Abstract
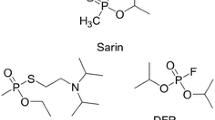
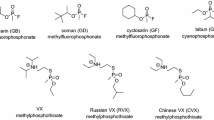
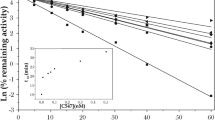
The reactivation of organophosphate (OP)-inhibited acetylcholinesterase (AChE) by oximes results inevitably in the formation of highly reactive phosphyloximes (POX), which may re-inhibit the enzyme. An impairment of net reactivation by stable POX was found with 4-pyridinium aldoximes, e.g. obidoxime, and a variety of OP compounds. In this study the effect of organophosphorus hydrolase (OPH), organophosphorus acid anhydrolase (OPAA) and diisopropylfluorophosphatase (DFPase) on obidoxime-induced reactivation of human acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibited by different OPs was investigated. Reactivation of paraoxon-, sarin-, soman- and VX-inhibited AChE by obidoxime was impaired by POX-induced re-inhibition whereas no deviation of pseudo first-order kinetics was observed with tabun, cyclosarin and VR. OPH prevented (paraoxon) or markedly reduced the POX-induced re-inhibition (VX, sarin, soman), whereas OPAA and DFPase were without effect. Additional experiments with sarin-inhibited AChE indicate that the POX hydrolysis by OPH was concentration-dependent. The activity of OP-inhibited AChE was not affected by OPH in the absence of obidoxime. In conclusion, OPH may be a valuable contribution to the therapeutic regimen against OP poisoning by accelerating the degradation of both the parent compound, OP, and the reaction product, POX.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldridge WN, Reiner E (1972) Enzyme inhibitors as substrates—interactions of esterases with esters of organophosphorus and carbamic acids. North-Holland Publishing, Amsterdam
Ashani Y, Leader H, Rothschild N, Dosoretz C (1998) Combined effect of organophosphorus hydrolase and oxime on the reactivation rate of diethylphosphoryl–acetylcholinesterase conjugates. Biochem Pharmacol 55:159–168
Ashani Y, Bhattacharjee AK, Leader H, Saxena A, Doctor BP (2003) Inhibition of cholinesterases with cationic phosphonyl oximes highlights distinctive properties of the charged pyridine groups of quaternary oxime reactivators. Biochem Pharmacol 66:191–202
Ballantyne B, Marrs TC (1992) Overview of the biological and clinical aspects of organophosphates and carbamates. In: Ballantyne B, Marrs TC (eds) Clinical and experimental toxicology of organophosphates and carbamates. Butterworth & Heinemann, Oxford, pp 3–14
Bismuth C, Inns RH, Marrs TC (1992) Efficacy, toxicity and clinical use of oximes in anticholinesterase poisoning. In: Ballantyne B Marrs TC (eds) Clinical and experimental toxicology of organophosphates and carbamates. Butterworth & Heinemann, Oxford, pp 555–577
de Jong LPA, Ceulen DI (1978) Anticholinesterase activity and rate of decomposition of some phosphylated oximes. Biochem Pharmacol 27:857–863
de Jong LPA, Wolring GZ (1978) Effect of 1-(AR)-alkyl-hydroxyiminomethyl-pyridinium salts on reactivation and aging of acetylcholinesterase inhibited ethyl dimethylphosphoramidocyanidate (tabun). Biochem Pharmacol 27:2229–2235
de Jong LPA, Wolring GZ (1984) Stereospecific reactivation by some Hagedorn-oximes of acetycholinesterases from various species including man inhibited by soman. Biochem Pharmacol 33:1119–1125
DeFrank JJ, Cheng TC (1991) Purification and properties of an organophosphorus acid anhydrase from a halophilic bacterial isolate. J Bacteriol 173:1938–1943
Dodge JT, Mitchell C, Hanahan DJ (1963) The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys 100:119–130
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Anders V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Erdmann WD, Bosse I, Franke P (1965) Zur Resorption und Ausscheidung von Toxogonin nach intramuskulärer Injektion am Menschen. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 90:1436–1438
Eyer P (1996) Optimal oxime dosage regimen, a pharmacokinetic approach. In: Szinicz L, Eyer P, Klimmek R (eds) Role of oximes in the treatment of anticholinesterase agent poisoning. Spektrum Akademischer Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 33–51
Hackley BE, Owens OO (1959) Preparation of O-(isopropylmethylphosphono)-4-formyl-1-methylpyridinium iodide oxime. J Org Chem 24:1120
Hackley BE, Steinberg GM, Lamb JC (1959) Formation of potent inhibitors of AChE by reaction of pyridinaldoximes with isopropyl methylphosphonofluoridate (GB). Arch Biochem Biophys 80:211–214
