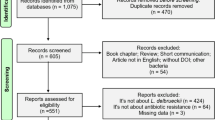
Abstract
Enterococcus mundtii AM_AQ_BC8 isolated from biofouled filtration membrane was characterised as a potential probiotic bacterium showing strong L-lactic acid-producing capability. Experimental studies revealed that E. mundtii AM_AQ_BC8 possess antibiofilm and antimicrobial ability too, as tested against strong biofilm-forming bacteria like Pseudomonas spp. The present study has evaluated the genetic potential of E. mundtii AM_AQ_BC8 through genome sequencing. Whole genome analysis revealed the presence of key genes like ldh_1 and ldh_2 responsible for lactic acid production along with genes encoding probiotic features such as acid and bile salt resistance (dnaK, dnaJ, argS), fatty acid synthesis (fabD, fabE) and lactose utilisation (lacG, lacD). The phylogenomic analysis based on OrthoANI (99.85%) and dDDH (96.8%) values revealed that the strain AM_AQ_BC8 shared the highest homology with E. mundtii. The genome sequence of strain AM_AQ_BC8 has been deposited to NCBI and released with GenBank accession no. SAMN32531201. The study primarily demonstrated the probiotic potential of E. mundtii AM_AQ_BC8 isolate, for L-lactate synthesis in high concentration (8.98 g/L/day), which also showed anti-biofilm and antimicrobial activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The whole genome sequence of E. mundtii AM_AQ_BC8 was deposited to NCBI GenBank under the BioProject number (PRJNA917242) and the accession number (SAMN32531201).
References
Aarti C, Khusro A, Varghese R, Arasu MV, Agastian P, Al-Dhabi NA, Ilavenil S, Choi KC (2017) In vitro studies on probiotic and antioxidant properties of Lactobacillus brevis strain LAP2 isolated from Hentak, a fermented fish product of North-East India. LWT 86:438–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.07.055
Araújo TF, Ferreira CL (2013) The genus Enterococcus as probiotic: safety concerns. Braz Arch Biol Technol 56:457–466. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132013000300014
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edward RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9(1):75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Ballén V, Ratia C, Cepas V, Soto SM (2020) Enterococcus faecalis inhibits Klebsiella pneumoniae growth in polymicrobial biofilms in a glucose-enriched medium. Biofouling 36(7):846–861. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2020.1824272
Barbosa J, Ferreira V, Teixeira P (2007) Biofilm development by Enterococcus spp. isolated from traditional fermented meat products and potential correlations with some virulence factors. J Biotechnol 131(1):S251
Belaouni HA, Compant S, Antonielli L, Nikolic B, Zitouni A, Sessitsch A (2022) In-depth genome analysis of Bacillus sp. BH32, a salt stress-tolerant endophyte obtained from a halophyte in a semiarid region. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 106(8):3113–3137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-11907-0
Ben Braiek O, Smaoui S (2019) Enterococci: between emerging pathogens and potential probiotics. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5938210
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinform 30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bonacina J, Suárez N, Hormigo R, Fadda S, Lechner M, Saavedra L (2017) A genomic view of food-related and probiotic enterococcus strains. DNA Res 24(1):11–24. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsw043
Borshchevskaya L, Gordeeva T, Kalinina A, Sineokii S (2016) Spectrophotometric determination of lactic acid. J Anal Chem 71:755–758. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1061934816080037
Byappanahalli M, Nevers M, Korajkic A, Staley Z, Harwood V (2012) Enterococci in the environmE. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 76:685–706
Carattoli A, Zankari E, Garcìa-Fernandez A, Larsen MV, Lund O, Villa L, Aarestrup FM, Hasman H (2014) PlasmidFinder and pMLST: in silico detection and typing of plasmids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(7):3895–3903
Carvalho FM, Teixeira Santos R, Mergulhao FJ, Gomes LC (2020) The use of probiotics to fight biofilms in medical devices: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Microorganisms 9(1):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9010027
Chen Z, Leng X, Zhou F, Shen W, Zhang H, Yu Q, Meng X, Fan H, Qin M (2022) Screening and identification of probiotic lactobacilli from the infant gut microbiota to alleviate lead toxicity. Probiotics Antimicro Prot 15:821–831. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09895-0
Comerlato CB, Resende MC, Caierão J, d’Azevedo PA (2013) Presence of virulence factors in Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium susceptible and resistant to vancomycin. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 108:590–595. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02762013000500009
