Abstract
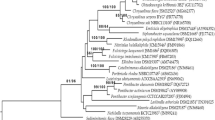
Four Gram-staining-negative, aerobic, yellow-pigmented and rod-shaped bacteria, named strains BD1B2-1T, NT2B1T, YF14B1 and DM2B3-1, were isolated from four rhizosphere soil samples of banana in China. Comparison of the 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that all these strains were most closely related to an invalidly published species, ‘Rhodocytophaga rosea’ 172606-1, with similarities ranging from 87.7 to 88.0%. According to the phylogenomic analysis, the four strains were clustered in an independent lineage and closely related to the genus Rhodocytophaga. The genomic sizes of these strains were approximately 9.49–9.77 Mbp with the DNA G + C contents of 38.8–39.0 mol%. They all contained C16:1 ω5c, iso-C15:0 and iso-C17:0 3-OH as the major fatty acids and menaquinone 7 as the only respiratory quinone. They all had phosphatidylethanolamine as the major polar lipids. Based on phenotypic and phylogenomic characteristics, the four strains should represent two novel species within a novel genus, for which the names Xanthocytophaga agilis gen. nov., sp. nov. (BD1B2-1T = GDMCC 1.2890T = JCM 35374T) and Xanthocytophaga flavus sp. nov. (NT2B1T = GDMCC 1.2889T = JCM 35375T) are proposed; the former is assigned as the type species of the novel genus Xanthocytophaga gen. nov. In addition, based on the phenotypic and phylogenomic data, we proposed to reclassify the existing genus Rhodocytophaga in the family Cytophagaceae into a novel family Rhodocytophagaceae fam. nov. The novel family consists of the type genus Rhodocytophaga and the novel genus Xanthocytophaga.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the 16S rRNA gene of strains BD1B2-1T, NT2B1T, YF14B1 and DM2B3-1 are OR024674, OR024675, OR024673 and OR024672, respectively. The whole genome shotgun projects for strains BD1B2-1T, NT2B1T, YF14B1, DM2B3-1 and Rhodocytophaga aerolata KACC 12507T have been deposited in the GenBank database under the accession numbers JASJOU000000000, JASJOR000000000, JASJOS000000000 JASJOT000000000 and JAUKPO000000000, respectively.
Abbreviations
- AAI:
-
Average amino acid identity
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- APL:
-
Unidentified aminophospholipid
- dDDH:
-
Digital DNA-DNA hybridization
- Foc:
-
Fusarium oxysporum F. sp. cubense
- L:
-
Unidentified lipid
- MK-7:
-
Menaquinone 7
- ML:
-
Maximum likelihood
- NJ:
-
Neighbor-joining
- PE:
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine
- POCP:
-
Percentage of conserved proteins
- TSA:
-
Tryptic soy agar
- UBCG:
-
Up-to-data bacteria core genes
References
Anandham R, Weon HY, Kim SJ, Kim YS, Kwon SW (2010) Rhodocytophaga aerolata gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae isolated from air. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1554–1558. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.015305-0
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T et al (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Barco RA, Garrity GM, Scott JJ, Amend JP, Nealson KH et al (2020) A genus definition for bacteria and archaea based on a standard genome relatedness index. Mbio 11:e02475-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02475-19
Bernardet JF, Nakagawa Y, Holmes B (2002) Proposed minimal standards for describing new taxa of the family Flavobacteriaceae and emended description of the family. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1049. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-52-3-1049
Chaudhary DK, Dahal RH, Altankhuu K, Kim J (2017) Ravibacter arvi gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from farmland soil during development of new culture techniques. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:5252–5260. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.002456
Chhetri G, Yang D, Choi J, Kim H, Seo T (2018) Edaphorhabdus rosea gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae isolated from soil in South Korea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:2385–2392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1127-4
Choi J, Yang D, Chhetri G, Cha S, Seo T (2019) Tellurirhabdus rosea gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae isolated from soil in South Korea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 112:1047–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01238-y
Collins MD, Jones D (1981) Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implications. Microbiol Rev 15:316–354. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.45.2.316-354.1981
Dita M, Barquero M, Heck D, Mizubuti ESG, Staver CP (2018) Fusarium wilt of banana: current knowledge on epidemiology and research needs toward sustainable disease management. Front Plant Sci 9:1468. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01468
Fautz E, Reichenbach H (1980) A simple test for flexirubin-type pigments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 8:87–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1980.tb05056.x
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
García-López M, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Tindall BJ, Gronow S, Woyke T et al (2019) Analysis of 1,000 type-strain genomes improves taxonomic classification of Bacteroidetes. Front Microbiol 10:2083. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02083
Hahnke RL, Meier-Kolthoff JP, García-López M, Mukherjee S, Huntemann M et al (2016) Genome-based taxonomic classification of Bacteroidetes. Front Microbiol 7:2003. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.02003
Hoang DT, Chernomor O, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ, Vinh LS (2018) UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol Biol Evol 35:518–522. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281
Kai B, Simon S, Alexander MK, Zach CP, Gilles PW et al (2021) antiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res 49:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab335
Kema GHJ, Drenth A, Dita M, Jansen K, Vellema S et al (2021) Editorial: Fusarium wilt of banana, a recurring threat to global banana production. Front Plant Sci 11:628888. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.628888
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Kim D, Park S, Chun J (2021) Introducing EzAAI: a pipeline for high throughput calculations of prokaryotic average amino acid identity. J Microbiol 59:476–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-1154-0
Konstantinidis KT, Rosselló-Móra R, Amann R (2017) Uncultivated microbes in need of their own taxonomy. ISME J 11:2399–2406. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.113
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Leadbetter ER (1974) Family I. Cytophagaceae Stanier 1940, 630, emend. mut. char. In: Buchanan RE, Gibbons NE (eds) Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore, pp 99–127
