Abstract
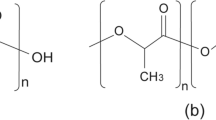
Polylactic acid (PLA) is a range of unique bioplastics that are bio-based and biodegradable. PLA is currently driving market expansion for lactic acid (LA) due to its high demand as a building block in production. One of the most practical and environmentally benign techniques for synthesising PLA is through enzymatic polymerisation of microbial LA monomers. However, microbial LA fermentation does have some limitations. Firstly, it requires the use of a nutritionally rich medium. Secondly, LA production can be disrupted by bacteriophage infection or other microorganisms. Lastly, the yield can be low due to the formation of by-products through heterofermentative pathway. Considering the potential use of PLA as a replacement for conventional petrochemical-based polymers in industrial applications, researchers are focused on exploring the diversity of LA-producing microorganisms from various niches. Their goal is to study the functional properties of these microorganisms and their ability to produce industrially valuable metabolites. This review highlights the advantages and disadvantages of lactic acid-producing microorganisms used in microbial fermentation for PLA synthesis.
Graphical Abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Rahman MA, Xiao Y, Tashiro Y et al (2015) Fed-batch fermentation for enhanced lactic acid production from glucose/xylose mixture without carbon catabolite repression. J Biosci Bioeng 119:153–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.07.007
Abdel-Rahman MA, Hassan SED, Roushdy MM et al (2019) Free-nutrient supply and thermo-alkaline conditions for direct lactic acid production from mixed lignocellulosic and food waste materials. Bioresour Technol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100256
Abdel-Rahman MA, Hassan SED, Alrefaey HMA et al (2021) Subsequent improvement of lactic acid production from beet molasses by Enterococcus hirae ds10 using different fermentation strategies. Bioresour Technol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2020.100617
Abedi E, Hashemi SMB (2020) Lactic acid production – producing microorganisms and substrates sources-state of art. Heliyon 6
Ajala EO, Olonade YO, Ajala MA, Akinpelu GS (2020) Lactic Acid Production from Lignocellulose – A Review of Major Challenges and Selected Solutions. ChemBioEng Reviews 7:38–49. https://doi.org/10.1002/cben.201900018
Alvarado-Morales M, Kuglarz M, Tsapekos P, Angelidaki I (2021) Municipal biopulp as substrate for lactic acid production focusing on downstream processing. J Environ Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105136
Alves de Oliveira R, Schneider R, Vaz Rossell CE et al (2019) Polymer grade L-lactic acid production from sugarcane bagasse hemicellulosic hydrolysate using Bacillus coagulans. Bioresour Technol Rep 6:26–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.02.003
Antunes A, Rainey FA, Nobre MF et al (2002) Leuconostoc ficulneum sp. nov., a novel lactic acid bacterium isolated from a ripe fig, and reclassification of Lactobacillus fructosus as Leuconostoc fructosum comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:647–655. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-2-647
Aso Y, Tsubaki M, Dang Long BH et al (2019) Continuous production of D-lactic acid from cellobiose in cell recycle fermentation using β-glucosidase-displaying Escherichia coli. J Biosci Bioeng 127:441–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.09.011
Bahry H, Abdalla R, Pons A et al (2019) Optimization of lactic acid production using immobilized Lactobacillus Rhamnosus and carob pod waste from the Lebanese food industry. J Biotechnol 306:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2019.09.017
Baral P, Pundir A, Kumar V et al (2020) Expeditious production of concentrated glucose-rich hydrolysate from sugarcane bagasse and its fermentation to lactic acid with high productivity. Food Bioprod Process 124:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2020.08.005
Behare PV, Mazhar S, Pennone V, McAuliffe O (2020) Evaluation of lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from fructose-rich environments for their mannitol-production and milk-gelation abilities. J Dairy Sci 103:11138–11151. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2020-19120
Bernardo MP, Coelho LF, Sass DC, Contiero J (2016) L-(+)-Lactic acid production by Lactobacillus rhamnosus B103 from dairy industry waste. Braz J Microbiol 47:640–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2015.12.001
Brown DM, Grunden AM, Pawlak JJ (2021) Statistical optimization of black liquor-containing media for growth and lactic acid production by Paenibacillus glucanolyticus SLM1. Bioresour Technol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100629
