Abstract.
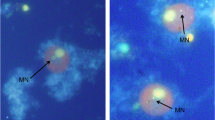
To date, a number of in vivo cytogenetic assays have studied the clastogenicity (chromosome aberrations, micronuclei formation) in bone marrow of rodents exposed to styrene by various routes. The majority of all these cytogenetic experiments yielded negative findings (Scott and Preston, Mutat Res 318:175–203, 1994). Recently published data from a micronucleus test in mice exposed via inhalation for up to 21 days showed some positive response, but was not fully conclusive (Vodicka et al., Chem Biol Interact 137:213–227, 2001). Since this exposure regimen has considerable relevance for workplace exposure, the present study was performed to further elucidate these findings. NMRI mice were exposed by whole body inhalation to styrene concentrations of 750 mg/m3 and 1,500 mg/m3 for 1, 3, 7, 14 and 21 consecutive days (6 h/day). Animals were killed directly after exposure and bone marrow was sampled for analysis of micronucleus induction. Under the experimental conditions used in the present investigation, there was no evidence of clastogenicity at any concentration or exposure interval.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Engelhardt, G., Gamer, A., Vodicka, P. et al. A re-assessment of styrene-induced clastogenicity in mice in a subacute inhalation study. Arch Toxicol 77, 56–61 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-002-0406-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-002-0406-y