Abstract
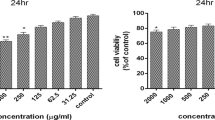
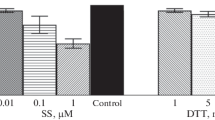
Zinc is involved in many physiological processes and plays a critical role in functional and structural cells. Zinc at concentrations ranging from 100 to 150 μmol L−1 has been shown to induce morphological transformation of Syrian hamster embryo (SHE) cells. At these concentrations, zinc inhibited apoptosis in SHE cells. The objective of this study was to elucidate the mechanisms of action of zinc on the apoptotic pathway. Effects of 100 and 150 μmol L−1 ZnCl2 on the expression of two members of the Bcl-2 family of proteins and on the transcription factor c-Myc in SHE cells was investigated using RT-PCR. No effect on the proto-oncogene c-myc was observed. Up-regulation of bcl-2 expression was found and bax expression was reduced. These changes have been corroborated by immunoblotting. Effects of Zn2+ on bcl-2/bax ratio were confirmed in apoptotic camptothecin-treated SHE cells. Cloned and sequenced cDNAs obtained from RT-PCR amplifications allowed us to check the RT-PCR products encoded the expected proteins. This study demonstrated that zinc acts in the early phases of the apoptotic process by modification of the bcl-2/bax ratio in normal and apoptotic SHE cells.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JM, Cory S (1998) The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281:1322–1326
Alexandre S, Rast C, Maire MA, Orfila L, Vasseur P (2003) ZnCl2 induces Syrian hamster embryo (SHE) cell transformation. Toxicol Lett 142:77–87
Alexandre S, Rast C, Nguyen-Ba G, Vasseur P (2000) Detection of apoptosis induced by topoisomerase inhibitors and serum deprivation in Syrian hamster embryo cells. Exp Cell Res 255:30–39
Alexandre S, Rast C, Nguyen-Ba G, Vasseur P (2002) ZnCl2 prevents c-myc repression and apoptosis in serum-deprived Syrian hamster embryo cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 11:191–196
Antonsson B, Conti F, Ciavatta AM, Montessuit S, Lewis S, Martinou I, Bernasconi L, Bernard A, Mermod JJ, Mazzei G, Maundrell K, Gambale F, Sadoul R, Martinou JC (1997) Inhibition of Bax channel-forming activity by Bcl-2. Science 277:370–372
Barrett J, Crawford DD, Mixter LO, Schechtmen LM, Ts’o POP, Pollack R (1979) Correlation of in vitro growth properties and tumorigenicity of Syrian hamster cell lines. Cancer Res 39:1507–1510
Berwald Y, Sachs L (1963) In vitro cell transformation with chemical carcinogens. Nature 200:1182–1184
Bessi H, Rast C, Nguyen-Ba G, Vasseur P (1994) Chlorothalonil promotes morphological transformation in hamster embryo cells but does not inhibit GAP junctional intercellular communication either in SHE cells or in the V79 cell line. Cancer J 7:248–253
Bissonnette RP, Echeverri F, Mahboubi A, Green DR (1992) Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature 359:552–554
Borner C (2003) The Bcl-2 protein family: sensors and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions. Mol Immunol 39:615–647
Brady HJ, Gil-Gomez G (1998) Bax. The pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member, Bax. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 30:647–650
Cain K, Bratton SB, Cohen GM (2002) The Apaf-1 apoptosome: a large caspase-activating complex. Biochimie 84:203–214
Castedo M, Ferri K, Roumier T, Metivier D, Zamzami N, Kroemer G (2002) Quantitation of mitochondrial alterations associated with apoptosis. J Immunol Methods 265:39–47
Chai F, Truong-Tran AQ, Evdokiou A, Young GP, Zalewski PD (2000) Intracellular zinc depletion induces caspase activation and p21 Waf1/Cip1 cleavage in human epithelial cell lines. J Infect Dis 182:85–92
Chao DT, Korsmeyer SJ (1998) BCL-2 family: regulators of cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 16:395–419
Chimienti F, Seve M, Richard S, Mathieu J, Favier A (2001) Role of cellular zinc in programmed cell death: temporal relationship between zinc depletion, activation of caspases, and cleavage of Sp family transcription factors. Biochem Pharmacol 62:51–62
Cohen JJ, Duke RC (1984) Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol 132:38–42
Combes R, Balls M, Curren RD, Fischbach M, Fusenig N, Kirkland D, Lasne C, Landolph J, LeBoeuf RA, Marquardt H, McCormick J, Müller L, Rivedal E, Sabbioni E, Tanaka N, Vasseur P, Yamasaki H (1999) Cell transformation assay as predictors of human carcinogenicity, the reports and recommendations of ECVAM, workshop 39. ATLA 27:745–767
Cosulich SC, Savory PJ, Clarke PR (1999) Bcl-2 regulates amplification of caspase activation by cytochrome c. Curr Biol 9:147–150
DelBino G, Lassota P, Darzynkiewicz Z (1991) The S-phase cytotoxicity of camptothecin. Exp Cell Res 193:27–35
DiPaolo JA, Casto BC (1979) Quantitative studies of in vitro morphological transformation of Syrian hamster embryo by inorganic metal salts. Cancer Res 39:1008–1013
Dreosti IE (2001) Zinc and the gene. Mutat Res 475:161–167
Elias Z, Poirot O, Daniere MC, Terzetti F, Marande AM, Dzwigaj S, Pezerat H, Fenoglio I, Fubini B (1989) Cytotoxic and transforming effects of silica particles with different surface properties in Syrian hamster embryo (SHE) cells. Toxicol in Vitro 14:409–422
Evan GI, Wyllie AH, Gilbert CS, Littlewood TD, Land H, Brooks M, Waters CM, Penn LZ, Hancock DC (1992) Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell 69:119–128
