Abstract
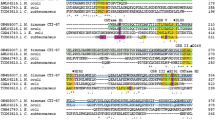
Bacillus cereus is a rod-shaped, gram-positive, motile, and β-hemolytic soil bacterium. B. cereus is an opportunistic pathogen, often responsible for human foodborne illness that is caused by ingestion of starchy foods with symptoms of diarrhea and vomiting. Among the numerous amylolytic enzymes in the genome of the pathogen, the one annotated as a putative neopullulanase (NPase) was cloned and its biochemical properties were characterized in this study. The corresponding gene encoded an enzyme of 586 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 68.25 kDa. The putative NPase shared 43.7–59.2% of identity with NPases, cyclomaltodextrinases (CDases), and maltogenic amylases from various bacteria, but shared very low similarity with other amylolytic enzymes of B. cereus. The optimal pH and temperature of the enzyme was 6.5 and 37 ℃, respectively. The enzyme activity was decreased by the cations tested in this study and completely inhibited by Co2+ and Cu2+. The purified enzyme showed substrate preference in the order of α-CD > β-CD > starch > maltodextrin > γ-CD and hydrolyzed them mainly to maltose. However, it did not hydrolyze maltose, pullulan, and glycogen. The enzyme was designated herein as a CDase of B. cereus (BcCDase). Furthermore, the enzyme could transfer the sugars released from CDs and maltotriose to acceptor molecules. BcCDase was likely to be involved in the maltodextrin metabolism in B. cereus.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Arnesen LPS, Fagerlund A, Granum PE (2008) From soil to gut: Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:579–606
Aron MB, Myra KD, Noreen RG, Shennan L, Farideh C, Lewis YG, Renata CG, Jane H, Marc G, David IH, Christopher JL, Fu L, Gabriele HM, James SS, Narmada T, Zhouxi W, Roxanne AY, Dachuan Z, Chanjuan Z, Stephen HB (2015) CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:222–226
Aroob I, Ahmad N, Rahid N (2021) Cyclodextrin-preferring glycoside hydrolases: properties and applications. Amylase 5:23–37
Bae H, Lee S, Park C, Shim J, Lee H, Kim M, Baek J, Roh H, Choi J, Choe E, Ahn D, Park H (2002) Modification of ascorbic acid using transglycosylation activity of Bacillus stearothermophilus maltogenic amylase to enhance its oxidative stability. J Agri Food Chem 50:3309–3316
Bender H (1993) Purification and characterization of a cyclodextrin-degrading enzyme from Flavobacterium sp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:714–719
Bottone EJ (2010) Bacillus cereus, a volatile human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:382–398
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cha H, Yoon H, Kim Y, Lee H, Kim J, Kweon K, Oh B, Park K (1998) Molecular and enzymatic characterization of a maltogenic amylase that hydrolyzes and transglycosylates acarbose. Eur J Biochem 253:251–262
Cho H, Kim Y, Kim T, Lee H, Kim D, Kim J, Lee Y, Lee S, Park K (2000) Molecular characterization of a dimeric intracellular maltogenic amylase of Bacillus subtilis SUH4-2. Biochim Biophys Acta 1478:333–340
Davaeifar S, Shariati P, Tabandeh F, Yakhchali B (2015) Isolation and identification of a new Bacillus cereus strain and characterization of its neopullulanase. Appl Food Biotech 2:39–45
Doman-Phyka M, Bardowski J (2004) Pullulan degrading enzymes of bacterial origin. Cri Rev Microbiol 30:107–121
Galvin MN, Kelly CT, Fogarty WM (1994) Purification and properties of the cyclodextrinase of Bacillus sphaericus ATCC 7055. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 42:46–50
Han A, Kim H, Park J, Kim J (2022) Characterization of a cold-adapted debranching enzyme and its role in glycogen metabolism and virulence of Vibrio vulnificus MO6-24/O. J Microbiol 60:375–386
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 280:309–316
Igarashi K, Ara K, Saeki K, Ozaki K, Kawai S, Ito S (1992) Nucleotide sequence of a gene that encodes a neopullulanase from an alkalophilic Bacillus. Biosci Biotech Biochem 56:514–516