Bustamante D, Marta T, Daniel R, Antonia R (2020) Production of D-lactic acid by the fermentation of orange peel waste hydrolysate by lactic acid bacteria. Fermentation. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6010001s
Campos J, Bao J, Lidén G (2021) Optically pure lactic acid production from softwood-derived mannose by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Biotechnol 335:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2021.06.007
Carpinelli Macedo JV, de Barros Ranke FF, Escaramboni B et al (2020) Cost-effective lactic acid production by fermentation of agro-industrial residues. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101706
Chambel L, Chelo IM, Zé-Zé L et al (2006) Leuconostoc pseudoficulneum sp. nov., isolated from a ripe fig. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1375–1381. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64054-0
Chen H, Huo W, Wang B et al (2019) L-lactic acid production by simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of dilute ethylediamine pre-treated rice straw. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111749
Chen H, Chen B, Su Z et al (2020a) Efficient lactic acid production from cassava bagasse by mixed culture of Bacillus coagulans and lactobacillus rhamnosus using stepwise pH controlled simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112175
Chen H, Su Z, Wang Y et al (2020b) Lactic acid production from pretreated corn stover with recycled streams. Process Biochem 91:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.12.004
Cizeikiene D, Juodeikiene G, Damasius J (2018) Use of wheat straw biomass in production of L-lactic acid applying biocatalysis and combined lactic acid bacteria strains belonging to the genus Lactobacillus. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 15:185–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.06.015
Cubas-Cano E, González-Fernández C, Ballesteros I, Tomás-Pejó E (2020a) Efficient utilization of hydrolysates from steam-exploded gardening residues for lactic acid production by optimization of enzyme addition and pH control. Waste Manage 107:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2020.04.003
Cubas-Cano E, Venus J, González-Fernández C, Tomás-Pejó E (2020b) Assessment of different Bacillus coagulans strains for L-lactic acid production from defined media and gardening hydrolysates: Effect of lignocellulosic inhibitors. J Biotechnol 323:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.07.017
Dave KK, Punekar NS (2015) Expression of lactate dehydrogenase in Aspergillus niger for L-lactic acid production. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145459
de la Torre I, Acedos MG, Ladero M, Santos VE (2019) On the use of resting L. delbrueckii spp. delbrueckii cells for D-lactic acid production from orange peel wastes hydrolysates. Biochem Eng J 145:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.02.012
de la Torre I, Ladero M, Santos VE (2020) D-lactic acid production from orange waste enzymatic hydrolysates with L. delbrueckii cells in growing and resting state. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112176
Dietz D, Schneider R, Papendiek F, Venus J (2016) Leguminose green juice as an efficient nutrient for L(+)-lactic acid production. J Biotechnol 236:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2016.07.008
Díez-Pascual AM (2019) Synthesis and applications of biopolymer composites. Int J Mol Sci 20:2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092321
Edwards C, Haag K, Hutson R, et al (1998) Lactobacillus kunkeei sp. nov. : a spoilage organism associated with grape juice fermentations
Efremenko EN, Spiricheva OV, Veremeenko DV et al (2006) L(+)-lactic acid production using poly(vinyl alcohol)-cryogel-entrapped Rhizopus oryzae fungal cells. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:519–522. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.1524
Efriwati SA, Rahayu G, Nuraida L (2013) Population dynamics of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria (LAB) During tempeh production. Hayati 20:57–64. https://doi.org/10.4308/hjb.20.2.57
Endo A, Okada S (2008) Reclassification of the genus Leuconostoc and proposals of Fructobacillus fructosus gen. nov., comb. nov., Fructobacillus durionis comb. nov., Fructobacillus ficulneus comb. nov. and Fructobacillus pseudoficulneus comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2195–2205. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65609-0
Endo A, Futagawa-Endo Y, Dicks LMT (2009) Isolation and characterization of fructophilic lactic acid bacteria from fructose-rich niches. Syst Appl Microbiol 32:593–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2009.08.002
Endo A, Futagawa-Endo Y, Sakamoto M et al (2010) Lactobacillus florum sp. nov., a fructophilic species isolated from flowers. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2478–2482. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.019067-0
