Abstract
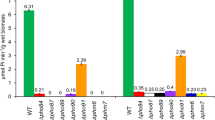
PHO-mutant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, NOF-1 and NBD82-1, which constitutively express PHO81 and PHO4, respectively, have been reported to accumulate phosphate in high-phosphate conditions. However, detailed analysis, including a quantitative evaluation of the accumulated phosphate, has not been performed for these mutants. In this study, NOF-1 and NBD82-1 mutant and double mutant strains were cultured in a high-phosphate medium to quantitatively analyze the amount, accumulation form, and physiological use of the accumulated phosphate in the cells. In control strains (BY4741 and NBW7), the percentage of phosphorus in total dry weight of cell was approximately 2%TDW; for the NBD82-1 mutant and double mutant strains, it was approximately 6%TDW; and for strain NOF-1, it was 8.5%TDW. When cells of the mutant strains were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), they showed a fluorescence peak at 540 nm, suggesting that phosphate accumulated as polyphosphoric acid (polyP). Quantitative evaluation revealed that for strain NOF-1, the percentage of phosphorus exiting as polyP in total dry weight of cell was approximately 5.0%TDW, equivalent to 60% of the total phosphorus in the cells. We also demonstrated that the mutant strains could grow well in phosphate-free medium, suggesting that phosphate accumulated in the cells was used as a phosphorus source. This is the first report concerning the quantitative analysis of phosphate accumulation and utilization of PHO regulatory system-mutant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author YO on request.
References
Andreeva N, Ledova L, Ryasanova L, Kulakovskaya T (2019) The acid phosphatase Pho5 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is not involved in polyphosphate breakdown. Folia Microbiol 64:867–873. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-019-00702-6
Brachmann CB et al (1998) Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14:115–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0061(19980130)14:2%3c115::aid-yea204%3e3.0.co;2-2
Bru S et al (2016) Polyphosphate is involved in cell cycle progression and genomic stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 101:367–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13396
Bun-Ya M, Nishimura M, Harashima S, Oshima Y (1991) The PHO84 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes an inorganic phosphate transporter. Mol Cell Biol 11:3229–3238. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.11.6.3229-3238.1991
Christ JJ, Blank LM (2018a) Analytical polyphosphate extraction from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Anal Biochem 563:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2018.09.021
Christ JJ, Blank LM (2018b) Enzymatic quantification and length determination of polyphosphate down to a chain length of two. Anal Biochem 548:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2018.02.018
Gerasimaitė R, Mayer A (2016) Enzymes of yeast polyphosphate metabolism: structure, enzymology and biological roles. Biochem Soc Trans 44:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst20150213
Groombridge AS et al (2013) High sensitive elemental analysis of single yeast cells (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) by time-resolved inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry using a high efficiency cell introduction system. Anal Sci 29:597–603. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.29.597
Kaffman A, Rank NM, O’Neill EM, Huang LS, O’Shea EK (1998) The receptor Msn5 exports the phosphorylated transcription factor Pho4 out of the nucleus. Nature 396:482–486. https://doi.org/10.1038/24898
Komeili A, O’Shea EK (1999) Roles of phosphorylation sites in regulating activity of the transcription factor Pho4. Science 284:977–980. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5416.977
Morohoshi T et al (2002) Accumulation of inorganic polyphosphate in phoU mutants of Escherichia coli and Synechocystis sp. strain PCC6803. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4107–4110. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.8.4107-4110.2002
Nakazawa N, Harashima S, Oshima Y (1991) AAR2, a gene for splicing pre-mRNA of the MATa1 cistron in cell type control of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 11:5693–5700. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.11.11.5693-5700.1991
Nguyen TQ, Dziuba N, Lindahl PA (2019) Isolated Saccharomyces cerevisiae vacuoles contain low-molecular-mass transition-metal polyphosphate complexes. Metallomics 11:1298–1309. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9mt00104b
Ogawa N, Oshima Y (1990) Functional domains of a positive regulatory protein, PHO4, for transcriptional control of the phosphatase regulon in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 10:2224–2236. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.10.5.2224-2236.1990
Ogawa N, Noguchi K, Sawai H, Yamashita Y, Yompakdee C, Oshima Y (1995) Functional domains of Pho81p, an inhibitor of Pho85p protein kinase, in the transduction pathway of Pi signals in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 15:997–1004. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.15.2.997
Ogawa N, DeRisi J, Brown PO (2000) New components of a system for phosphate accumulation and polyphosphate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae revealed by genomic expression analysis. Mol Biol Cell 11:4309–4321. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.11.12.4309
Oshima Y (1997) The phosphatase system in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Genet Syst 72:323–334. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.72.323
Persson BL et al (2003) Regulation of phosphate acquisition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 43:225–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0400-9
Sasano Y, Sakata T, Okusaki S, Sugiyama M, Kaneko Y, Harashima S (2018) Genetic analysis of suppressor mutants of a pho84 disruptant in the search for genes involved in intracellular inorganic phosphate sensing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Genet Syst 93:199–207. https://doi.org/10.1266/ggs.18-00014
Schneider KR, Smith RL, O’Shea EK (1994) Phosphate-regulated inactivation of the kinase PHO80-PHO85 by the CDK inhibitor PHO81. Science 266:122–126. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7939631
Sheman F, Fink G, Hicks J (1982) Methods in yeast genetics: a Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview
Tong W et al (2019) Phosphorus-rich microorganism-enabled synthesis of cobalt phosphide/carbon composite for bisphenol A degradation through activation of peroxymonosulfate. Chem Eng J 378:122187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122187
Urech K, Dürr M, Boller T, Wiemken A, Schwencke J (1978) Localization of polyphosphate in vacuoles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 116:275–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00417851
Watanabe T, Ozaki N, Iwashita K, Fujii T, Iefuji H (2008) Breeding of wastewater treatment yeasts that accumulate high concentrations of phosphorus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:331–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1529-8
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Dr. Y. Kaneko for helpful discussions. We thank Edanz (https://jp.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Osaka Metropolitan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YO and MA proposed the research concept and provided necessary tools for experiments and experimental instructions. YO wrote the manuscript. KN and RA designed and conducted the experiments and analyzed data. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ojima, Y., Naoi, K., Akiyoshi, R. et al. Quantitative analysis of phosphate accumulation in PHO regulatory system-mutant strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 205, 138 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03488-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03488-x