Ivanova N, Sorokin A, Anderson I, Galleron N, Candelon B, Kapatral V, Bhattacharyya A, Reznik G, Mikhailova N, Lapidus A, Chu L, Mazur M, Goltsman E, Larsen N, D’Souza M, Walunas T, Grechkin Y, Pusch G, Haselkorn R, Fonstein M, Ehrlich SD, Overbeek R, Kyrpides N (2003) Genome sequence of Bacillus cereus and comparative analysis with Bacillus anthracis. Nature 423:87–91
Janeček S (1997) α-Amylase family: molecular biology and evolution. Progr Biophys Mol Biol 67:67–97
Kim I, Cha J, Kim J, Jang S, Seo B, Cheong T, Lee DS, Choi YD, Park K (1992) Catalytic properties of the cloned amylase from Bacillus licheniformis. J Biol Chem 267:22108–22114
Kim IC, Yoo SH, Lee SJ, Oh BH, Kim JW, Park KH (1994) Synthesis of branched oligosaccharides from starch by two amylases cloned from Bacillus licheniformis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:416–418
Kim T, Shin J, Oh J, Kim M, Lee S, Ryu S, Kwon K, Kim J, Choi E, Robyt JF, Park K (1998) Analysis of the gene encoding cyclomaltodextrinase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. I-5 and characterization of enzymatic properties. Arch Biochem Biophys 353:221–227
Kim TJ, Kim MJ, Kim BC, Kim JC, Cheong TK, Kim JW, Park KH (1999) Modes of action of acarbose hydrolysis and transglycosylation catalyzed by a thermostable maltogenic amylase, the gene for which was cloned from a Thermus strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1644–1651
Kim TJ, Nguyen VD, Lee HS, Kim MJ, Cho HY, Kim YW, Moon TW, Park CS, Kim JW, Oh BH, Lee SB, Svensson B, Park KH (2001) Modulation of the multisubstrate specificity of Thermus maltogenic amylase by truncation of the N-terminal domain and by a salt-induced shift of the monomer/dimer equilibrium. Biochem 40:14182–14190
Kim D, Cha C, Oh W, Yoon Y, Kim J (2004) Expression of the promoter for the maltogenic amylase gene in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Microbiol 42:319–327
Kotiranta A, Lounatmaa K, Haapasalo M (2000) Epidemiology and pathogenesis of Bacillus cereus infections. Microbes Infect 2:189–198
Kuriki T, Imanaka T (1989) Nucleotide sequence of the neopullulanase gene from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Gen Microbiol 135:1521–1528
Kuriki T, Imanaka T (1999) The concept of the alpha-amylase family: structural similarity and common catalytic mechanism. J Biosci Bioeng 87:557–565
Kuriki T, Kaneko H, Yanase M, Takata H, Shimada J, Handa S, Takada T, Umeyama H, Okada S (1996) Controlling substrate preference and transglycosylation activity of neopullulanase by manipulating steric constraint and hydrophobicity in active center. J Biol Chem 271:17321–17329
Lee SJ, Yoo SH, Kim MJ, Kim JW, Seok HM, Park KH (1995) Production and characterization of branched oligosaccharides from liquefied starch by the action of Bacillus licheniformis amylase. Starch 47:127–134
Lee HS, Kim MS, Cho HS, Kim JI, Kim TJ, Choi JH, Park CS, Lee HS, Oh BH, Park KH (2002a) Cyclomaltodextrinase, neopullulanase, and maltogenic amylase are nearly indistinguishable from each other. J Biol Chem 277:21891–21897
Lee MH, Lee YH, Kim YW, Kim TJ, Park CS, Kim JW, Moon TW, Park KH (2002b) A novel amylolytic enzyme from Thermotoga maritima, resembling cyclodextrinase and α-glucosidase, that liberates glucose from the reducing end of the substrates. Biochem Biophysic Res Com 295:818–825
Li D, Park S, Shim J, Lee H, Tang S, Park C, Park K (2004) In vitro enzymatic modification of puerarin to puerarin glycosides by maltogenic amylase. Carbo Res 339:2789–2797
Li X, Li D, Yin Y, Park K (2010) Characterization of a recombinant amylolytic enzyme of hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermofilum pendens with extremely thermostable maltogenic amylase activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:1821–1830
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicyclic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Min B, Yoon S, Kim J, Lee Y, Kim Y, Park K (1998) Cloning of novel maltooligosaccharide producing amylases as antistaling agents for bread. J Agri Food Chem 46:779–782