Fukamachi Y, Karasaki Y, Sugiura T, Itoh H, Abe T, Yamaraura K, Higashi K (1998) Zinc suppresses apoptosis of U937 cells induced by hydrogen peroxide through an increase of the Bcl-2/Bax ratio. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 246:364–369
Ganju N, Eastman A (2003) Zinc inhibits Bax and Bak activation and cytochrome c release induced by chemicals inducers of apoptosis but not by death-receptor-initiated pathways. Cell Death Differ, 10:652–661
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Holcik M, Gibson H, Korneluk RG (2001) XIAP: apoptotic brake and promising therapeutic target. Apoptosis 6:253–261
Jankowski-Hennig MA, Clegg MS, Daston GP, Rogers JM, Keen CL (2000) Zinc-deficient rat embryos have increased caspase 3-like activity and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 271:250–256
Juin P, Hueber AO, Littlewood T, Evan G (1999) c-Myc-induced sensitization to apoptosis is mediated through cytochrome c release. Genes Dev 13:1367–1381
Jurgensmeier JM, Xie Z, Deveraux Q, Ellerby L, Bredesen D, Reed JC (1998) Bax directly induces release of cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4997–5002
Kerr JFR, Winterford CM, Harmon BV (1993) Apoptosis: its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 73:2013–2026
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR, Newmeyer DD (1997) The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science 275:1132–1136
Larsen AK, Skladanowski A (1998) Cellular resistance to topoisomerase-targeted drugs: from uptake to cell death. Biochim Biophys Acta 1400:257–274
LeBoeuf RA, Kerckaert GA, Poiley JA, Raineri R (1989) An interlaboratory comparison of enhanced morphological transformation of Syrian hamster embryo cells cultured under conditions of reduced bicarbonate concentration and pH. Mutat Res 222:205–218
Nakatani T, Tawaramoto M, Kennedy DO, Kojima A, Matsui-Yuasa I (2000) Apoptosis induced by chelation of intracellular zinc is associated with depletion of cellular reduced glutathione level in rat hepatocytes. Chem Biol Interact 125:151–153
Pearson WR, Lipman DJ (1988) Improved tools for biological sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2444–2448
Perry DK, Smyth MJ, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Duriez P, Poirier GG, Hannun YA (1997) Zinc is a potent inhibitor of the apoptotic protease, caspase-3. J Biol Chem 30:18530–18533
Pienta RJ, Poiley JA, Lebherz WB (1977) Morphological transformation of early passage golden Syrian hamster embryo cells derived from cryopreserved primary cultures as a reliable in vitro bioassay for identifying diverse carcinogens. Int J Cancer 19:642–655
Prendergast GC (1999) Mechanisms of apoptosis by c-Myc. Oncogene 18:2967–2987
Reed JC (1994) Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol 124:1–6
Seve M, Chimienti F, Favier A (2002) Role du zinc intracellulaire dans la mort cellulaire programmée: role of intracellular zinc in programmed cell death. Pathol Biol 50:212–221
Shimoda R, Achanzar WE, Qu W, Nagamine T, Takagi H, Mori M, Waalkes MP (2003) Metallothionein is a potential negative regulator of apoptosis. Toxicol Sci 73:294–300
Soucie EL, Annis MG, Sedivy J, Filmus J, Leber B, Andrews DW, Penn LZ (2001) Myc potentiates apoptosis by stimulating Bax activity at the mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol 21:4725–4736
Sunderman FW (1995) The influence of zinc on apoptosis. Ann Clin Lab Sci 25:134–142
Tamura T, Sadakata N, Oda T, Muramatsu T (2002) Role of zinc ions in ricin-induced apoptosis in U937 cells. Toxicol Lett 132:141–151
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y (1998) Caspases: enemies within. Science 281:1312–1316
Truong-Tran AQ, Carter J, Ruffin RE, Zalewski PD (2001) The role of zinc in caspase activation and apoptotic cell death. Biometals 14:315–330
Tu A, Hallowell W, Pallota S, Sivak A, Lubet RA, Curren RD, Avery MD, Jones C, Sedita BA, Huberman E, Tennant R, Spalding J, Kouri RE (1986) An interlaboratory comparison of transformation in Syrian hamster embryo cells with model and coded chemicals. Environ Mutagen 8:77–98
Wyllie AH (1980) Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68:251–306
Wyllie AH (1992) Apoptosis and the regulation of cell numbers in normal and neoplasic tissues: an overview. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11:95–103
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado AM, Cai J, Peng T-I, Jones DP, Wang X (1997) Prevention of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science 275:1129–1132
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr P. Poupin for constructive discussions and Pr A. Hammond for assistance in revising the English form of this paper. They are grateful to Dr Methlin and his colleagues from the “Claude Bernard Hospital—Departement de Radiotherapie et de Chimiotherapie” for preparation of irradiated SHE cells. This study was funded by the French Ministry of Research and Direction for Prevention of Pollution and Environmental Risk of the Ministry of the Environment. The authors declare that the experiments comply with the current law in France and with safety requirements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maire, M.A., Rast, C., Pagnout, C. et al. Changes in expression of bcl-2 and bax in Syrian hamster embryo (SHE) cells exposed to ZnCl2. Arch Toxicol 79, 90–101 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-004-0611-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-004-0611-y