Abstract
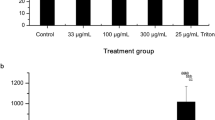
Alveolar macrophages (AM) have an important role in clearing particles from the lungs. In response to different stimuli they can release reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory mediators and promote pulmonary inflammation. We exposed rat AM to carbon black (CB) particles (0.63–20 μg/ml) and measured the generation of ROS by using the fluorescent probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate. Fluorescence was elevated in a concentration dependent manner in the AM exposed to CB. Follow-up experiments using a series of enzyme inhibitors indicate that the ERK MAP kinase pathway and the p38 MAP kinase pathway may be involved in the formation of ROS.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aam BB, Myhre O, Fonnum F (2003) Transcellular signalling pathways and TNF-alpha release involved in formation of reactive oxygen species in rat alveolar macrophages exposed to tert-butylcyclohexane. Arch Toxicol 77(12):678–684
Bonvallot V, Baeza-Squiban A, Boland S, Marano F (2000) Activation of transcription factors by diesel exhaust particles in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro. Inhal Toxicol 12(Suppl 3):359–364
Braunauer S, Emmet HP, Teller E (1938) Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J Am Chem Soc 60:309–319
Chin BY, Choi ME, Burdick MD, Strieter RM, Risby TH, Choi AM (1998) Induction of apoptosis by particulate matter: role of TNF-alpha and MAPK. Am J Physiol 275(5 Pt 1):L942–L949
Dang PM, Morel F, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, Benna JE (2003) Phosphorylation of the NADPH oxidase component p67(PHOX) by ERK2 and P38MAPK: selectivity of phosphorylated sites and existence of an intramolecular regulatory domain in the tetratricopeptide-rich region. Biochemistry 42(15):4520–4526
Dellinger B, Pryor WA, Cueto R, Squadrito GL, Hegde V, Deutsch WA (2001) Role of free radicals in the toxicity of airborne fine particulate matter. Chem Res Toxicol 14(10):1371–1377
Dewas C, Fay M, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, El-Benna J (2000) The mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway is involved in formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced p47phox phosphorylation in human neutrophils. J Immunol 165(9):5238–5244
Dockery DW, Schwartz J, Spengler JD (1992) Air pollution and daily mortality: associations with particulates and acid aerosols. Environ Res 59(2):362–373
Duncia JV, Santella JB III, Higley CA, Pitts WJ, Wityak J, Frietze WE, Rankin FW, Sun JH, Earl RA, Tabaka AC, Teleha CA, Blom KF, Favata MF, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, Horiuchi K, Copeland RA, Scherle PA, Trzaskos JM, Magolda RL, Trainor GL, Wexler RR, Hobbs FW, Olson RE (1998) MEK inhibitors: the chemistry and biological activity of U0126, its analogs, and cyclization products. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8(20):2839–2844
Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, Feeser WS, Van Dyk DE, Pitts WJ, Earl RA, Hobbs F, Copeland RA, Magolda RL, Scherle PA, Trzaskos JM (1998) Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem 273(29):18623–18632
Goldsmith CA, Imrich A, Danaee H, Ning YY, Kobzik L (1998) Analysis of air pollution particulate-mediated oxidant stress in alveolar macrophages. J Toxicol Environ Health A 54(7):529–545
Ito T, Ikeda M, Yamasaki H, Sagai M, Tomita T (2000) Peroxynitrite formation by diesel exhaust particles in alveolar cells: links to pulmonary inflammation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 9(1–2):1–8
Kamakura S, Moriguchi T, Nishida E (1999) Activation of the protein kinase ERK5/BMK1 by receptor tyrosine kinases. Identification and characterization of a signaling pathway to the nucleus. J Biol Chem 274(37):26563–26571
Kawabata Y, Iwai K, Udagawa T, Tukagoshi K, Higuchi K (1986) Effects of diesel soot on unscheduled DNA synthesis of tracheal epithelium and lung tumor formation. Dev Toxicol Environ Sci 13:213–222
Keston AS, Brandt R (1965) The fluorometric analysis of ultramicro quantities of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Biochem 11:1–5
