Abstract
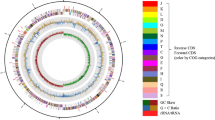
Hahella is a genus that has not been well-studied, with only two identified species. The potential of this genus to produce cellulases is yet to be fully explored. The present study isolated Hahella sp. CR1 from mangrove soil in Tanjung Piai National Park, Malaysia, and performed whole genome sequencing (WGS) using NovaSeq 6000. The final assembled genome consists of 62 contigs, 7,106,771 bp, a GC ratio of 53.5%, and encoded for 6,397 genes. The CR1 strain exhibited the highest similarity with Hahella sp. HN01 compared to other available genomes, where the ANI, dDDH, AAI, and POCP were 97.04%, 75.2%, 97.95%, and 91.0%, respectively. In addition, the CAZymes analysis identified 88 GTs, 54 GHs, 11 CEs, 7 AAs, 2 PLs, and 48 CBMs in the genome of strain CR1. Among these proteins, 11 are related to cellulose degradation. The cellulases produced from strain CR1 were characterized and demonstrated optimal activity at 60 ℃, pH 7.0, and 15% (w/v) sodium chloride. The enzyme was activated by K+, Fe2+, Mg2+, Co2+, and Tween 40. Furthermore, cellulases from strain CR1 improved the saccharification efficiency of a commercial cellulase blend on the tested agricultural wastes, including empty fruit bunch, coconut husk, and sugarcane bagasse. This study provides new insights into the cellulases produced by strain CR1 and their potential to be used in lignocellulosic biomass pre-treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The 16S rRNA partial gene sequence obtained from Sanger sequencing can be retrieved in GenBank (accession number OQ607710). The raw reads from the Illumina sequencing were deposited in NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database with accession number SRR22726834. The genome assembly can be retrieved from the NCBI database under the accession number JAPELK000000000 (BioProject ID: PRJNA896735; BioSample ID: SAMN31564167).
References
Akram F, Ul-Haq I, Aqeel A, Ahmed Z, Shah FI (2021) Thermostable cellulases: Structure, catalytic mechanisms, directed evolution and industrial implementations. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 151:111597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111597
Andlar M, Rezić T, Marđetko N, Kracher D, Ludwig R, Šantek B (2018) Lignocellulose degradation: An overview of fungi and fungal enzymes involved in lignocellulose degradation. Eng Life Sci 18(11):768–778. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201800039
Astuti T, Akbar SA, Rofiq MN, Jamarun N, Huda N, Fudholi A (2022) Activity of cellulase and ligninase enzymes in a local bioactivator from cattle and buffalo rumen contents. Biocat Agricult Biotechnol 45:102497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102497
Aytaş ZG, Tunçer M, Kul ÇS, Cilmeli S, Aydın N, Doruk T, Adıgüzel AO (2023) Partial characterization of β-glucosidase, β-xylosidase, and α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Jiangella alba DSM 45237 and their potential in lignocellulose-based biorefining. Sustain Chem Pharmacy 31:100900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scp.2022.100900
Bagewadi Z, Ninnekar H (2015) Production, purification and characterization of endoglucanase from Aspergillus fumigatus and enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic waste. Int J Biotechnol Biomed Sci 1:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0227-x
Bai H, Wang H, Sun J, Irfan M, Han M, Huang Y, Han X, Yang Q (2013) Purification and characterization of beta 1, 4-glucanases from Penicillium simplicissimum H-11. BioResources 8(3):3657–3671. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.8.3.3657-3671
Baik KS, Seong CN, Kim EM, Yi H, Bae KS, Chun J (2005) Hahella ganghwensis sp. nov., isolated from tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55(2):681–684. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63411-0
Bakare M, Adewale I, Ajayi A and Shonukan O (2005) Purification and characterization of cellulase from the wild-type and two improved mutants of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Afr J Biotechnol 4(9):898–904. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB2005.000-3178
Behera BC, Sethi B, Mishra R, Dutta S, Thatoi H (2017) Microbial cellulases–diversity & biotechnology with reference to mangrove environment: a review. J Genetic Eng Biotechnol 15(1):197–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2016.12.001
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30(15):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Buchfink B, Reuter K, Drost H-G (2021) Sensitive protein alignments at tree-of-life scale using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 18(4):366–368. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-021-01101-x
Cantalapiedra CP, Hernández-Plaza A, Letunic I, Bork P, Huerta-Cepas J (2021) eggNOG-mapper v2: functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol Biol Evol 38(12):5825–5829. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab293
Carbonaro M, Aulitto M, Gallo G, Contursi P, Limauro D, Fiorentino G (2023) Insight into CAZymes of Alicyclobacillus mali FL18: characterization of a New Multifunctional GH9 Enzyme. Int J Mol Sci 24(1):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010243
Chaudhari NM, Gupta VK, Dutta C (2016) BPGA-an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci Rep 6(1):24373. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24373
Cri P, Gallantiswara D, Dong H, Kayansamruaj P, Senapin S, Rodkhum C (2019) Genome characterization on the virulence determinants of Hahella chejuensis HN01 causing red eggs disease in Tilapia hatcheries.