Endo A, Irisawa T, Futagawa-Endo Y et al (2011) Fructobacillus tropaeoli sp. nov., a fructophilic lactic acid bacterium isolated from a flower. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:898–902. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.023838-0
Endo A, Irisawa T, Futagawa-Endo Y et al (2012) Characterization and emended description of Lactobacillus kunkeei as a fructophilic lactic acid bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:500–504. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.031054-0
Endo A, Tanizawa Y, Tanaka N et al (2015) Comparative genomics of Fructobacillus spp and Leuconostoc spp. reveals niche-specific evolution of Fructobacillus spp. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-2339-x
Endo A, Maeno S, Tanizawa Y, et al (2018) Fructophilic lactic acid bacteria, a unique group of fructose-fermenting microbes. Appl Environ Microbiol 84
Filannino P, Di Cagno R, Tlais AZA et al (2019) Fructose-rich niches traced the evolution of lactic acid bacteria toward fructophilic species. Crit Rev Microbiol 45:65–81
Garlotta D (2001) A literature review of poly(lactic acid). J Polym Environ 9:63–84. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020200822435
Ge XY, Qian H, Zhang WG (2009) Improvement of l-lactic acid production from Jerusalem artichoke tubers by mixed culture of Aspergillus niger and Lactobacillus sp. Bioresour Technol 100:1872–1874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.09.049
Ghosh S, Lahiri D, Nag M et al (2021) Bacterial biopolymer: Its role in pathogenesis to effective biomaterials. Polymers (basel) 13:1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13081242
Gustaw K, Michalak M, Polak-Berecka M, Waśko A (2018) Isolation and characterization of a new fructophilic Lactobacillus plantarum FPL strain from honeydew. Ann Microbiol 68:459–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1350-2
Hassan SED, Abdel-Rahman MA, Roushdy MM et al (2019) Effective biorefinery approach for lactic acid production based on co-fermentation of mixed organic wastes by Enterococcus durans BP130. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101203
Henton DE, Gruber P, Lunt J, Randall J (2005) Polylactic acid technology: a review. Natural Fibers, Biopolymers and Biocomposites 48674:527–578
Heriban V, Šturdík E, Zalibera Ľ, Matuš P (1993) Process and metabolic characteristics of Bacillus coagulans as a lactic acid producer. Lett Appl Microbiol 16:243–246. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.1993.tb01409.x
Hu Y, Daoud WA, Cheuk KKL, Lin CSK (2016) Newly developed techniques on polycondensation, ring-opening polymerization and polymer modification: Focus on poly(lactic acid). Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9030133
Huang J, Wang J, Liu S (2023) Advanced fermentation techniques for lactic acid production from agricultural waste. Fermentation 9:765. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9080765
Jamshidian M, Tehrany EA, Imran M et al (2010) Poly-Lactic Acid: Production, applications, nanocomposites, and release studies. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 9:552–571. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2010.00126.x
Jang BK, Ju Y, Jeong D et al (2021) L-lactic acid production using engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae with improved organic acid tolerance. J Fungi. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7110928
Jiang S, Xu P, Tao F (2019) L-Lactic acid production by Bacillus coagulans through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulosic corncob residue. Bioresour Technol Rep 6:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.02.005
Jukonyte R, Zadeike D, Bartkiene E et al (2018) A potential of brown rice polish as a substrate for the lactic acid and bioactive compounds production by the lactic acid bacteria newly isolated from cereal-based fermented products. LWT 97:323–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.07.012
Juodeikiene G, Zadeike D, Bartkiene E, Klupsaite D (2016) Application of acid tolerant Pedioccocus strains for increasing the sustainability of lactic acid production from cheese whey. LWT 72:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.05.023
Kanafusa S, Uhlig E, Uemura K et al (2021) The effect of nanosecond pulsed electric field on the production of metabolites from lactic acid bacteria in fermented watermelon juice. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2021.102749
Kumar, B. V., Muthumari, B., Kavitha, M., Kumar, J. K. J. P., & Basu, M. J. (2023). Unraveling the role of intra-cellular metabolites in the lactic acid production by novel Bacillus amyloliquefaciens using sugarcane molasses as a substratum. Molecular Omics.