Lim HB, Ichinose T, Miyabara Y, Takano H, Kumagai Y, Shimojyo N, Devalia JL, Sagai M (1998) Involvement of superoxide and nitric oxide on airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness induced by diesel exhaust particles in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 25(6):635–644
Lovik M, Hogseth AK, Gaarder PI, Hagemann R, Eide I (1997) Diesel exhaust particles and carbon black have adjuvant activity on the local lymph node response and systemic IgE production to ovalbumin. Toxicology 121(2):165–178
Ma JY, Ma JK (2002) The dual effect of the particulate and organic components of diesel exhaust particles on the alteration of pulmonary immune/inflammatory responses and metabolic enzymes. J Environ Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev 20(2):117–147
Matsuda S, Shibasaki F, Takehana K, Mori H, Nishida E, Koyasu S (2000) Two distinct action mechanisms of immunophilin–ligand complexes for the blockade of T-cell activation. EMBO Rep 1(5):428–434
Mendes AF, Carvalho AP, Caramona MM, Lopes MC (2001) Diphenyleneiodonium inhibits NF-kappaB activation and iNOS expression induced by IL-1beta: involvement of reactive oxygen species. Mediators Inflamm 10(4):209–215
Myhre O, Andersen JM, Aarnes H, Fonnum F (2003) Evaluation of the probes 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate, luminol, and lucigenin as indicators of reactive species formation. Biochem Pharmacol 65(10):1575–1582
Nikula KJ, Snipes MB, Barr EB, Griffith WC, Henderson RF, Mauderly JL (1995) Comparative pulmonary toxicities and carcinogenicities of chronically inhaled diesel exhaust and carbon black in F344 rats. Fundam Appl Toxicol 25(1):80–94
Nilsen A, Hagemann R, Eide I (1997) The adjuvant activity of diesel exhaust particles and carbon black on systemic IgE production to ovalbumin in mice after intranasal instillation. Toxicology 124(3):225–232
Reistad T, Mariussen E, Fonnum F (2005) The effect of a brominated flame retardant, tetrabromobisphenol-A, on free radical formation in human neutrophil granulocytes: the involvement of the MAP kinase pathway and protein kinase C. Toxicol Sci 83(1):89–100
Rengasamy A, Barger MW, Kane E, Ma JK, Castranova V, Ma JY (2003) Diesel exhaust particle-induced alterations of pulmonary phase I and phase II enzymes of rats. J Toxicol Environ Health A 66(2):153–167
Shukla A, Timblin C, BeruBe K, Gordon T, McKinney W, Driscoll K, Vacek P, Mossman BT (2000) Inhaled particulate matter causes expression of nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-related genes and oxidant-dependent NF-kappaB activation in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23(2):182–187
Sibille Y, Reynolds HY (1990) Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury. Am Rev Respir Dis 141(2):471–501
Squadrito GL, Cueto R, Dellinger B, Pryor WA (2001) Quinoid redox cycling as a mechanism for sustained free radical generation by inhaled airborne particulate matter. Free Radic Biol Med 31(9):1132–1138
van Zijverden M, van der Pijl A, Bol M, van Pinxteren FA, de Haar C, Penninks AH, van Loveren H, Pieters R (2000) Diesel exhaust, carbon black, and silica particles display distinct Th1/Th2 modulating activity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 168(2):131–139
Yang HM, Ma JY, Castranova V, Ma JK (1997) Effects of diesel exhaust particles on the release of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha from rat alveolar macrophages. Exp Lung Res 23(3):269–284
Yang HM, Barger MW, Castranova V, Ma JK, Yang JJ, Ma JY (1999) Effects of diesel exhaust particles (DEP), carbon black, and silica on macrophage responses to lipopolysaccharide: evidence of DEP suppression of macrophage activity. J Toxicol Environ Health A 58(5):261–278
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge support by VISTA (The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters/Statoil).
This investigation was carried out in accordance with the law and rules for experimental animals in Norway.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aam, B.B., Fonnum, F. Carbon black particles increase reactive oxygen species formation in rat alveolar macrophages in vitro. Arch Toxicol 81, 441–446 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0164-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0164-3