Dadheech T, Shah R, Pandit R, Hinsu A, Chauhan PS, Jakhesara S, Kunjadiya A, Rank D, Joshi C (2018) Cloning, molecular modeling and characterization of acidic cellulase from buffalo rumen and its applicability in saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass. Int J Biol Macromol 113:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.100
Dar MA, Pawar KD, Rajput BP, Rahi P, Pandit RS (2019) Purification of a cellulase from cellulolytic gut bacterium, Bacillus tequilensis G9 and its evaluation for valorization of agro-wastes into added value byproducts. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 20:101219
Del Angel VD, Hjerde E, Sterck L, Capella-Gutierrez S, Notredame C, Pettersson OV, Amselem J, Bouri L, Bocs S, Klopp C, Gibrat JF (2018) Ten steps to get started in genome assembly and annotation. F1000Research 2018, 7(ELIXIR):148. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.13598.1
Feng J, Hu Z, Wang H (2019) Complete genome sequence of Hahella sp KA22, a prodigiosin-producing algicidal bacterium. Mar Genomics 47:100678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2019.04.003
Gaur R, Tiwari S (2015) Isolation, production, purification and characterization of an organic-solvent-thermostable alkalophilic cellulase from Bacillus vallismortis RG-07. BMC Biotechnol 15(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-015-0129-9
Ghatge SS, Telke AA, Kang S-H, Arulalapperumal V, Lee K-W, Govindwar SP, Um Y, Oh D-B, Shin H-D, Kim S-W (2014) Characterization of modular bifunctional processive endoglucanase Cel5 from Hahella chejuensis KCTC 2396. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(10):4421–4435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5446-0
Gundupalli, M., P. Tantayotai, K. Rattanaporn, W. Pongprayoon, T. Phusantisampan and M. Sriariyanun (2021). Effects of inorganic salts on enzymatic saccharification kinetics of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuel Production. In: 2021 The 10th International Conference on Informatics, Environment, Energy and Applications.
He S, Li P, Wang J, Zhang Y, Lu H, Shi L, Huang T, Zhang W, Ding L, He S (2022) Discovery of new secondary metabolites from marine bacteria Hahella based on an omics strategy. Mar Drugs 20(4):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040269
Henciya S, Vengateshwaran TD, Gokul MS, Dahms H-U, James RA (2020) Antibacterial activity of halophilic bacteria against drug-resistant microbes associated with diabetic foot infections. Curr Microbiol 77(11):3711–3723
Holmes B, Willcox W, Lapage S (1978) Identification of Enterobacteriaceae by the API 20E system. J Clin Pathol 31(1):22–30
Holt J, Krieg N, Snealth P, Staley J (1994). Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology. Nocardioform Actinomycetes I
Houfani AA, Anders N, Spiess AC, Baldrian P, Benallaoua S (2020) Insights from enzymatic degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose to fermentable sugars–a review. Biomass Bioenergy 134:105481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2020.105481
Hwang IH, Lee CH, Kim SW, Sung HG, Lee SY, Lee SS, Hong HO, Kwak Y-C, Ha JK (2008) Effects of mixtures of Tween80 and cellulolytic enzymes on nutrient digestion and cellulolytic bacterial adhesion. Asian Australas J Anim Sci 21(11):1604–1609. https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2008.80333
Kim D, Park S, Chun J (2021) Introducing EzAAI: a pipeline for high throughput calculations of prokaryotic average amino acid identity. J Microbiol 59:476–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-1154-0
Lee HK, Chun J, Moon EY, Ko S-H, Lee D-S, Lee HS, Bae KS (2001) Hahella chejuensis gen nov., sp. nov., an extracellular-polysaccharide-producing marine bacterium. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 51(2):661–666. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-2-661
Lee Y-J, Kim B-K, Lee B-H, Jo K-I, Lee N-K, Chung C-H, Lee Y-C, Lee J-W (2008) Purification and characterization of cellulase produced by Bacillus amyoliquefaciens DL-3 utilizing rice hull. Biores Technol 99(2):378–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.12.013
Lee IC, Kim OY, Park SC, Chun JS (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66(2):1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Li P, He S, Zhang X, Gao Q, Liu Y, Liu L (2022) Structures, biosynthesis, and bioactivities of prodiginine natural products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12245-x
Li X, Li K, Wang Y, Huang Y, Yang H, Zhu P, Li Q (2023) Diversity of lignocellulolytic functional genes and heterogeneity of thermophilic microbes during different wastes composting. Biores Technol 372:128697
Liu M, Huang H, Bao S, Tong Y (2019) Microbial community structure of soils in Bamenwan mangrove wetland. Sci Rep 9(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44788-x