Hartleib J, Rüterjans H (2001) High-yield expression, purification, and characterization of the recombinant diisopropylfluorophosphatase from Loligo vulgaris. Protein Expr Purif 21:210–219
Harvey B, Sellers DJ, Watts P (1984) The reactivation by oximes of phosphonylated acetylcholinesterase: the possible erroneous interpretation of reactivating potency. Biochem Pharmacol 33:3499–3501
Harvey B, Scott RP, Sellers DJ, Watts P (1986) In vitro studies on the reactivation by oximes of phosphylated acetylcholinesterase-I. Biochem Pharmacol 35:737–744
Kiderlen D, Worek F, Klimmek R, Eyer P (2000) The phosphoryl oxime-destroying activity of human plasma. Arch Toxicol 74:27–32
Lamb JC, Steinberg GM, Hackley BE (1964) Isopropyl methylphosphonylated bisquaternary oximes, powerful inhibitors of cholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta 89:174–176
Leader H, Vincze A, Manisterski B, Rothschild N, Dosoretz C, Ashani Y (1999) Characterization of O,O-diethylphosphoryl oximes as inhibitors of cholinesterases and substrates of phosphotriesterases. Biochem Pharmacol 58:503–515
Lee EC (2003) Clinical manifestations of sarin nerve gas exposure. JAMA 290:659–662
MacIlwain C (1993) Study proves Iraq used nerve gas. Nature 363:3
Marrs TC (1993) Organophosphate poisoning. Pharmacol Ther 58:51–66
Mulbry WJ, Karns JS (1989) Parathion hydrolase specified by the Flavobacterium opd gene: relationship between the gene and the protein. J Bacteriol 171:6740–6746
Nagao M, Takatori T, Matsuda Y, Nakajima M, Iwase H, Iwadate K (1997) Definitive evidence for the acute sarin poisoning diagnosis in the Tokyo subway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 144:198–203
Nenner M (1974) Phosphonylierte Aldoxime Hemmwirkung auf Acetylcholinesterase und hydrolytischer Abbau. Biochem Pharmacol 23:1255–1262
Scaife JF (1959) Oxime reactivation studies of inhibited true and pseudo cholinesterase. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:1301–1311
Schoene K (1973) Phosphonyloxime aus Soman: Bildung und Reaktion mit Acetylcholinesterase in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 22:2997–3003
Sidell FR (1992) Clinical considerations in nerve agent intoxication. In: Somani SM (ed) Chemical warfare agents. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 155–194
Sogorb MA, Vilanova E (2002) Enzymes involved in the detoxification of organophosphorus, carbamate and pyrethroid insecticides through hydrolysis. Toxicol Lett 128:215–228
Thiermann H, Szinicz L, Eyer F, Worek F, Eyer P, Felgenhauer N, Zilker T (1999) Modern strategies in therapy of organophosphate poisoning. Toxicol Lett 107:233–239
Volans AP (1996) Sarin: guidelines on the management of victims of a nerve gas attack. J Accid Emerg Med 13:202–206
Wilson IB, Ginsburg S (1955) A powerful reactivator of alkylphosphate-inhibited acetylcholinesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta 18:168–170
Worek F, Szinicz L (2000) Reaktivierung Nervenkampfstoff-gehemmter humaner Erythrozyten-Acetylcholinesterase und Butyrylcholinesterase mit Oximen—Einfluß von Enzymkonzentration und Plasmabestandteilen. Interim Report Project 07/94
Worek F, Eyer P, Szinicz L (1998a) Inhibition, reactivation and aging kinetics of cyclohexylmethylphosphonofluoridate-inhibited human cholinesterases. Arch Toxicol 72:580–587
Worek F, Widmann R, Knopff O, Szinicz L (1998b) Reactivating potency of obidoxime, pralidoxime, HI 6 and HLö 7 in human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase inhibited by highly toxic organophosphorus compounds. Arch Toxicol 72:237–243
Worek F, Diepold C, Eyer P (1999a) Dimethylphosphoryl-inhibited human cholinesterases: inhibition, reactivation, and aging kinetics. Arch Toxicol 73:7–14
Worek F, Mast U, Kiderlen D, Diepold C, Eyer P (1999b) Improved determination of acetylcholinesterase activity in human whole blood. Clin Chim Acta 288:73–90
Worek F, Eyer P, Kiderlen D, Thiermann H, Szinicz L (2000) Effect of human plasma on the reactivation of sarin-inhibited human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Arch Toxicol 74:21–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herkenhoff, S., Szinicz, L., Rastogi, V.K. et al. Effect of organophosphorus hydrolysing enzymes on obidoxime-induced reactivation of organophosphate-inhibited human acetylcholinesterase. Arch Toxicol 78, 338–343 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-004-0547-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-004-0547-2