Lech M (2020) Optimisation of protein-free waste whey supplementation used for the industrial microbiological production of lactic acid. Biochem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2020.107531
Lefeber T, Gobert W, Vrancken G, Camu N, De Vuyst L (2011) Dynamics and species diversity of communities of lactic acid bacteria and acetic acid bacteria during spontaneous cocoa bean fermentation in vessels. Food Microbiol 28(3):457–464
Leisner JJ, Vancanneyt M, Van der Meulen R et al (2005) Leuconostoc durionis sp. nov., a heterofermenter with no detectable gas production from glucose. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1267–1270. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63434-0
Li J, Shi S, Wang Y, Jiang Z (2021) Integrated production of optically pure L-lactic acid from paper mill sludge by simultaneous saccharification and co-fermentation (SSCF). Waste Manage 129:35–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.05.008
Liu Y, Wen Z, Liao W et al (2005) Optimization of the process for the production of L(+)-lactic acid from cull potato by Rhizopus oryzae. Eng Life Sci 5:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200520079
Liu Y, Liao W, Chen S (2008) Co-production of lactic acid and chitin using a pelletized filamentous fungus Rhizopus oryzae cultured on cull potatoes and glucose. J Appl Microbiol 105:1521–1528. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03913.x
Liu P, Zheng Z, Xu Q et al (2018) Valorization of dairy waste for enhanced D-lactic acid production at low cost. Process Biochem 71:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.05.014
López-Gómez JP, Alexandri M, Schneider R et al (2020) Organic fraction of municipal solid waste for the production of L-lactic acid with high optical purity. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119165
Lu Z, Wei M, Yu L (2012) Enhancement of pilot scale production of l(+)-lactic acid by fermentation coupled with separation using membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem 47:410–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.11.022
Maeno S, Nishimura H, Tanizawa Y et al (2021) Unique niche-specific adaptation of fructophilic lactic acid bacteria and proposal of three Apilactobacillus species as novel members of the group. BMC Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-021-02101-9
Maeno S, Dicks L, Nakagawa J, Endo A (2017) Lactobacillus apinorum belongs to the fructophilic lactic acid bacteria
McFrederick QS, Vuong HQ, Rothman JA (2018) Lactobacillus micheneri sp. nov., Lactobacillus timberlakei sp. nov. and Lactobacillus quenuiae sp. nov., lactic acid bacteria isolated from wild bees and flowers. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1879–1884. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002758
Meng Y, Xue Y, Yu B et al (2012) Efficient production of l-lactic acid with high optical purity by alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. WL-S20. Bioresour Technol 116:334–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.103
Mis Solval K, Chouljenko A, Chotiko A, Sathivel S (2019) Growth kinetics and lactic acid production of Lactobacillus plantarum NRRL B-4496, L. acidophilus NRRL B-4495, and L. reuteri B-14171 in media containing egg white hydrolysates. LWT 105:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.01.058
Mitsui R, Yamada R, Matsumoto T et al (2020) Construction of lactic acid-tolerant Saccharomyces cerevisiae by using CRISPR-Cas-mediated genome evolution for efficient d-lactic acid production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:9147–9158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10906-3
Mladenović D, Pejin J, Kocić-Tanackov S et al (2018) Lactic acid production on molasses enriched potato stillage by Lactobacillus paracasei immobilized onto agro-industrial waste supports. Ind Crops Prod 124:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.07.081
Mohanty AK, Misra M, Drzal LT et al (2005) Natural Fibers, Biopolymers, and Biocomposites. CRC Press
Murakami N, Oba M, Iwamoto M et al (2016) L-Lactic acid production from glycerol coupled with acetic acid metabolism by Enterococcus faecalis without carbon loss. J Biosci Bioeng 121:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.05.009
Nguyen CM, Choi GJ, Choi YH et al (2013) D- and l-lactic acid production from fresh sweet potato through simultaneous saccharification and fermentation. Biochem Eng J 81:40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.10.003
Nwamba MC, Sun F, Mukasekuru MR et al (2021) Trends and hassles in the microbial production of lactic acid from lignocellulosic biomass. Environ Technol Innov 21:101337
Olofsson TC, Alsterfjord M, Nilson B et al (2014) Lactobacillus apinorum sp. nov., Lactobacillus mellifer sp. nov., Lactobacillus mellis sp. nov., Lactobacillus melliventris sp. nov., Lactobacillus kimbladii sp. nov., Lactobacillus helsingborgensis sp. nov. and Lactobacillus kullabergensis sp. nov., isolated from the honey stomach of the honeybee Apis mellifera. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3109–3119. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.059600-0
