Abstract
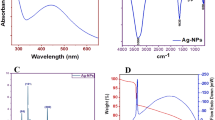
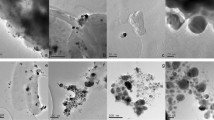
Biofilm formation and resistance to antibiotics in pathogenic bacteria are important concerns in the treatment of infectious diseases. A new rapid, eco-friendly and cost-effective strategy to overcome these problems is the use of microbial exopolysaccharides (EPS) for green synthesis of various metal nanoparticles (NPs). This study used EPS from a native probiotic Lactobacillus isolate to synthesize silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with effective antimicrobial, antibiofilm and antioxidant properties. AgNPs were synthesized by 10 mg of EPS of Lactobacillus paracasei (L. paracasei MN809528) isolated from a local yogurt. The characteristics of EPS AgNPs were confirmed using UV–VIS, FT-IR, DLS, XRD, EDX, FE-SEM, and zeta potential. Antimicrobial, antibiofilm and antioxidant activities of EPS AgNPs were evaluated by the agar well diffusion, microtiter dilution, SEM electron microscopy, and DPPH radical absorption methods, respectively. Spectroscopy data indicated the presence of a 466-nm peak as a feature of AgNPs. FT-IR confirmed the presence of biological agents in the synthesis of AgNPs. FE-SEM results showed that the synthesized AgNPs had a spherical shape with the size of 33–38 nm. Synthesized AgNPs at a concentration of 100 mg/ml demonstrated a significant inhibitory activity compared to chemically synthesized AgNPs. These NPs, exhibited the greatest effect of inhibiting the Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation at sub-MIC concentration, and the best effect of DPPH radical as antioxidant activity was determined at 50-μg/ml concentration. Our findings reveal that EPS AgNPs synthesized by the native isolate of L. paracasei (MN809528) is an inexpensive and environment-friendly candidate for application in pharmaceuticals fields.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data underlying this article will be shared on reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Change history
24 June 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03600-1
References
Abinaya M, Vaseeharan B, Divya M, Sharmili A, Govindarajan M, Alharbi NS, Kadaikunnan S, Khaled JM, Benelli G (2018) Bacterial exopolysaccharide (EPS)-coated ZnO nanoparticles showed high antibiofilm activity and larvicidal toxicity against malaria and Zika virus Vectors. J Trace Elem Med Biol 45:93–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.10.002
Abishad P, Vergis J, Unni Y et al (2022) Green synthesized silver nanoparticles using lactobacillus acidophilus as an antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti- biofilm agent against multi-drug resistant entero-aggregative Escherichia coli. Probiotics and Antimicro Prot 14:904–914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-022-0996-1
Adebayo-Tayo B, Fashogbon R (2020) In vitro antioxidant, antibacterial, in vivo immunomodulatory, antitumor and hematological potential of exopolysaccharide produced by wild type and mutant Lactobacillus delbureckii subsp. Bulgaricus, Heliyon 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03268
Ahmed S, Ahmed MZ, Rafique S, Almasoudi SE, Shah M, Jalil NAC, Ojha SC. (2023). Recent approaches for downplaying antibiotic resistance: Molecular mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. 23: 5250040. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/5250040
Aswathanarayan JB, Vittal RR (2017) Antimicrobial, biofilm inhibitory and anti-infective activity of metallic nanoparticles against pathogens MRSA and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. Pharm Nanotechnol 5(2):148–153. https://doi.org/10.2174/2211738505666170424121944
Bachtarzi N, Kharroub K, Ruas-Madiedo P (2019) Exopolysaccharide-producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional Algerian dairy products and their application for skim-milk fermentations. LWT 107:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.03.005
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005
Bankura KP, Maity D, Mollick MMR, Mondal D, Bhowmick B, Bain MK (2012) Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of dextran stabilized silver nanoparticles in aqueous medium. Carbohydr Polym 89:1159–1165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbol.2012.03.089.Epub2012
Du R, Yu L, Yu N, Ping W, Song G, Ge J (2022) Characterization of exopolysacharide produced by Levilactobacillus brevis HDE-9 and evaluation of its potential use in dairy products. Int J Biol Macromol 217:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.057.Epub2022
Gomaa EZ (2016) Exopolysaccharide-mediated silver nanoparticles produced by Lactobacillus brevis NM101-1 as antibiotic adjuvant. Microbiol 85:207–219. https://doi.org/10.1134/S002626171
Hamouda RA, Hussein M, Elhadary AM, Abuelmagd MA (2020) Extruded polysaccharide/protein matrix from Arthrospira platensis cultures mediated silver nanoparticles biosynthesis and capping. App Nanosci 10:3839–3855. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01490-z