Mamangkey J, Suryanto D, Munir E, Mustopa AZ, Sibero MT, Mendes LW, Hartanto A, Taniwan S, Ek-Ramos MJ, Harahap A (2021) Isolation and enzyme bioprospection of bacteria associated to Bruguiera cylindrica, a mangrove plant of North Sumatra. Indonesia. Biotechnology Reports 30:e00617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00617
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Carbasse JS, Peinado-Olarte RL, Göker M (2022) TYGS and LPSN: a database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 50(D1):D801–D807. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab902
Mujtaba, M., L. Fraceto, M. Fazeli, S. Mukherjee, S. M. Savassa, G. A. de Medeiros, A. d. E. Santo Pereira, S. D. Mancini, J. Lipponen and F. Vilaplana (2023). Lignocellulosic biomass from agricultural waste to the circular economy: A review with focus on biofuels, biocomposites and bioplastics. Journal of Cleaner Production: 136815.
Nanda S, Mohammad J, Reddy SN, Kozinski JA, Dalai AK (2014) Pathways of lignocellulosic biomass conversion to renewable fuels. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 4:157–191
Naresh S, Kunasundari B, Gunny AAN, Teoh YP, Shuit SH, Ng QH, Hoo PY (2019) Isolation and partial characterisation of thermophilic cellulolytic bacteria from north Malaysian tropical mangrove soil. Tropical Life Sci Res 30(1):123
Nazir A, Soni R, Saini H, Manhas R, Chadha B (2009) Purification and characterization of an endoglucanase from Aspergillus terreus highly active against barley β-glucan and xyloglucan. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25(7):1189–1197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0001-y
Okolie JA, Nanda S, Dalai AK, Kozinski JA (2021) Chemistry and specialty industrial applications of lignocellulosic biomass. Waste Biomass Valorizat 12:2145–2169
Okonkwo I (2019) Effect of metal ions and enzyme inhibitor on the activity of cellulase enzyme of Aspergillus flavus. Int J Environ, Agricult Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.22161/ijeab/4.3.20
Palit K, Rath S, Chatterjee S, Das S (2022) Microbial diversity and ecological interactions of microorganisms in the mangrove ecosystem: Threats, vulnerability, and adaptations. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19048-7
Patel AK, Singhania RR, Sim SJ, Pandey A (2019) Thermostable cellulases: current status and perspectives. Biores Technol 279:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.01.049
Paul M, Mohapatra S, Mohapatra PKD, Thatoi H (2021) Microbial cellulases–An update towards its surface chemistry, genetic engineering and recovery for its biotechnological potential. Bioresource Technol 340:125710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125710
Poli A, Anzelmo G, Nicolaus B (2010) Bacterial exopolysaccharides from extreme marine habitats: production, characterization and biological activities. Mar Drugs 8(6):1779–1802
Prawisut A, Choknud S, Cairns JRK (2020) Expression of rice β-exoglucanase II (OsExoII) in Escherichia coli, purification, and characterization. Protein Exp Purif 175:105708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2020.105708
Prjibelski A, Antipov D, Meleshko D, Lapidus A, Korobeynikov A (2020) Using SPAdes de novo assembler. Current Protocols Bioinformat 70(1):e102. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpbi.102
Qin Q-L, Xie B-B, Zhang X-Y, Chen X-L, Zhou B-C, Zhou J, Oren A, Zhang Y-Z (2014) A proposed genus boundary for the prokaryotes based on genomic insights. J Bacteriol 196(12):2210–2215. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.01688-14
Reiner K (2010) Catalase test protocol. Am Soc Microbiol: 1–6
Sam K-K, Lau N-S, Furusawa G, Amirul A-AA (2017) Draft genome sequence of halophilic Hahella sp. strain CCB-MM4, isolated from Matang Mangrove Forest in Perak Malaysia. Genome Announc 5(42):e01147-e11117. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomea.01147-17
Seddouk L, Jamai L, Tazi K, Ettayebi M, Alaoui-Mhamdi M, Aleya L, Janati-Idrissi A (2022) Isolation and characterization of a mesophilic cellulolytic endophyte Preussia africana from Juniperus oxycedrus. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(30):45589–45600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19151-9
Shields P, Cathcart L (2010) Oxidase test protocol. Am Soc Microbiol: 1–9
Sidar A, Albuquerque ED, Voshol GP, Ram AF, Vijgenboom E, Punt PJ (2020) Carbohydrate binding modules: diversity of domain architecture in amylases and cellulases from filamentous microorganisms. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:871. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00871
Sun C, Meng X, Sun F, Zhang J, Tu M, Chang J-S, Reungsang A, Xia A, Ragauskas AJ (2022) Advances and perspectives on mass transfer and enzymatic hydrolysis in the enzyme-mediated lignocellulosic biorefinery: a review. Biotechnol Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.108059