Ou MS, Ingram LO, Shanmugam KT (2011) L(+)-Lactic acid production from non-food carbohydrates by thermotolerant Bacillus coagulans. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:599–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0796-4
Pontes R, Romaní A, Michelin M et al (2021) L-lactic acid production from multi-supply autohydrolyzed economically unexploited lignocellulosic biomass. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113775
Prasirtsak B, Thitiprasert S, Tolieng V et al (2017) Characterization of D-lactic acid, spore-forming bacteria and Terrilactibacillus laevilacticus SK5-6 as potential industrial strains. Ann Microbiol 67:763–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-017-1306-y
Radosavljević M, Lević S, Belović M et al (2021) Encapsulation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in Polyvinyl Alcohol for the production of L-(+)-Lactic Acid. Process Biochem 100:149–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.10.006
Rangberg A, Mathiesen G, Amdam GV, Diep DB (2015) The paratransgenic potential of Lactobacillus kunkeei in the honey bee Apis mellifera. Benef Microbes 6:513–523. https://doi.org/10.3920/BM2014.0115
Saito K, Hasa Y, Abe H (2012) Production of lactic acid from xylose and wheat straw by Rhizopus oryzae. J Biosci Bioeng 114:166–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.03.007
Santamaría-Fernández M, Schneider R, Lübeck M, Venus J (2020) Combining the production of L-lactic acid with the production of feed protein concentrates from alfalfa. J Biotechnol 323:180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2020.08.010
Sharma V, Mishra HN (2014) Unstructured kinetic modeling of growth and lactic acid production by Lactobacillus plantarum NCDC 414 during fermentation of vegetable juices. LWT Food Sci Technol 59:1123–1128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.05.039
Sharma A, Mukherjee S, Reddy Tadi SR et al (2021a) Kinetics of growth, plantaricin and lactic acid production in whey permeate based medium by probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum CRA52. LWT. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110744
Sharma P, Sharma A, Singh J et al (2021b) Co-production of gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) and lactic acid using Lactobacillus plantarum LP-9 from agro-residues. Environ Technol Innov. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101650
Singh J, Sharma A, Sharma P et al (2022) Production of ethanol, lipid and lactic acid from mixed agrowastes hydrolysate. Nat Prod Res. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2022.2061480
Singhvi M, Gurjar G, Gupta V, Gokhale D (2015) Biocatalyst development for lactic acid production at acidic pH using inter-generic protoplast fusion. RSC Adv 5:2024–2031. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra11104d
Singhvi M, Zendo T, Iida H et al (2017) Stimulation of D- and L-lactate dehydrogenases transcriptional levels in presence of diammonium hydrogen phosphate resulting to enhanced lactic acid production by Lactobacillus strain. J Biosci Bioeng 124:674–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2017.07.009
Singhvi MS, Zinjarde SS, Gokhale DV (2019) Polylactic acid: synthesis and biomedical applications. J Appl Microbiol 127:1612–1626
Sudhakar MP, Dharani G (2022) Evaluation of seaweed for the production of lactic acid by fermentation using Lactobacillus plantarum. Bioresour Technol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100890
Sugiyama K, Iijima K, Yoshino M et al (2021) Nicotinamide mononucleotide production by fructophilic lactic acid bacteria. Sci Rep 11:7662. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87361-1
Taherzadeh MJ, Fox M, Hjorth H, Edebo L (2003) Production of mycelium biomass and ethanol from paper pulp sulfite liquor by Rhizopus oryzae. Bioresour Technol 88:167–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00010-5
Thapa LP, Lee SJ, Park C, Kim SW (2017) Production of L-lactic acid from metabolically engineered strain of Enterobacter aerogenes ATCC 29007. Enzyme Microb Technol 102:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2017.03.003
Tkacz JS, Lange L (eds) (2004) Advances in Fungal Biotechnology for Industry, Agriculture, and Medicine. Springer, US, Boston, MA
Verma D, Fortunati E (2019) Biopolymer processing and its composites: An introduction. Elsevier Ltd
Verma D, Subudhi S (2021) Lactobacillus sp. strain TERI-D3’, as microbial cell factory for fermentative production of lactic acid. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100059
Viesser JA, de Melo PGV, de Carvalho Neto DP et al (2020) Exploring the contribution of fructophilic lactic acid bacteria to cocoa beans fermentation: Isolation, selection and evaluation. Food Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109478
Vignesh Kumar B, Muthumari B, Kavitha M et al (2022) Studies on optimization of sustainable lactic acid production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens from sugarcane molasses through microbial fermentation. Sustainability (switzerland) 14:7400. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU14127400