Ming H, Chang JC, Chen J (1993) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of an extracellular α-amylase gene from Aeromonas hydrophila MCC-1. J Gen Microbiol 139:3215–3223
Nair SU, Singhal RS, Kamat MY (2007) Induction of pullulanase production in Bacillus cereus FDTA-13. Bioresour Technol 98:856–859
Oh KW, Kim MJ, Kim HY, Kim BY, Baik MY, Auh JH, Park C (2005) Enzymatic characterization of a maltogenic amylase from Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC 33323 expressed in Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 252:175–181
Park KH, Kim TJ, Cheong TK, Kim JW, Oh BH, Svensson B (2000) Structure, specificity and function of cyclomaltodextrinase, a multispecific enzyme of the α-amylase family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1478:165–185
Park KH, Lee HS, Kim TJ, Cheong KA, Nguyen VD, Min MJ, Cho HY, Kim YW, Park CS, Oh BH, Kim JW (2002) N- and C-terminal region mediated oligomerization of the cyclodextrin-/pullulan degrading enzymes. Biologia Bratislava 57(Suppl):87–92
Rowan NJ, Anderson JG (1997) Maltodextrin stimulates growth of Bacillus cereus and synthesis of diarrheal enterotoxin in infant milk formulae. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1182–1184
Schönert S, Seitz S, Krafft H, Feuerbaum EA, Andernach I, Witz G, Dahl MK (2006) Maltose and maltodextrin utilization by Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 188:3911–3922
Shim JH, Park JH, Hong JS, Kim KW, Kim MJ, Auh JH, Kim YM, Park CS, Boos W, Kim JW, Park KH (2009) Role of maltogenic amylase and pullulanase in maltodextrin and glycogen metabolism of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol 191:4835–4844
Slock JA, Sthaly DP (1974) Polysaccharide that may serve as a carbon and energy storage compound for sporulation in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol 120:399–406
Stam MR, Danchin EGJ, Rancurel C, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2006) Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: towards improved functional annotations of α-amylase-related proteins. Protein Eng Des Sel 19:555–562
Svensson B (1994) Protein engineering in the α-amylase family: catalytic mechanism, substrate specificity, and stability. Plant Mol Biol 25:141–157
Takata H, Kuriki T, Okada S, Takesada Y, Iizuka M, Minamiura N, Imanaka T (1992) Action of neopullulanase. J Biol Chem 267:18447–18452
Tonozuka T, Ohtsuka M, Mogi S, Sakai H, Ohta T, Sakano Y (1993) A Neopullulanase-type α-Amylase gene from Thermoactinomyces vulgaris R-47. Biosci Biotech Biochem 57:395–401
Vihinen M, Mäntsälä P (1989) Microbial amylolytic enzymes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 24:329–418
Yebra MJ, Arroyo J, Sanz P, Prieto JA (1997) Characterization of novel neopullulanase from Bacillus polymyxa. Appl Biochem Biotech 68:113–120
Yoshida A, Iwasaki Y, Akiba T, Horikoshi K (1991) Purification and properties of cyclomaltodextrinase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. J Ferment Bioeng 71:226–229
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. YB Ko for assistance in collecting reference materials.
Funding
This study was supported by the INU grant in the year of 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B-RP performed investigation, DM prepared the manuscript, and J-WK contributed to funding acquisition, supervision of investigation, and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All authors consented to participate investigation and publication.
Consent to publish
All authors consented to publish the results.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, BR., MubarakAli, D. & Kim, JW. Identification of a novel cyclomaltodextrinase annotated as a neopullulanase in the genome of Bacillus cereus. Arch Microbiol 205, 86 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03390-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03390-y