Ispirli H, Sagdic O, Dertli E (2021) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles prepared with a dextran-type exopolysacharide from Weissella cibaria MED17 with antimicrobial functions.PrepBiochemBiotechnol51:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2020.1795673
Jian W, Zhang L, Siu KC, Song A, Wu JY (2016) Formation and physiochemical properties of silver nanoparticles with various exopolysaccharides of a medicinal fungus in aqueous solution. Molecules 22(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010050
Juraskova D, Ribeiro SC, Silva CCG (2022) Exopolysaccharides produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria: from biosynthesis to health promoting properties. Foods 11(2):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020156
Kanmani P, Lim S (2013) Synthesis and structural characterization of silver nanoparticles using bacterial exopolysaccharide and its antimicrobial activity against food and multidrug resistant pathogens. Proc Biochem 48:1099–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2013.05.011
Kanmani P, Yuvaraj N, Paari K, Pattukumar V, Arul V (2011) Production and purification of a novel exopolysaccharide from lactic acid bacterium Streptococcus phocae PI80 and its functional characteristics activity in vitro. Bioresour Technol 102(7):4827–4833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.118.Epub2011
Khan AU, Wei Y, Ahmad A, Khan ZUH, Tahir K, Khan SU et al (2016) Enzymatic browning reduction in white cabbage, potent antibacterial and antioxidant activities of biogenic silver nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 215:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.12.0919
Khorrami S, Zarrabi A, Khaleghi M, Danaei M, Mozafari M (2018) Selective cytotoxicity of green synthesized silver nanoparticles against the MCF-7 tumor cell line and their enhanced antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Int J Nanomedicine 13:138013–138024. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S189295
Krishnaraj R, Berchmans S (2013) In vitro antiplatelet activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using the microorganism Gluconobacter roseus: an AFM-based study. RSC Adv 3:8953–8959. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA41246F
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35(6):1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Lellouche J, Friedman A, Lahmi R, Gedanken A, Banin E (2012) Antibiofilm surface functionalization of catheters by magnesium fluoride nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 7:1175–1188. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S266770
Magudapathy P, Gangopadhyay P, Panigrahi BK, Nair KGM, Dhara S (2001) Electrical transport studies of ag nanoclusters embedded in glass matrix. Phys B 299:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(00)00580-9
Manosalva N, Tortella G, Cristina Diez M, Schalchli H, Seabra A, Duran N, Rubilar O (2019) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: effect of synthesis reaction parameters on antimicrobial activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2664-3
Marra D, Perna I, Pota G, Vitiello G, Pazzella A, Toscano G, Luciani G, Caserta S (2023) Nanoparticle coatings on glass surfaces to prevent Pseudomonas fluorescens AR11 biofilm formation. Microorganisms 11(3):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11030621
Mohamed AA, Abu –Elghait M, Ahmed NE, et al. (2021) Eco-friendly mycogenic synthesis of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles for in vitro antibacterial , Antibiofilm, and antifuingal . Applications. Biol Trace Elem Res 199: 2788-2799
Murray CJL, Ikuta KS, Sharara F et al (2019) Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in a systematic analysis. Lancet. 12:399(10325), 629–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02724-0
Olanike P, Christianah A (2017) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using supernatant from lactobacillus casei lpw2 cultured in modified exopolysaccharides selection medium. J Appl Life Sci Inter 13:1–8. https://doi.org/10.9734/JALSI/2017/34590
Olyksy M, Klewicka E (2018) Exopolysaccharides produced by Lactobacillus sp: biosynthesis and applications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:450–462. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1187112
Pan F, Xu A, Xia D, Yu Y, Chen G, Meyer M (2015) Effects of octahedral molecular sieve on treatment performance, microbial metabolism, and microbial community in expanded granular sludge bed reactor Effects of octahedral molecular sieve on treatment performance, microbial metabolism, and microbial community in expanded granular sludge bed reactor. Water Res [internet] 87(December):127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2015.09.022