Vitetta L, Coulson S, Thomsen M, Nguyen T, Hall S (2017) Probiotics, D-Lactic acidosis, oxidative stress and strain specificity. Gut Microbes. 8(4):311–322. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2017.1279379
Wang J, Huang J, Laffend H et al (2020a) Optimization of immobilized Lactobacillus pentosus cell fermentation for lactic acid production. Bioresour Bioprocess 15:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-00305-x
Wang J, Huang J, Guo H et al (2020b) Optimization of immobilization conditions for Lactobacillus pentosus cells. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 43:1071–1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-020-02305-9
Wang J, Huang J, Jiang S, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Ning Y et al (2021a) Parametric optimization and kinetic study of l-lactic acid production by homologous batch fermentation of Lactobacillus pentosus cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 68(4):809–822. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1994
Wang J, Guo H, Huang J, Jiang S, Hou S, Chen X et al (2021b) l-Lactic acid production from fructose by chitosan film-coated sodium alginate-polyvinyl alcohol immobilized Lactobacillus pentosus cells and its kinetic analysis. Bioresources Bioprocess 8(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-021-00380-8
Wang J, Jiang S, Huang J et al (2021c) Appl Biochem Biotechnol 193:1496–1512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-021-03492-1
Watanabe M, Makino M, Kaku N et al (2013) Fermentative l-(+)-lactic acid production from non-sterilized rice washing drainage containing rice bran by a newly isolated lactic acid bacteria without any additions of nutrients. J Biosci Bioeng 115:449–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.11.001
Wu X, Jiang S, Liu M et al (2011) Production of L-lactic acid by Rhizopus oryzae using semicontinuous fermentation in bioreactor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0804-8
Xiao T, Shah NP (2021) Lactic acid produced by Streptococcus thermophilus activated glutamate decarboxylase (GadA) in Lactobacillus brevis NPS-QW 145 to improve γ-amino butyric acid production during soymilk fermentation. LWT. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110474
Yadav N, Pranaw K, Khare SK (2020) Screening of lactic acid bacteria stable in ionic liquids and lignocellulosic by-products for bio-based lactic acid production. Bioresour Technol Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2020.100423
Yamane T, Tanaka R (2013) Highly accumulative production of l(+)-lactate from glucose by crystallization fermentation with immobilized Rhizopus oryzae. J Biosci Bioeng 115:90–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.08.005
Yao K, Zhou QX, Liu DM et al (2019) Comparative proteomics of the metabolic pathways involved in L-lactic acid production in Bacillus coagulans BCS13002 using different carbon sources. LWT. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108445
Zhang C, Yang HQ, Wu DJ (2019) Study on the reuse of anaerobic digestion effluent in lactic acid production. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118028
Zhang Z, Tsapekos P, Alvarado-Morales M, Angelidaki I (2021) Bio-augmentation to improve lactic acid production from source-sorted organic household waste. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123714
Zhang Z, Tsapekos P, Alvarado-Morales M et al (2022) Enhanced fermentative lactic acid production from source-sorted organic household waste: Focusing on low-pH microbial adaptation and bio-augmentation strategy. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152129
Zhao Z, Xie X, Wang Z et al (2016) Immobilization of Lactobacillus rhamnosus in mesoporous silica-based material: An efficiency continuous cell-recycle fermentation system for lactic acid production. J Biosci Bioeng 121:645–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.11.010
Zheng J, Wittouck S, Salvetti E et al (2020) A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:2782–2858. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004107
Acknowledgements
All the authors thank DST-PURSE, Department of Botany (Phase II—3rd Instalment), and RUSA 2.0, Alagappa University, for the financial support. The first author thanks the Taiwan Education Exchange Programme (TEEP) internship. This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (MOST 111-2621-B-018-001 to Jui-Yu Chou).
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BVK: conceptualisation; formal analysis; methodology; writing—original draft; writing—review and editing. MJB, YPC, and JYC: conceptualisation; formal analysis; funding acquisition; investigation; resources; supervision; validation; visualisation; writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. MJB and JYC—equally contributed.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramanian, V.K., Muthuramalingam, J.B., Chen, YP. et al. Recent trends in lactic acid-producing microorganisms through microbial fermentation for the synthesis of polylactic acid. Arch Microbiol 206, 31 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03745-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03745-z