Abstract
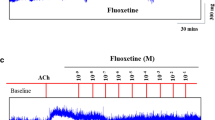
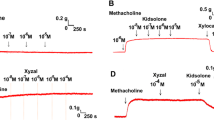
Ozone is a potent oxidizing agent with a variety of potential uses, including its antimicrobial and deodorising properties. The recent increased use of ozone led to questions regarding its safety in humans. This study specifically focussed on the in vitro effect of ozone on isolated guinea pig tracheal tissue as well as its effect on the isolated trachea in the presence of various drugs with well-known effects, including methacholine and isoproterenol. The results found in this study identified two direct effects on the isolated trachea due to ozone exposure: (1) a definite contraction of the isolated trachea immediately after exposure to ozone, and (2) a clearly visible and significant hyper responsiveness of the isolated trachea to irritants, e.g. methacholine. Although ozone has a negative effect on the trachea, it was concluded that ozone has no adverse effect on muscarinic receptors. We found that ozone has a significant desensitizing effect on the pharmacological response of β sympathomimetics (isoproterenol), while isoproterenol itself has a relaxing effect on the ozone-induced contraction of the isolated trachea. Observations in this in vitro study further emphasised that ozone does have a negative effect on respiratory health. It is underlined that the inhalation of ozone should be avoided by workers who are often in contact with the gas, and especially by those with existing airway diseases. An apparent EC50 value of ozone on the trachea was established by two different methods as 5.71 and 9.78 × 10−3 M, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 19th edn. American Water Works Association, Washington (Method 4500-O3)
Barnes PJ (1995) Beta-adrenergic receptors and their regulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 152:838–860
Hyde DM, Hubbard WC, Wong V, Wu R, Pinkerton K, Plopper CG (1992) Ozone induced acute tracheobronchial epithelial injury: relationship to granulocyte emigration in the lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 6(5):481–497
Kafoury RM, Pryor WA, Squadrito GL, Salgo MG, Zou X, Friedman M (1999) Induction of inflammatory mediators in human airway epithelial cells by lipid ozonation products. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160(6):1934–1942
Kume H, Takagi K (1997) Inhibitory effects of Gs on desensitization of beta-adrenergic receptors in tracheal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 273(3 Pt 1):L556–L564
Linn WS, Medway DA, Anzar UT, Valencia LM, Spier CE, Tsao FS, Fischer DA, Hackney JD (1982) Persistence of adaptation to ozone in volunteers exposed repeatedly for six weeks. Am Rev Respir Dis 125(5):491–495
Park JW, Taube C, Joetham A, Takeda K, Kodama T, Dakhama A, McConville G, Allen CB, Sfyroera G, Shultz LD, Lambris JD, Giclas PC, Holers VM, Gelfand EW (2004) Complement activation is critical to airway hyperresponsiveness after acute ozone exposure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169(6):726–732
Patil PN, Jacobwitz D (1968) Steric aspects of adrenergic drugs. IX. Pharmacologic and histochemical studies on isomers of cobefrin (alpha-methylnorepinephrine). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 161(2):279–295
Pretorius A (2005) The effects of ozone exposure on the viability and function of cultured human cell lines. M.Sc. Dissertation North-West University, Potchefstroom 2520, South Africa
Pryor WA (1992) How far does ozone penetrate into the pulmonary air/tissue boundary before it reacts? Free Radic Biol Med 12(1):83–88
Schelegle ES, Siefkin AD, McDonald RJ (1991) Time course of ozone induced neutrophilia in normal humans. Am Rev Respir Dis 143(6):1353–1358
Stokinger HE (1965) Ozone toxicology. A review of research and industrial experience: 1954–1964. Arch Environ Health 10:719–731
Timmerman H, Scheffer NG (1968) A new tracheal strip preparation for the evaluation of beta-adrenergic activity. J Pharm Pharmacol 20(1):78–79
Van Rossum JM (1963) Cumulative dose-response curves II. Technique for the making of dose response curves in isolated organs and the evaluation of drug parameters. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 143:299–330
Wright D, Wheeler C (1990) Cellular, biochemical and functional effects of ozone: new research and perspectives on ozone health effects. Toxicol lett 51(2):125–145
Acknowledgments
The South African National Research Foundation (NRF) and North-West University are thanked for financial support. All experiments on laboratory animals were approved by the ethical committee of the North-West University and the experiments comply with the current laws of South Africa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lotriet, C.J., Oliver, D.W. & Venter, D.P. The pharmacological effects of ozone on isolated guinea pig tracheal preparations. Arch Toxicol 81, 433–440 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0159-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-006-0159-0