Ding W, Baumdicker F, Neher RA (2018) panX: pan-genome analysis and exploration. Nucleic Acids Res 46(1):e5. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx977
Dopson M, Holmes DS, Lazcano M, McCredden TJ, Bryan CG, Mulroney KT, Steuart R, Jackaman C, Watkin EL (2016) Multiple osmotic stress responses in acidihalobacter prosperus result in tolerance to chloride ions. Front Microbiol 7:2132. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.02132
Draker KA, Northrop DB, Wright GD (2003) Kinetic mechanism of the GCN5-related chromosomal aminoglycoside acetyltransferase AAC (6 ‘)-Ii from Enterococcus faecium: evidence of dimer subunit cooperativity. Biochem 42(21):6565–6574. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi034148h
Emms DM, Kelly S (2019) OrthoFinder: phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol 20(1):238. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1832-y
Feldman Salit A, Hering S, Messiha HL, Veith N, Cojocaru V, Sieg A, Westerhoff HV, Kreikemeyer B, Wade RC, Fiedler T (2013) Regulation of the activity of lactate dehydrogenases from four lactic acid bacteria. J Biol Chem 288(29):21295–21306. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.458265
Franz CM, Stiles ME, Schleifer KH, Holzapfel WH (2003) Enterococci in foods—a conundrum for food safety. Int J Food Microbiol 88(2–3):105–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00174-0
Franz CM, Huch M, Abriouel H, Holzapfel W, Gálvez A (2011) Enterococci as probiotics and their implications in food safety. Int J Food Microbiol 151(2):125–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.08.014
Frassinetti S, Gabriele M, Moccia E, Longo V, GioiaD Di (2020) Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of Cannabis sativa L. seeds extract against Staphylococcus aureus and growth effects on probiotic Lactobacillus spp. Lwt 124:109149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109149
Giraffa G (2002) Enterococci from foods. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26(2):163–217. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2002.tb00608.x
Gurevich A, Saveliev V, Vyahhi N, Tesler G (2013) QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinform 29(8):1072–1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt086
Harold FM, Levin E (1974) Lactic acid translocation: terminal step in glycolysis by Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol 117(3):1141–1148. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.117.3.1141-1148.1974
Hassanzadazar H, Ehsani A, Mardani K, Hesari J (2012) Investigation of antibacterial, acid and bile tolerance properties of lactobacilli isolated from Koozeh cheese. Vet Res Forum 3(3):181–185
Hudzicki J (2009) Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion susceptibility test protocol. ASM 15:55–63
Jamet E, Akary E, Poisson MA, Chamba JF, Bertrand X, Serror P (2012) Prevalence and characterization of antibiotic resistant Enterococcus faecalis in French cheeses. Food Microbiol 31(2):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2012.03.009
Johansson MH, Bortolaia V, Tansirichaiya S, Aarestrup FM, Roberts AP, Petersen TN (2021) Detection of mobile genetic elements associated with antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica using a newly developed web tool: MobileElementFinder. J Antimicrob Chemothe 76(1):101–109. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkaa390
Jung DH, Seo DH, Shin JH, Park CS, Chung WH (2020) Genome analysis of Enterococcus mundtii Pe103, a human gut-originated pectinolytic bacterium. Curr Microbiol 77:1839–1847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-01932-5
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kaur S, Sharma P, Kalia N, Singh J, Kaur S (2018) Anti-biofilm properties of the faecal probiotic lactobacilli against Vibrio spp. Front Cell Infect 8:120. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2018.00120
Klein G (2003) Taxonomy, ecology and antibiotic resistance of enterococci from food and the gastro-intestinal tract. Int J Food Microbiol 88(2–3):123–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00175-2
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Laganenka L, Colin R, Sourjik V (2016) Chemotaxis towards autoinducer 2 mediates autoaggregation in Escherichia coli. Nat Commun 7(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12984
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Staerfeldt HH, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35(9):3100–3108. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkm160
Lam MM, Seemann T, Bulach DM, Gladman SL, Chen H, Haring V, Moore RJ, Ballard S, Grayson ML, Johnson PD (2012) Comparative analysis of the first complete Enterococcus faecium genome. J Bacteriol 194(9):2334–2341. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00259-12