Panacek A, Kolar M, Vecerova R, Prucek R, Soukupova J, Krystof V, Hamal P, Zboril R, Kvítek L (2009) Antifungal activity of silver nanoparticles against Candida spp. Biomater 30:6333–6340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2009.07.065
Pandey S, Goswami GK, Nanda KK (2012) Green synthesis of biopolymer–silver nanoparticle nanocomposite: an optical sensor for ammonia detection. Int J Biol Macromol 51:583–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.06.033
Prabha S, Arya G, Chandra R, Ahmed B, Nimesh S (2016) Effect of size on biological properties of nanoparticles employed in gene delivery. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44:83–91. https://doi.org/10.3109/21691401.2014.913054.Epub2014
Prasad TN, Kambala VSR, Naidu R (2013) Phyco nanotechnology: synthesis of silver nanoparticles using brown marine algae Cystophora moniliformis and their characterisation. J Appl Phycol 25(1):177–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-012-9851-z
Prete R, Khairul Alam M, Perpetuini G, Perla C, Pittia P, Corsetti A (2021) Lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides producers: a sustainable tool for functional foods. Foods 10(7):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071653
Priyadarshini S, Gopinath V, Meera Priyadharsshini N, MubarakAli D, Velusamy P (2013) Synthesis of anisotropic silver nanoparticles using novel strain, Bacillusflexus and its biomedical application. Colloid Surf b 102:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.08.018.Epub2012
Quintero-Quiroz C, Acevedo N, Zapata – Giraldo J, Botero LE, Quintero J, Zarate-Trivino D, Saldarriaga J, Perez VZ (2019) Optimization of silver nanoparticle synthesis by chemical reduction and evalution of its antimicrobial and toxic activity. Biomaterials Research 23:27. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11060800
Rajoka MS, Mehwish HM, Siddiq M, Haobin Z, Zhu YL, Shao D, Xu X, Shi J (2017) Identification, characterization, and probiotic J potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus isolated from human milk. LWT-Food Sci Technol 84:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.IWT.2017.05.055
Rani RP, Anandharaj M, Ravindran AD (2018) Characterization of a novel exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus gasseri FR4 and demonstration of its in vitro biologicalproperties. Int J Biol Macromol 109:772–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.1.062.Epub2017
Raveendran AC, Poulose Y, Yoshida T (2013) Bacterial exopolysaccharide-based nanoparticles for sustained drug delivery, cancer chemotherapy and bioimaging. Carbohyd Polym 91:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.079.Epub2012
Riaz Rajoka MS, Jin M, Haobin Z, Li Q, Shao D, Jiang C, Huang Q, Yang H, Shi J, Hussain N (2018) Functional characterization and biotechnological potential of exopolysaccharide produced by Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains isolated from human breast milk. LWT-Food Sci Technol 89:638–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.11.034
Salem SS, Green FA (2021) synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their prospective biotechnological applications: an overview. Biol Trace Elem Res 199:344–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-020-02138-3
Salem SS, Ali OM, Reyad AM, Abd-Elsalam KA, Hashem AH (2022) Pseudomonas indica- mediated silver nanoparticles: antifungal and antioxidant biogenic tool for suppressing mucormycosis fungi. J Fungi 8(2):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8020126
Salem SS, Baker’s (2022) Yeast –mediated silver nanoparticles: characterization and antimicrobial biogenic tool for suppressing pathogenic microbes. Bio Nano Sci 12: 1220-1229
Sanjivkumar M, Vaishnavi R, Neelakannan M, Kannan D, Silambarasan T (2019) Immanuel G. Investigation on characterization and biomedical properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized by an actinobacterium streptomyces olivaceus (MSU3). Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 17:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.11.014
Saravanan C, Rajesh R, Kaviarasan T, Muthukumar K, Kavitake D, Halady Shetty P (2017) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using bacterial exopolysaccharide and its application for degradation of azo-dyes. Biotechnol Rep 15:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2017.02.006
Sastry M, Mayya K, Patil V, Paranjape D, Hegde S (1997) Langmuir−Blodgett Films of Carboxylic Acid Derivatized Silver Colloidal Particles: Role of Subphase pH on Degree of Cluster Incorporation. J Phys Chem B 101:4954–5495. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp964087f
Sathiyanarayanan G, Vignesh V, Saibaba G, Vinothkanna A, Dineshkumar K, Viswanathan MB, Selvin J (2014) Synthesis of carbohydrate polymer encrusted gold nanoparticles using bacterial exopolysaccharide: a novel and greener approach. RSC Adv 4:22817–22827. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA01428F