Tanaka D, Ohnishi K-I, Watanabe S, Suzuki S (2021) Isolation of cellulase-producing Microbulbifer sp. from marine teleost blackfish (Girella melanichthys) intestine and the enzyme characterization. J General Appl Microbiol 67(2):47–53. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.2020.05.001
Tandon K, Ricci F, Costa J, Medina M, Kühl M, Blackall LL, Verbruggen H (2022) Genomic view of the diversity and functional role of archaea and bacteria in the skeleton of the reef-building corals Porites lutea and Isopora palifera. GigaSci. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giac127
Tatusova T, DiCuccio M, Badretdin A, Chetvernin V, Nawrocki EP, Zaslavsky L, Lomsadze A, Pruitt KD, Borodovsky M, Ostell J (2016) NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res 44(14):6614–6624. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw569
Thaochan N, Drew R, Hughes J, Vijaysegaran S, Chinajariyawong A (2010) Alimentary tract bacteria isolated and identified with API-20E and molecular cloning techniques from Australian tropical fruit flies, Bactrocera cacuminata and B. tryoni. J Insect Sci 10(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.010.13101
Tripathi N, Sapra A (2021) Gram Staining. StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL)
Vasconcellos V, Tardioli P, Giordano R, Farinas C (2016) Addition of metal ions to a (hemi) cellulolytic enzymatic cocktail produced in-house improves its activity, thermostability, and efficiency in the saccharification of pretreated sugarcane bagasse. New Biotechnol 33(3):331–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2015.12.002
Wayne, P. (2015). CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-fifth informational supplement: CLSI Document M100-S25, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2015, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Wayne, PA.
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173(2):697–703
Wu Y, Shresth S, Guo H, Zhang J, Wang H, Qin W (2022a) Enhancement of saccharification of corn stover by cellulolytic enzyme produced from biomass-degrading bacteria. BioResources. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.17.1.1301-1318
Wu Z, Peng K, Zhang Y, Wang M, Yong C, Chen L, Qu P, Huang H, Sun E, Pan M (2022b) Lignocellulose dissociation with biological pretreatment towards the biochemical platform: a review. Materials Today Bio 28:100445
Xie R, Dong C, Wang S, Danso B, Dar MA, Pandit RS, Pawar KD, Geng A, Zhu D, Li X (2023) Host-specific diversity of culturable bacteria in the gut systems of fungus-growing termites and their potential functions towards lignocellulose bioconversion. InSects 14(4):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040403
Zhang G, Li S, Xue Y, Mao L, Ma Y (2012) Effects of salts on activity of halophilic cellulase with glucomannanase activity isolated from alkaliphilic and halophilic Bacillus sp. BG-CS10. Extremophiles 16(1):35–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-011-0403-2
Zhang H, Yohe T, Huang L, Entwistle S, Wu P, Yang Z, Busk PK, Xu Y, Yin Y (2018) dbCAN2: a meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 46(W1):W95–W101. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky418
Acknowledgements
M.C.Y.T. would like to thank UTMNexus of Universiti Teknologi Malaysia for scholarship support. K.J.L. is a researcher under the Post-Doctoral Fellowship Scheme provided by Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
Funding
This work was supported by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2019/WAB13/UTM/02/1) as main sponsor. This work was also supported by Professional Development Research University Grant (Q.J130000.21A2.06E00).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MCYT performed the genome analysis, carried out the enzyme experiments and wrote the manuscript. MRZ collected the sequencing data. KJL reviewed and edited the manuscript. CSC conceived the project. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Wen-Jun Li.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
203_2023_3617_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 The effect of temperature (A), pH (B) and salinity (C) on the crude cellulase activity from Hahella sp. CR1. Mean values (n=3) are expressed and standard deviations is indicated as error bars (TIF 21757 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, M.C.Y., Zakaria, M.R., Liew, K.J. et al. Draft genome sequence of Hahella sp. CR1 and its ability in producing cellulases for saccharifying agricultural biomass. Arch Microbiol 205, 278 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03617-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03617-6