Lee I, Kim YO, Park SC, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(2):1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Lee JS, Park SW, Lee HB, Kang SS (2021) Bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance (BLIS) activity of Enterococcus faecium DB1 against biofilm formation by Clostridium perfringens. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13(5):1452–1457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-021-09813-4
Lin X, Chen X, Chen Y, Jiang W, Chen H (2015) The effect of five probiotic lactobacilli strains on the growth and biofilm formation of S treptococcus mutans. Oral Dis 21(1):e128–e134. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12257
Lindsey RL, Pouseele H, Chen JC, Strockbine NA, Carleton HA (2016) Implementation of whole genome sequencing (WGS) for identification and characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) in the United States. Front Microbiol 7:766. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00766
Liu F, Li B, Du J, Yu S, Li W, Evivie SE, Guo L, Ding X, Xu M, Huo G (2016) Complete genome sequence of Enterococcus durans KLDS6. 0930, a strain with probiotic properties. J Biotechno 217:49–50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13099-018-0260-y
Liu B, Zheng D, Zhou S, Chen L, Yang J (2022) VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res 50(D1):D912–D917. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab1107
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25(5):955–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.5.955
Manero A, Blanch AR (1999) Identification of Enterococcus spp. with a biochemical key. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(10):4425–4430. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.10.4425-4430.199
McKenney PT, Ling L, Wang G, Mane S, Pamer EG (2016) Complete genome sequence of Enterococcus faecium ATCC 700221. Genome Announc. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomea.00386-00316
Medini D, Donati C, Tettelin H, Masignani V, Rappuoli R (2005) The microbial pan-genome. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15(6):589–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2005.09.006
Mehmeti I, Faergestad EM, Bekker M, Snipen L, Nes IF, Holo H (2012) Growth rate-dependent control in Enterococcus faecalis: effects on the transcriptome and proteome, and strong regulation of lactate dehydrogenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(1):170–176. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.06604-11
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M (2019) TYGS is an automated high-throughput platform for state-of-the-art genome-based taxonomy. Nat Commun 10(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10210-3
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Merzoug M, Mosbahi K, Walker D, Karam NE (2019) Screening of the enterocin-encoding genes and their genetic determinism in the bacteriocinogenic enterococcus faecium GHB21. Probiotics Antimicrob Prot 11:325–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-018-9448-1
Molham F, Khairalla AS, Azmy AF, El-Gebaly E, El-Gendy AO, AbdelGhani S (2021) Anti-proliferative and anti-biofilm potentials of bacteriocins produced by non-pathogenic Enterococcus sp. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 13(2):571–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-020-09711-1
Moreno MF, Sarantinopoulos P, Tsakalidou E, De Vuyst L (2006) The role and application of enterococci in food and health. Int J Food Microbiol 106(1):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.06.026
Nawaz F, Khan MN, Javed A, Ahmed I, Ali N, Ali MI, Bakhtiar SM, Imran M (2019) Genomic and functional characterization of Enterococcus mundtii QAUEM2808, isolated from artisanal fermented milk product dahi. Front Microbiol 10:434. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00434
Nguyen TL, Kim DH (2018) Genome-wide comparison reveals a probiotic strain Lactococcus lactis WFLU12 isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) harboring genes supporting probiotic action. Mar Drugs 16(5):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050140
Ni K, Wang Y, Li D, Cai Y, Pang H (2015) Characterization, identification and application of lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage paddy rice silage. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0121967. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121967
O’Toole GA, Kolter R (1998) Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28(3):449–461. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0121967
Page AJ, Cummins CA, Hunt M, Wong VK, Reuter S, Holden MT, Fookes M, Falush D, Keane JA, Parkhill J (2015) Roary: rapid large-scale prokaryote pan genome analysis. Bioinform 31(22):3691–3693. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv421