Liu ZT, Liu L, Xian WD, Lian ZH, Dai JY et al (2023) Rhodoflexus caldus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the phylum Bacteroidota isolated from a hot spring sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 115:889–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-022-01742-8
Maejima Y, Iino T, Muraguchi Y, Fukuda K, Ohkuma M et al (2020) Chryseotalea sanaruensis gen. nov., sp., nov., a member of the family Cytophagaceae, isolated from a Brackish Lake in Hamamatsu Japan. Curr Microbiol 77:306–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-019-01823-4
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Na SI, Kim YO, Yoon SH, Ha SM, Baek I, Chun J (2018) UBCG: up-to-date bacterial core gene set and pipeline for phylogenomic tree reconstruction. J Microbiol 56:280–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-018-8014-6
Noman M, Ahmed T, Ijaz U, Shahid M, Azizullah et al (2021) Plant-microbiome crosstalk: dawning from composition and assembly of microbial community to improvement of disease resilience in plants. Int J Mol Sci 22:6852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136852
Oren A, Garrity GM (2021) Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 71:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.005056
Park Y, Maeng S, Han JH, Lee SE, Zhang J et al (2020) Rhodocytophaga rosea sp. nov. and Nibribacter ruber sp. nov., two radiation-resistant bacteria isolated from soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113:2177–2185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01488-1
Parks DH, Imelfort M, Skennerton CT, Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2015) CheckM: assessing the quality of microbial genomes recovered from isolates, single cells, and metagenomes. Genome Res 25:1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.186072.114
Parks DH, Chuvochina M, Rinke C, Mussig AJ, Chaumeil PA et al (2022) GTDB: an ongoing census of bacterial and archaeal diversity through a phylogenetically consistent, rank normalized and complete genome-based taxonomy. Nucleic Acids Res 50:785–794. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab776
Pitt A, Schmidt J, Koll U, Hahn MW (2019) Aquirufa antheringensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Aquirufa nivalisilvae sp. nov., representing a new genus of widespread freshwater bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:2739–2749. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003554
Qin QL, Xie BB, Zhang XY, Chen XL, Zhou BC et al (2014) A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196:2210–2215. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01688-14
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI Technical Note #101. Newark, DE: MIDI Inc. 1
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Seemann T (2014) Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 30:2068–2069. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
Shen Z, Ruan Y, Xue C, Zhong S, Li R et al (2015) Soils naturally suppressive to banana Fusarium wilt disease harbor unique bacterial communities. Plant Soil 393:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2474-9
Sheu SY, Chen TY, Chen WM (2020) Aquirufa rosea sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:3145–3153. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004147
Shimkets LJ, Dworkin M, Reichenbach H (2006) The myxobacteria. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer KH, Stackebrandt E et al (eds) The prokaryotes: a handbook on the biology of bacteria, vol 7. Springer, New York, pp 31–115
Subhash Y, Tushar L, Sasikala Ch, Ramana ChV (2013) Mongoliicoccus alkaliphilus sp. nov. and Litoribacter alkaliphilus sp. nov., isolated from salt pans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:3457–3462. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.049924-0
Szuróczki S, Khayer B, Spröer C, Toumi M, Szabó A et al (2019) Arundinibacter roseus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:2076–2081. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003436
Tian SP, Wang YX, Hu B, Zhang XX, Xiao W et al (2010) Litoribacter ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., an alkaliphilic, halotolerant bacterium isolated from a soda lake sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2996–3001. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.021626-0
Tindall BJ, Sikorski J, Smibert RA, Krieg NR (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM et al (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 330–393
Trivedi P, Leach JE, Tringe SG, Sa T, Singh BK (2020) Plant-microbiome interactions: from community assembly to plant health. Nat Rev Microbiol 18:607–621. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0412-1
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703
Yarza P, Yilmaz P, Pruesse E, Glöckner FO, Ludwig W et al (2014) Uniting the classification of cultured and uncultured bacteria and archaea using 16S rRNA gene sequences. Nat Rev Microbiol 12:635–645. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3330
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y et al (2017a) Introducing Ezbiocloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim JM, Kwon SJ, Chun J (2017b) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4
Zhang L, Shen X, Liu Y, Li S (2013) Nafulsella turpanensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the phylum Bacteroidetes isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1639–1645. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.044651-0
Funding
This work was jointly supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (32000007), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong Province (2021B1212050022), the Guangdong Special Support Program (2021JC06N628), the Guangdong Strategic Special Fund for Rural Revitalization (2022-440000-43010104-9463) and the GDAS’ Special Project of Science and Technology Development (2021GDASYL-20210103020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HHZ designed the research and project outline. XJZ, YF, YXL and XQD: carried out the experiments. XJZ and YL: performed genome analysis. XJZ, XQD, YQ and HHZ: funding acquisition. XJZ: wrote the manuscript. GDF, YL, QY and HHZ: revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Feng, GD., Liu, Y. et al. Description of Xanthocytophaga agilis sp. nov. and Xanthocytophaga flavus sp. nov. of the new genus Xanthocytophaga gen. nov and the proposal of Rhodocytophagaceae fam. nov. within the order Cytophagales. Arch Microbiol 205, 345 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03685-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03685-8