces apoptotic cell death in WI 38 cells via caspase-dependent Bid cleavage and calpain-mediated mitochondrial Bax cleavage by Bcl-2-independent pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 68:1845–1855
Susumu O, Ying X, Motohide T (1998) Effects of uranium ore dust on cultured human lung cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 5(4):267–271
The Royal Society Working Group on the Health Hazards of Depleted Uranium Munitions (2002) The health effects of depleted uranium munitions: a summary. J Radiol Prot 22:131–139
US Department of Health and Human Services (1999) Toxicological profile for uranium. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry 462
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1–40
Veronique M, Odette P, Elisabeth D, Frederic B, Nicole S, Eric Q (2005) Proteomic analysis of the response of human lung cells to uranium. Proteomics 5:4568–4580
Vincent G, Saadia K, Gerard G, Marc P, Herve R (2004) Uranium induces TNF-α secretion and MAPK activation in a rat alveolar macrophage cell line. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 194:49–59
Virginia CH, Diane SM (2006) Molecular analysis of hprt mutations generated in Chinese hamster ovary EM9 cells by uranyl acetate, by hydrogen peroxide, and spontaneously. Mol Carcinog 45:60–72
World Health Organization (2001) Health effects of depleted uranium. Fifty-fourth World Health Assembly A54/19:Add.1
Yang ZH, Fan BX, Lu Y, Cao ZS, Yu S, Fan FY, Zhu MX (2002) Malignant transformation of human bronchial epithelial cell (BEAS-2B) induced by depleted uranium. Ai-Zheng (Chin J Cancer) 21(9):944–948
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NASA funding NCC 9-165: NCC-1-02038: NAG 9-1414: NIH 1P20MD001822-1 (GR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Periyakaruppan, A., Sarkar, S., Ravichandran, P. et al. Uranium induces apoptosis in lung epithelial cells. Arch Toxicol 83, 595–600 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0396-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0396-5