Shehabeldin AM, Amin BH. Hagras FA. et al. (2023) Potential antimicrobial and antibioilm properties of copper oxide nanoparticles: Time-Kill kinetic essay and ultrastructure of pathogenic bacterial cells. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 195: 467-485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04120-2
Shokri D, Khorasgani MR, Mohkam M, Fatemi SM, Ghasemi Y, Taheri-Kafrani A (2017) The Inhibition Effect of Lactobacilli Against Growth and Biofilm Formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 10:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-017-9267-9
Singh M, Singh S, Prasad S, Gambhir IS (2008) Nanotechnology in medicine and antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles. Dig J Nanomate Bios 3:115–122
Soliman MKY, Abu-Elghait M, Salem SS et al (2022) Multifunctional properties of silver and gold nanoparticles synthesis by fusarium pseudonygamai. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03507-9
Soliman MKY, Salem SS, Abu-Elghait M et al (2023) Biosynthesis of Silver and Gold nanoparticles and their efficacy towards antibacterial, antibiofilm. Cytotoxicity, and antioxidant activities. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195:1158–1183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04199-7
Sorensen HM, Rochfort KD, Maye S, Macleod G, Brabazon D, Loscher CH, Freeland B (2022) Exopolysaccharides of lactic acid bacteria: production, purification, and health benefits towards functional food. Nutrients 14(14):2938. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14142938
Sudheer Khan S, Mukherjee A, Chandrasekaran N (2011) Interaction of colloidal silver nanoparticles (SNPs) with exopolysaccharides (EPS) and its adsorption isotherms and kinetics. Colloid Surf A 381:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.03.032
Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S (2004) Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 101(30):11030–11035. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0404206101
Thomas R, Janardhanan A, Varghese R, Soniya E, Mathew J, Radhakrishnan E (2014) Antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles synthesized by marine Ochrobactrum sp. Braz J Microbiol 45(4):1221–1227. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1517-8382201400012
Veeraapandian S, Sawant SN, Doble M (2012) Antibacterial and antioxidant activity of protein capped silver and gold nanoparticles synthesized with Escherichia coli. J Biomed Nanotechnol 8:140–148. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2012.1356
Vijayabaskar P, Babinastarlin S, Shankar T, Sivakumar T, Anandapandian K (2011) Quantification and characterization of exopolysaccharides from Bacillus subtilis (MTCC 121). Adv Biol Res 5(2):71–76
Vijayakumar G, Kim HJ, Rangarajulu SK (2023) In vitro antibacterial and wound healing activities evoked by silver nanoparticles synthesized through probiotic bacteria. Antibiotics 12:141. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12010141
Wang Y, Li C, Liu P, Ahmed Z, Xiao P, Bai X (2017) Physical characterization of exopolysacharide produced by Lactobacillus plantarum KF5 isolated from from Tibet Kefir,carbohydr polym 82(3) 895–903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.062
Yang X, Wu JY (2022) Synthetic conditions, physical properties, and antibacterial activities of silver nanoparticles with exopolysaccharides of a medicinal fungus. Materials 15(16):5620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165620
Zhang J, Yin Yunxue Hu, Shuo WG, Tong Y, Zen M, Liang Z, Li M, Yan R, Wang Y (2023) Green synthesis of anti-bacterial nano silver by polysaccharide from bletilla striata. Inorganics 11(1):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11010040
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Zand for sample analysis by HPLC and FT-IR and to the Pasteur Institute of Iran (Tehran) for providing the pathogenic strains. We also thank Department of Metallurgy of Materials, Tehran University, for examining the instrumental analyzes (FE-SEM, DLS, XRD, EDAX). We also acknowledge the Qom Branch of the Islamic Azad University (Qom, Iran) for providing the opportunity to conduct this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MZE, SSA: design of study. MZE, MZA, MAG: acquisition of data. MZA, MAG, SS: evaluation of data, preparation of the manuscript. SSA, MZA: assessment of data. All authors read and approved the last manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by Gharieb El-Sayyad.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised due to update in text.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeinivand, M., Aghaei, S.S., Zargar, M. et al. Exopolysaccharide-mediated silver nanoparticles synthesized from Lactobacillus paracasei with antimicrobial, antibiofilm and antioxidant activities. Arch Microbiol 205, 210 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03497-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03497-w