Pal S, Qureshi A, Purohit HJ (2016) Antibiofilm activity of biomolecules: gene expression study of bacterial isolates from brackish and fresh water biofouled membranes. Biol 71(3):239–246. https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2016-0045
Palmer KL, Kos VN, Gilmore MS (2010) Horizontal gene transfer and the genomics of enterococcal antibiotic resistance. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(5):632–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2010.08.004
Panthee S, Paudel A, Hamamoto H, Ogasawara AA, Iwasa T, Blom J, Sekimizu K (2021) Complete genome sequence and comparative genomic analysis of Enterococcus faecalis EF-2001, a probiotic bacterium. Genomics 113(3):1534–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.03.021
Pessione A, Zapponi M, Mandili G, Fattori P, Mangiapane E, Mazzoli R, Pessione E (2014) Enantioselective lactic acid production by an Enterococcus faecium strain showing potential in agro-industrial waste bioconversion: physiological and proteomic studies. J Biotechnol 173:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.01.014
Puranik S, Talkal R, Qureshi A, Khardenavis A, Kapley A, Purohit HJ (2013) Genome sequence of the pigment-producing bacterium Pseudogulbenkiania ferrooxidans, isolated from Loktak Lake. Genome Announc 1(6):e01115-e1113. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomea.01115-13
Qin X, Galloway-Peña JR, Sillanpaa J, Roh JH, Nallapareddy SR, Chowdhury S, Bourgogne A, Choudhury T, Muzny DM, Buhay CJ (2012) Complete genome sequence of Enterococcus faecium strain TX16 and comparative genomic analysis of Enterococcus faecium genomes. BMC Microbiol 12(1):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-12-135
Qureshi A, Itankar Y, Ojha R, Mandal M, Khardenavis A, Kapley A, Purohit HJ (2014) Genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum EGD-AQ4, isolated from fermented product of northeast India. Genome Announc 2(1):e1122–e1113. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomea.01122-13
Qureshi A, Smita P, Saheli G, Atya K, Purohit HJ (2015) Antibiofouling biomaterials. Int J Rec Adv Multidiscip Res 2(8):677–684
Rahman SK, Jalil A, Rahman SM, Hossain KM (2015) A study on probiotic properties of isolated and identified bacteria from regional yoghurts. Int J Biosci 7:139–149. https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/7.4.139-149
Ramsey M, Hartke A, Huycke M (2014) The Physiology and metabolism of enterococci. In: Enterococci: from commensals to leading causes of drug resistant infection [Internet]. PMID: 24649507
Rawoof SAA, Kumar PS, Devaraj K, Devaraj T, Subramanian S (2020) Enhancement of lactic acid production from food waste through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation using selective microbial strains. Biomass Conver Bioref 2:5947–5958. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00998-2
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R, Oliver Glöckner F, Peplies J (2016) JSpeciesWS: a web server for prokaryotic species circumscription based on pairwise genome comparison. Bioinform 32(6):929–931. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv681
Santos KM, Vieira AD, Salles HO, Oliveira JD, Rocha CR, Borges MD, Bruno LM, Franco BD, Todorov SD (2015) Safety, beneficial and technological properties of Enterococcus faecium isolated from Brazilian cheeses. Braz J Microbiol 46:237–249
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinform 30(14):2068–2069. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Shaaban M, Abd El-Rahman OA, Al-Qaidi B, Ashour HM (2020) Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of probiotic Lactobacilli on antibiotic-resistant Proteus mirabilis. Microorganisms 8(6):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8060960
Shokri D, Khorasgani MR, Mohkam M, Fatemi SM, Ghasemi Y, Taheri-Kafrani A (2018) The inhibition effect of lactobacilli against growth and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 10(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9267-9
Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinform 31(19):3210–3212. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351
Smits TH (2019) The importance of genome sequence quality to microbial comparative genomics. BMC Genom 20(1):662. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6014-5
Stothard P, Grant JR, Van Domselaar G (2019) Visualizing and comparing circular genomes using the CGView family of tools. Brief Bioinform 20(4):1576–1582. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbx081
Tan CA, Lam LN, Biukovic G, Soh EY, Toh XW, Lemos JA, Kline KA (2022) Enterococcus faecalis antagonizes Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth in mixed-species interactions. J Bacteriol 204(7):e00615-00621. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.00615-21
Uwamahoro HP, Li F, Timilsina A, Liu B, Wang X, Tian Y (2022) An assessment of the lactic acid-producing potential of bacterial strains isolated from food waste. Microbiol Res 13(2):278–291. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13020022
Van Heel AJ, de Jong A, Song C, Viel JH, Kok J, Kuipers OP (2018) BAGEL4: a user-friendly web server to thoroughly mine RiPPs and bacteriocins. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W278–W281. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky383
Van Tyne D, Gilmore MS (2014) Friend turned foe: evolution of enterococcal virulence and antibiotic resistance. Annu Rev Microbiol 68:337–356. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres13020022
Ventura M, Turroni F, Van Sinderen D (2012) Probiogenomics as a tool to obtain genetic insights into adaptation of probiotic bacteria to the human gut. Bioengineered 3(2):73–79. https://doi.org/10.4161/bbug.185404
Wang HH, Ye KP, Zhang QQ, Dong Y, Xu XL, Zhou GH (2013) Biofilm formation of meat-borne Salmonella enterica and inhibition by the cell-free supernatant from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Control 32(2):650–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.01.047
Wasfi R, Abd El-Rahman O, Mansour L, Hanora A, Hashem A, Ashour M (2012) Antimicrobial activities against biofilm formed by Proteus mirabilis isolates from wound and urinary tract infections. Indian J Med Microbiol 30(1):76–80. https://doi.org/10.4103/0255-0857.93044
Wassenaar M, Zschüttig T, Beimfohr A, Geske C, Auerbach T, Cook C, Zimmermann HK, Gunzer F (2015) Virulence genes in a probiotic E. coli product with a recorded long history of safe use. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 5(1):81–93. https://doi.org/10.1556/eujmi-d-14-00039
Werner G, Fleige C, Geringer U, van Schaik W, Klare I, Witte W (2011) IS element IS16 as a molecular screening tool to identify hospital-associated strains of Enterococcus faecium. BMC Infect Dis 11(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2334-11-80
Wick RR, Judd LM, Gorrie CL, Holt KE (2017) Completing bacterial genome assemblies with multiplex MinION sequencing. Microb Genom 3(10):e000132. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.000132
Xia M, Mu S, Fang Y, Zhang X, Yang G, Hou X, He F, Zhao Y, Huang Y, Zhang W (2023) Genetic and probiotic characteristics of urolithin a producing Enterococcus faecium FUA027. Foods 12(5):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051021
Yesankar PJ, Qureshi A, Purohit HJ (2022) Biofilm-mediated biodegradation of hydrophobic organic compounds in the presence of metals as co-contaminants. Microbial biodegradation and bioremediation. Elsevier, pp 441–460
Yuehua J, Lanwei Z, Fei L, Huaxi Y, Xue H (2016) Complete genome sequence of Enterococcus faecalis LD33, a bacteriocin-producing strain. J Biotechnol 227:79–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.04.030
Zankari E, Hasman H, Cosentino S, Vestergaard M, Rasmussen S, Lund O, Aarestrup FM, Larsen MV (2012) Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J Antimicrob Chemother 67(11):2640–2644. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dks261
Zulkifli M, Ong M, Nomanbhay S, Shamsuddin A (2020) Optimization of hydrolysis and acidogenesis of food waste for production of organic acid. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 476:012140. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/476/1/012140
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge Director, CSIR-NEERI and AcSIR-NEERI for providing support and essential resources for research work. The manuscript has been internally checked for plagiarism through iThenticate software [KRC No: CSIR-NEERI/KRC/2023/SEP/EBGD/3]. Anuja Maitreya is thankful to the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) [31/016(0137)/2020-EMR-I] for carrying out this research. Also, the authors acknowledge the Indo-Egypt Project (DST/INT/Egypt/P-03/2019) Department of Science and Technology, International Bilateral Cooperation Division, New Delhi.
Funding
The authors are grateful to CSIR-NEERI for providing infrastructure facilities, AcSIR- NEERI and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) Fellowship of Anuja Maitreya, New Delhi 20 [31/016(0137)/2020-EMR-I] for financial support. Also, funds from the Indo-Egypt Project (DST/INT/Egypt/P-03/2019) Department of Science and Technology, International Bilateral Cooperation Division, New Delhi are acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AM Investigation, Formal analysis, Visualization, conducted experiments, Analysed data. Bioinformatics analysis, Writing- Original draft; AQ Conceptualization, Supervision, Formal analysis, Reviewing and Editing. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maitreya, A., Qureshi, A. Genomic and phenotypic characterisation of Enterococcus mundtii AM_AQ_BC8 for its anti-biofilm, antimicrobial and probiotic potential. Arch Microbiol 206, 84 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03816-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03816-1